A backroom deal refers to a secret agreement made outside of public scrutiny, often involving negotiations that lack transparency and fairness. Such deals can influence decisions in politics, business, or other fields by prioritizing private interests over the common good. Discover how backroom deals impact your environment and why understanding them is crucial by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
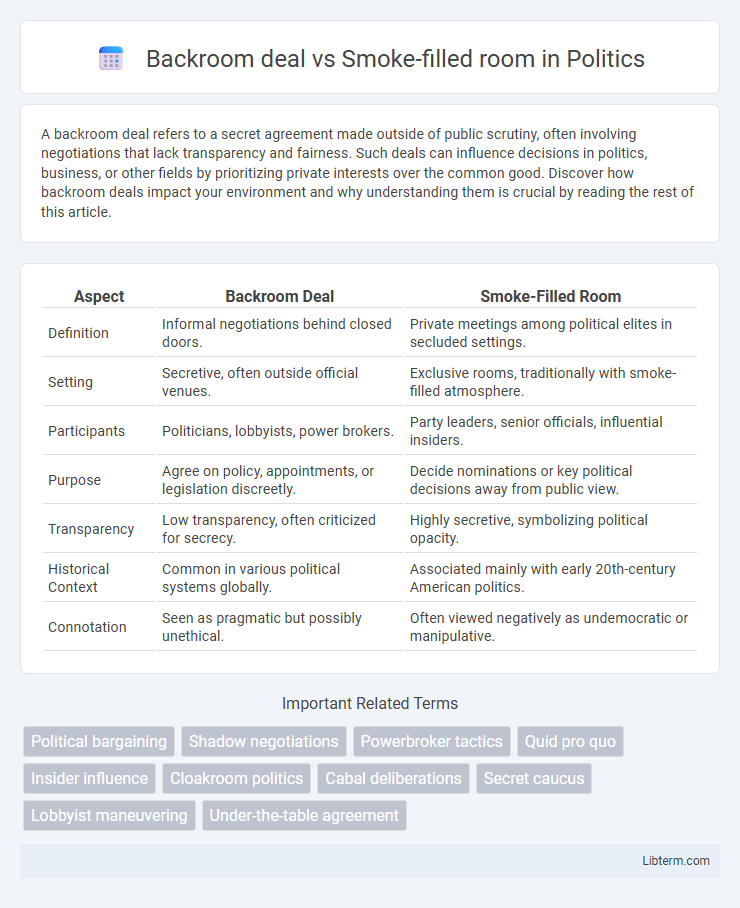
| Aspect | Backroom Deal | Smoke-Filled Room |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Informal negotiations behind closed doors. | Private meetings among political elites in secluded settings. |
| Setting | Secretive, often outside official venues. | Exclusive rooms, traditionally with smoke-filled atmosphere. |
| Participants | Politicians, lobbyists, power brokers. | Party leaders, senior officials, influential insiders. |
| Purpose | Agree on policy, appointments, or legislation discreetly. | Decide nominations or key political decisions away from public view. |
| Transparency | Low transparency, often criticized for secrecy. | Highly secretive, symbolizing political opacity. |
| Historical Context | Common in various political systems globally. | Associated mainly with early 20th-century American politics. |
| Connotation | Seen as pragmatic but possibly unethical. | Often viewed negatively as undemocratic or manipulative. |
Understanding Backroom Deals: Definition and Origins
Backroom deals refer to secretive agreements made privately by a small group of individuals, often bypassing standard procedures or public scrutiny. Originating from political and business settings, these deals historically facilitated decision-making away from formal negotiations, allowing flexibility but raising concerns about transparency and fairness. Understanding the origins of backroom deals highlights their role in shaping policies or contracts discreetly, impacting accountability in governance and corporate environments.
What Does "Smoke-filled Room" Really Mean?
A "smoke-filled room" refers to a secretive space where influential political figures or decision-makers gather to negotiate and make critical decisions without public transparency, often bypassing broader democratic processes. The term originated from early 20th-century American politics, where party leaders would convene in private rooms filled with cigarette smoke to determine candidates or policies behind closed doors. This practice contrasts with open, transparent decision-making, highlighting concerns about elitism and lack of accountability in political negotiations.
Historical Roots of Political Intrigue
Backroom deals trace back to early legislative assemblies where informal negotiations shaped policy outside public scrutiny, highlighting the power of secrecy in political maneuvering. Smoke-filled rooms emerged prominently in 1920s American politics, notably during the Republican National Convention of 1920, symbolizing elite party insiders deciding candidacies away from voters' eyes. Both concepts epitomize the historical roots of political intrigue, revealing how behind-the-scenes bargaining influenced governance and undermined transparent democratic processes.
Key Differences: Backroom Deal vs. Smoke-filled Room
Backroom deals occur in private settings where negotiations and agreements happen discreetly between a few key participants, typically to bypass formal procedures. Smoke-filled rooms refer to secretive gatherings, often involving political leaders or influential figures, where decisions are made informally amid opaque, exclusive discussions. The key difference lies in the context and connotation: backroom deals emphasize the covert nature of specific agreements, while smoke-filled rooms highlight the secretive environment of power brokering.
Notorious Examples in Political History
Backroom deals often involve private negotiations like the 1919 Treaty of Versailles drafting, where world leaders shaped post-WWI Europe away from public scrutiny. Smoke-filled rooms gained notoriety during the 1920 Republican National Convention when party bosses selected Warren G. Harding as a compromise presidential nominee. Both tactics highlight how clandestine political maneuvering influenced major historical outcomes through exclusive, opaque decision-making processes.
Power Players: Who Makes These Decisions?
Backroom deals are typically orchestrated by influential power players such as senior executives, lobbyists, or political strategists who operate behind closed doors to finalize agreements without public scrutiny. Smoke-filled rooms refer to exclusive gatherings of top-tier decision-makers, often party leaders or key legislators, wielding significant authority to shape policies or candidate selections through confidential negotiations. Both settings concentrate decision-making power among elite insiders, emphasizing control and secrecy in critical political or corporate choices.
Transparency vs. Secrecy: Public Perception
Backroom deals often evoke perceptions of secrecy and manipulation, fueling public distrust due to their private and opaque nature. In contrast, smoke-filled rooms symbolize exclusive decision-making environments where transparency is minimal, reinforcing skepticism about fairness and accountability. Both settings diminish public confidence by obscuring the decision-making process and limiting citizen involvement.
Impact on Policy and Governance
Backroom deals often involve secretive negotiations between a limited number of stakeholders, enabling swift policy decisions but raising concerns about transparency and accountability. Smoke-filled rooms historically describe opaque gatherings of elite political insiders that shape major governance outcomes, potentially sidelining broader democratic input. Both practices can expedite policy formulation but may undermine public trust and democratic legitimacy by excluding diverse perspectives.
Modern Equivalents in Today’s Politics
Backroom deals in modern politics often manifest as closed-door negotiations among influential party leaders or lobbyists, shaping policy outcomes without public scrutiny. Smoke-filled rooms have evolved into exclusive, high-stakes strategy sessions, frequently involving political action committees (PACs) and corporate donors orchestrating campaign financing and candidate endorsements. These practices underscore the ongoing tension between democratic transparency and concentrated influence in legislative and electoral processes.
Ethical Concerns and Calls for Reform
Backroom deals often raise ethical concerns due to their lack of transparency, fostering distrust among stakeholders and undermining democratic processes. Smoke-filled rooms symbolize secretive political negotiations where influential figures make decisions without public input, prompting calls for reform to ensure accountability and inclusivity. Advocates argue for increased openness and stricter regulations to prevent corruption and protect the integrity of decision-making institutions.
Backroom deal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com