Electoral mapping plays a crucial role in visualizing voting patterns and demographic distributions, allowing for more accurate predictions and campaign strategies. By analyzing geographic and population data, you can identify key areas that influence election outcomes and gain insight into voter behavior. Discover how electoral mapping can transform your understanding of political landscapes in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
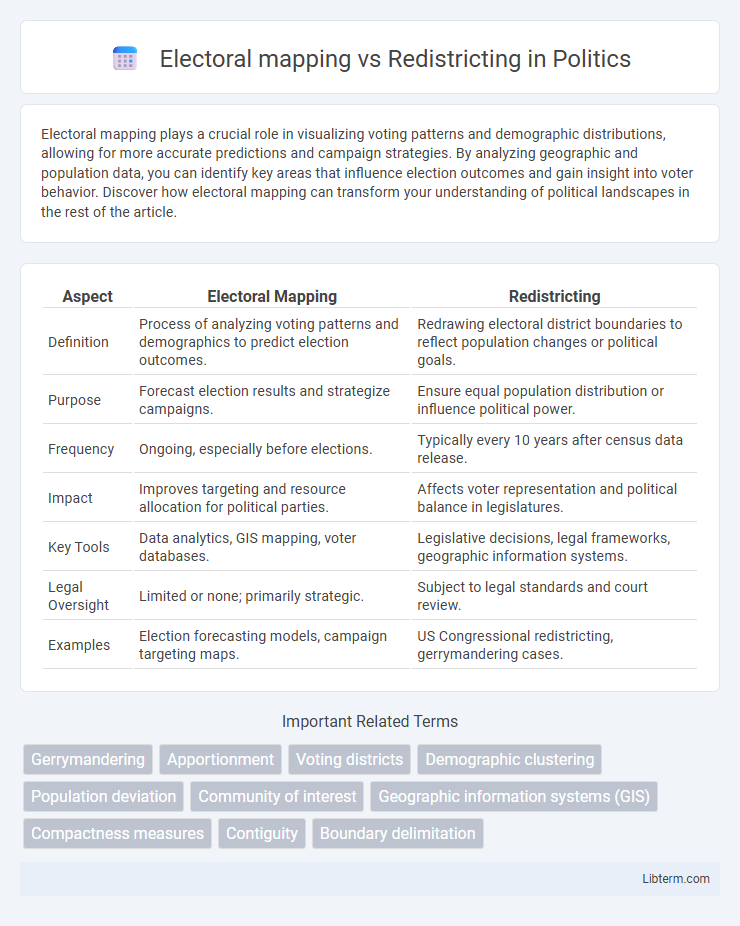
| Aspect | Electoral Mapping | Redistricting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of analyzing voting patterns and demographics to predict election outcomes. | Redrawing electoral district boundaries to reflect population changes or political goals. |
| Purpose | Forecast election results and strategize campaigns. | Ensure equal population distribution or influence political power. |
| Frequency | Ongoing, especially before elections. | Typically every 10 years after census data release. |
| Impact | Improves targeting and resource allocation for political parties. | Affects voter representation and political balance in legislatures. |
| Key Tools | Data analytics, GIS mapping, voter databases. | Legislative decisions, legal frameworks, geographic information systems. |
| Legal Oversight | Limited or none; primarily strategic. | Subject to legal standards and court review. |
| Examples | Election forecasting models, campaign targeting maps. | US Congressional redistricting, gerrymandering cases. |
Introduction to Electoral Mapping and Redistricting
Electoral mapping involves analyzing voting patterns, demographic shifts, and historical election data to inform decisions on political boundaries. Redistricting is the formal process of redrawing electoral district boundaries, typically conducted every ten years following the census to ensure equal representation. Both practices are crucial for maintaining fair political representation and addressing population changes within jurisdictions.
Defining Electoral Mapping
Electoral mapping involves the detailed analysis and visualization of voting patterns, demographic data, and political boundaries to understand electoral behavior and trends. It utilizes geographic information systems (GIS) and spatial data to create precise representations of electoral districts, aiding in the assessment of voter distribution and election outcomes. This process provides a foundational tool for decision-making in redistricting, enabling more informed and equitable boundary definitions.
Understanding Redistricting
Redistricting refers to the process of redrawing electoral district boundaries to reflect population changes identified by the latest census, ensuring equal representation in legislative bodies. It impacts political power distribution by potentially altering district demographics, which can influence election outcomes and party control. Understanding redistricting requires analyzing legal criteria, demographic data, and the political context to assess its effects on fair representation and electoral competitiveness.
Key Differences Between Electoral Mapping and Redistricting
Electoral mapping involves the creation of visual representations of voting patterns and demographic data to analyze electoral behavior, while redistricting is the process of redrawing electoral district boundaries to ensure equal population distribution. Electoral mapping primarily supports decision-making with data insights, whereas redistricting has direct legal and political implications by shaping electoral districts for representation. Key differences include the purpose--analytical versus boundary adjustment--and the impact on electoral fairness and political control.
Purposes of Electoral Mapping in Elections
Electoral mapping serves to analyze and visualize voter distribution, demographic patterns, and electoral trends to enhance the accuracy of election forecasting and campaign strategies. It supports political parties and candidates in identifying key constituencies, optimizing resource allocation, and targeting voter outreach effectively. This data-driven approach improves the understanding of voter behavior and election dynamics, facilitating informed decision-making during electoral processes.
The Redistricting Process Explained
The redistricting process involves redrawing electoral district boundaries to reflect population changes and ensure equal representation, guided by census data and legal criteria such as the Voting Rights Act. Electoral mapping is a tool used within this process to analyze demographic trends and voting patterns, helping policymakers design districts that comply with legal standards and promote fair competition. Redistricting aims to balance district populations while preventing gerrymandering and preserving communities of interest.
Impact of Electoral Mapping on Political Representation
Electoral mapping significantly influences political representation by determining how voting districts are drawn, affecting the balance of party power and minority group influence. Precise electoral maps can enhance fair representation by reflecting demographic diversity and voting patterns, whereas manipulative mapping practices like gerrymandering distort electoral outcomes. The impact on political representation is profound, as electoral mapping shapes the electorate's voice and legislative responsiveness.
The Role of Redistricting in Preventing Gerrymandering
Redistricting plays a critical role in preventing gerrymandering by redrawing electoral district boundaries to ensure equal population distribution and fair representation. Electoral mapping uses geographic and demographic data to analyze voting patterns, but redistricting enacts changes that can eliminate biased district shapes favoring specific parties. Independent redistricting commissions and legally mandated criteria help create balanced districts that uphold the principle of one person, one vote.
Challenges and Controversies in Mapping vs Redistricting
Electoral mapping faces challenges in accurately reflecting demographic diversity and voting patterns, often leading to gerrymandering that undermines fair representation. Redistricting processes are frequently controversial due to political manipulation, where district boundaries are redrawn to favor specific parties or candidates, compromising electoral equity. Both mapping and redistricting grapple with balancing legal criteria and community interests while ensuring transparency and public trust.
Future Trends in Electoral Mapping and Redistricting
Future trends in electoral mapping and redistricting emphasize the integration of advanced geospatial technologies and data analytics to enhance precision and fairness in district boundary design. Machine learning algorithms and big data analysis are increasingly employed to detect and prevent gerrymandering while ensuring equitable representation. Growing adoption of transparent, publicly accessible mapping tools fosters community involvement and accountability in the redistricting process.
Electoral mapping Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com