A unity government combines multiple political parties, often from opposing sides, to create a shared administration that promotes stability and cooperation during times of crisis or transition. This form of governance aims to bridge divides and ensure inclusive decision-making for the benefit of all citizens. Explore the rest of the article to understand how a unity government can impact your country's political landscape.
Table of Comparison
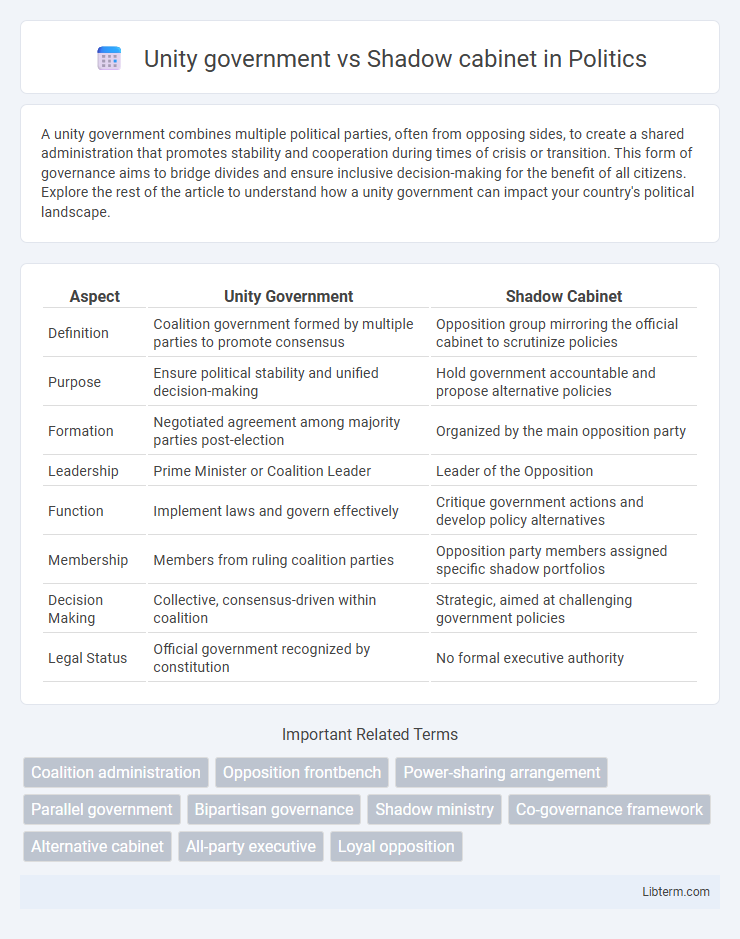
| Aspect | Unity Government | Shadow Cabinet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coalition government formed by multiple parties to promote consensus | Opposition group mirroring the official cabinet to scrutinize policies |
| Purpose | Ensure political stability and unified decision-making | Hold government accountable and propose alternative policies |
| Formation | Negotiated agreement among majority parties post-election | Organized by the main opposition party |
| Leadership | Prime Minister or Coalition Leader | Leader of the Opposition |
| Function | Implement laws and govern effectively | Critique government actions and develop policy alternatives |
| Membership | Members from ruling coalition parties | Opposition party members assigned specific shadow portfolios |
| Decision Making | Collective, consensus-driven within coalition | Strategic, aimed at challenging government policies |
| Legal Status | Official government recognized by constitution | No formal executive authority |
Definition of Unity Government
A Unity Government is a coalition formed by multiple political parties, usually during times of national crisis, to maintain stability and share executive power. It aims to create consensus-driven decision-making and avoid political polarization by including representatives from across the political spectrum. In contrast, a Shadow Cabinet consists of opposition party members who scrutinize and challenge the policies of the ruling government, acting as an alternative government-in-waiting.
Definition of Shadow Cabinet
The Shadow Cabinet is a group of senior opposition party members who monitor and critique the policies and actions of their corresponding government ministers, serving as a government-in-waiting. Unlike the Unity government, which consists of representatives from multiple political parties working collaboratively in official governance, the Shadow Cabinet operates outside the ruling administration to provide alternative policies and hold the government accountable. This structure is essential in parliamentary systems to ensure transparency and robust policy debate.
Key Differences Between Unity Government and Shadow Cabinet
Unity governments are formed during national crises, involving multiple political parties collaboratively sharing power to ensure stability and collective decision-making. Shadow cabinets consist of opposition party members who scrutinize government policies and propose alternatives without participating in executive power. The key difference lies in the unity government's inclusive governance approach versus the shadow cabinet's role in holding the government accountable through structured opposition.
Historical Examples of Unity Governments
Historical examples of unity governments include the United Kingdom's coalition government during World War II, led by Winston Churchill, which brought together major political parties to address national crises effectively. Another significant instance is the National Unity Government in South Africa post-apartheid in 1994, uniting the African National Congress, National Party, and Inkatha Freedom Party to facilitate democratic transition. These unity governments contrast with shadow cabinets, which function as official opposition teams in parliamentary systems, offering alternative policies without shared executive power.
Notable Shadow Cabinets in Political History
Notable shadow cabinets in political history have played a crucial role in parliamentary democracies by providing organized opposition to unity governments, ensuring government accountability and alternative policy proposals. Examples include the UK's Conservative shadow cabinet during Labour governments, which effectively scrutinized policies and prepared for electoral challenges, and Australia's shadow cabinet, recognized for institutionalizing the role of the opposition in governance. These shadow cabinets have historically shaped political discourse by offering structured critiques and ready governance teams, reinforcing democratic principles through robust political debate.
Formation Processes: Unity Government vs Shadow Cabinet
The formation of a unity government involves multiple political parties coming together, often in response to a national crisis or to ensure broad representation, requiring negotiations to share executive power and ministerial posts. In contrast, a shadow cabinet is formed by the main opposition party in parliamentary systems to mirror the official cabinet, assigning shadow ministers to scrutinize and challenge government policies without holding executive authority. The unity government aims for cooperation and policy consensus across parties, while the shadow cabinet functions as a structured alternative for accountability and policy debate.
Roles and Responsibilities in Both Systems
Unity government involves collaboration between major political parties sharing executive responsibilities to foster stability and address national crises, with all members having formal roles in decision-making and policy implementation. Shadow cabinet members in a parliamentary system serve as the official opposition, scrutinizing government actions, proposing alternative policies, and holding ministers accountable without direct executive power. The unity government emphasizes collective governance and joint administration, while the shadow cabinet focuses on oversight, critique, and preparing to assume office.
Impact on Political Stability and Governance
Unity governments enhance political stability by fostering cooperation among diverse parties, reducing legislative gridlock, and facilitating consensus-driven policy-making. In contrast, shadow cabinets serve as a check on the ruling party, promoting accountability and readiness for governance without directly influencing current policy decisions. The balance between these structures impacts governance effectiveness, with unity governments ensuring continuity during crises and shadow cabinets strengthening democratic oversight.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each System
Unity governments promote political stability by including multiple parties, enabling broader representation and cooperative policymaking, but they can lead to diluted decision-making and prolonged consensus-building. Shadow cabinets provide clear opposition and accountability, offering alternative policies and scrutinizing government actions; however, they may deepen partisan divides and limit collaborative governance. Each system balances inclusivity and efficiency with distinct impacts on political dynamics and legislative effectiveness.
Choosing Between Unity Government and Shadow Cabinet: Contextual Factors
Choosing between a unity government and a shadow cabinet depends on political stability, election outcomes, and national crises. Unity governments often emerge in post-conflict or coalition scenarios aimed at inclusive governance to restore public trust and ensure major policy decisions reflect consensus. Shadow cabinets serve as organized opposition, crucial in parliamentary democracies for policy scrutiny and accountability, especially when political polarization demands clear alternatives without disrupting government functioning.
Unity government Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com