Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional institutions, values, and social order to maintain stability and continuity within society. It often advocates for limited government intervention, individual responsibility, and respect for established customs. Explore the rest of this article to understand how conservatism shapes political and cultural landscapes today.
Table of Comparison
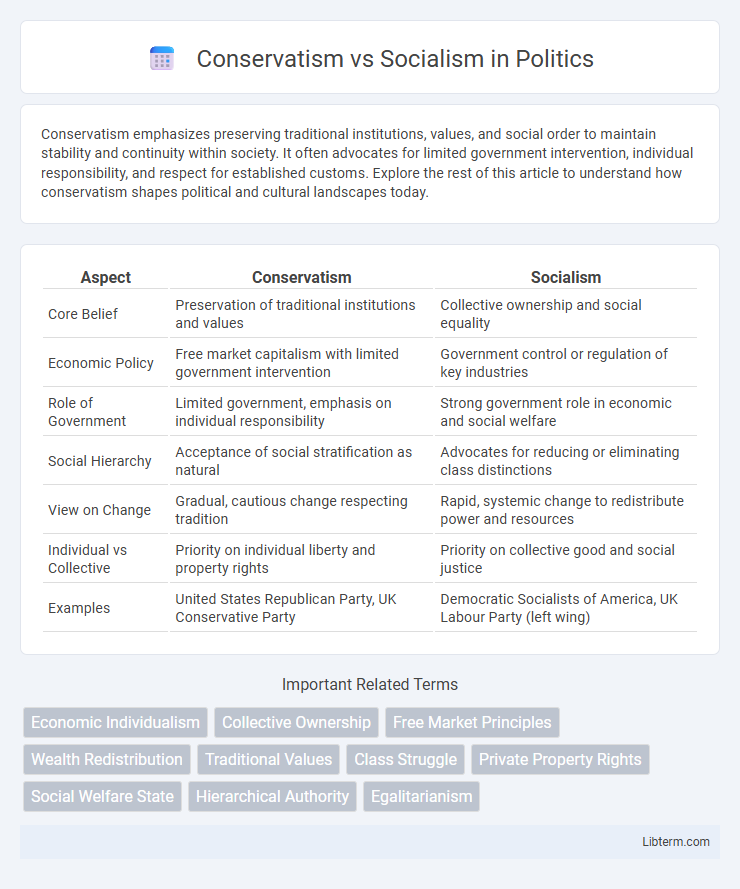
| Aspect | Conservatism | Socialism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Belief | Preservation of traditional institutions and values | Collective ownership and social equality |
| Economic Policy | Free market capitalism with limited government intervention | Government control or regulation of key industries |
| Role of Government | Limited government, emphasis on individual responsibility | Strong government role in economic and social welfare |
| Social Hierarchy | Acceptance of social stratification as natural | Advocates for reducing or eliminating class distinctions |
| View on Change | Gradual, cautious change respecting tradition | Rapid, systemic change to redistribute power and resources |
| Individual vs Collective | Priority on individual liberty and property rights | Priority on collective good and social justice |
| Examples | United States Republican Party, UK Conservative Party | Democratic Socialists of America, UK Labour Party (left wing) |
Introduction to Conservatism and Socialism
Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional institutions, values, and social stability, advocating for gradual change rooted in historical continuity. Socialism calls for collective ownership and redistribution of resources to achieve social equality and reduce class disparities. These ideologies present contrasting views on governance, economic systems, and social justice.
Historical Origins of Conservatism and Socialism
Conservatism originated in the late 18th century as a reaction to the radical changes brought by the French Revolution, emphasizing tradition, social stability, and hierarchical authority rooted in the works of Edmund Burke. Socialism emerged in the early 19th century amid the Industrial Revolution, advocating for collective ownership and redistribution of wealth to address economic inequalities, influenced by thinkers such as Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. Both ideologies developed as responses to rapid social and economic transformations, shaping distinct political philosophies around order and equality.
Core Principles of Conservatism
Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional institutions, valuing social stability, and promoting gradual change rather than radical reforms. It prioritizes individual responsibility, free-market economies, and limited government intervention to maintain order and protect personal freedoms. Core principles include respect for established customs, belief in the importance of hierarchy, and a cautious approach to societal evolution.
Fundamental Beliefs of Socialism
Socialism is grounded in the belief that wealth and resources should be distributed more equally to reduce social inequalities and promote collective welfare. It advocates for public or communal ownership of the means of production, aiming to prevent exploitation and ensure that economic benefits serve the entire society rather than a privileged few. Socialism emphasizes social justice, economic planning, and the provision of universal access to essential services like healthcare, education, and housing.
Economic Models: Market vs. State Control
Conservatism advocates for a market-driven economy emphasizing private property rights, minimal government intervention, and free enterprise to foster innovation and economic growth. Socialism supports state control or significant regulation of economic resources to promote wealth redistribution, reduce inequality, and ensure public welfare through centralized planning or cooperative ownership. The tension between market freedom and state oversight defines the core economic debate, influencing policies on taxation, social services, and regulatory frameworks.
Social Policies: Tradition vs. Progress
Conservatism emphasizes maintaining traditional social policies that preserve established norms, family structures, and cultural heritage, prioritizing stability and gradual change. Socialism advocates for progressive social policies aimed at reducing inequality, expanding welfare programs, and promoting social justice through government intervention. The tension between tradition and progress underpins debates on education, healthcare, and labor rights, reflecting differing views on the role of state and society in shaping social order.
Government Role and Individual Freedoms
Conservatism emphasizes limited government intervention, advocating for free-market principles and individual responsibility to preserve personal freedoms and social order. Socialism supports extensive government involvement in economic and social affairs, aiming to reduce inequality through redistribution and public ownership, often prioritizing collective welfare over individual autonomy. The fundamental tension lies in balancing state authority and personal liberty, with conservatism stressing minimal regulation and socialism endorsing centralized control for social justice.
Conservatism and Socialism in Modern Politics
Conservatism in modern politics emphasizes preserving traditional institutions, advocating for limited government intervention, free markets, and individual responsibility, often prioritizing national sovereignty and cultural continuity. Socialism promotes social ownership, economic equality, and wealth redistribution through expanded government roles in healthcare, education, and social welfare programs to address systemic inequalities. Both ideologies influence contemporary policy debates on taxation, social justice, and economic regulation across global political landscapes.
Global Influence and Case Studies
Conservatism has shaped global political landscapes by emphasizing tradition, free markets, and limited government intervention, evident in countries like the United States and the United Kingdom where policies often prioritize economic liberalism and national sovereignty. Socialism, with its focus on social equity, wealth redistribution, and state ownership, has influenced governments such as those in Sweden and Venezuela, creating contrasting outcomes in social welfare and economic stability. Case studies in Scandinavia illustrate successful mixed economies balancing free enterprise with strong social safety nets, while Venezuela's experience highlights challenges of resource dependence and authoritarianism under socialist policies.
Comparing Future Prospects: Conservatism vs. Socialism
Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional institutions and incremental change, which can ensure political stability and gradual economic growth in future societies. Socialism advocates for extensive government involvement and wealth redistribution, aiming to reduce inequality and provide universal social welfare, potentially transforming economic structures. Future prospects hinge on balancing economic efficiency with social equity, where conservatism prioritizes market-driven solutions and socialism stresses collective well-being.
Conservatism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com