Liberalism emphasizes individual freedoms, political equality, and economic rights, advocating for limited government interference in personal lives. It supports democratic governance, free markets, and the protection of civil liberties to foster social progress and personal development. Explore how liberalism shapes modern societies and influences your daily life in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
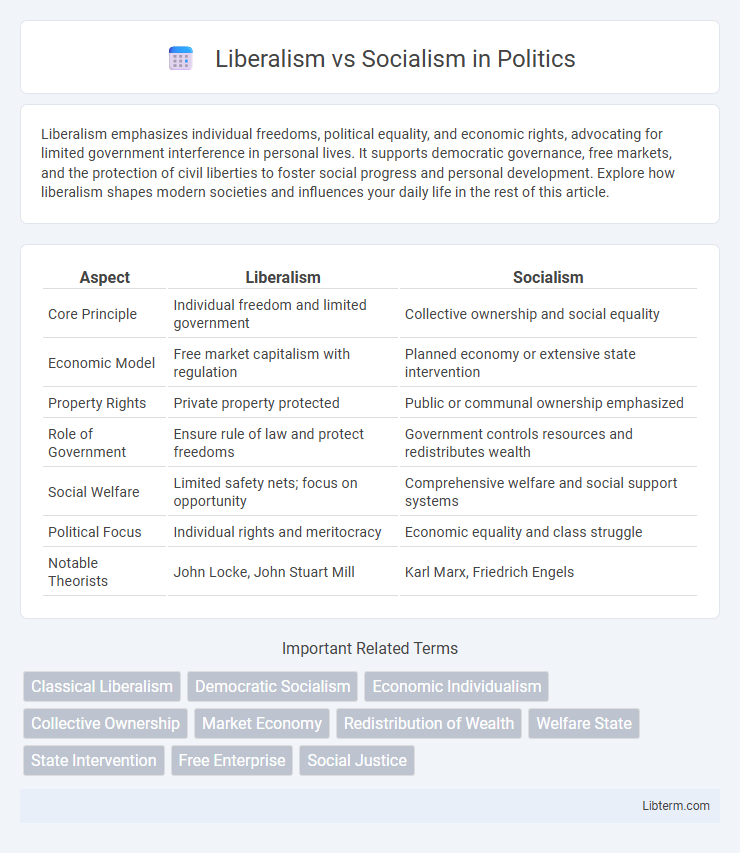
| Aspect | Liberalism | Socialism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Individual freedom and limited government | Collective ownership and social equality |
| Economic Model | Free market capitalism with regulation | Planned economy or extensive state intervention |
| Property Rights | Private property protected | Public or communal ownership emphasized |
| Role of Government | Ensure rule of law and protect freedoms | Government controls resources and redistributes wealth |
| Social Welfare | Limited safety nets; focus on opportunity | Comprehensive welfare and social support systems |
| Political Focus | Individual rights and meritocracy | Economic equality and class struggle |
| Notable Theorists | John Locke, John Stuart Mill | Karl Marx, Friedrich Engels |
Introduction to Liberalism and Socialism
Liberalism emphasizes individual freedom, political equality, and free markets, advocating limited government intervention to protect civil liberties and promote economic growth. Socialism prioritizes social ownership, economic equality, and redistribution of wealth through state control or cooperative management of resources. Both ideologies offer contrasting approaches to governance, economic policies, and the role of the state in society.
Core Principles of Liberalism
Liberalism centers on individual freedom, private property rights, and limited government intervention to protect personal liberties and promote free markets. It emphasizes the rule of law, equality before the law, and the protection of civil rights such as freedom of speech and religion. Economic liberalism advocates for minimal state interference in the economy, encouraging competition and innovation to drive prosperity.
Fundamental Values of Socialism
Socialism prioritizes collective ownership and equitable distribution of resources to reduce social inequalities and promote social justice. It emphasizes cooperation, social welfare, and government intervention to ensure equal access to education, healthcare, and employment. Fundamental values of socialism also include the pursuit of economic democracy, solidarity, and the protection of workers' rights.
Historical Origins and Development
Liberalism emerged in the 17th and 18th centuries during the Age of Enlightenment, emphasizing individual rights, private property, and limited government, with key influences from thinkers like John Locke and Adam Smith. Socialism developed in the early 19th century as a response to the inequalities of industrial capitalism, advocating for collective ownership and social justice, inspired by figures like Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. Both ideologies evolved through political movements and revolutions, shaping modern democratic and economic systems worldwide.
Economic Policies: Free Market vs Central Planning
Liberalism emphasizes free market economics, advocating minimal government intervention to promote competition, innovation, and individual entrepreneurship. Socialism supports central planning, where the government controls resources and production to ensure equitable distribution and reduce economic inequalities. The economic policies reflect fundamental differences in prioritizing market efficiency versus social welfare.
Social Justice and Individual Rights
Socialism emphasizes social justice through promoting economic equality and collective welfare by advocating for wealth redistribution and public ownership of resources. Liberalism prioritizes individual rights, safeguarding personal freedoms such as free speech and private property while supporting limited government intervention. The core tension lies in balancing social equity with protecting individual autonomy within political and economic systems.
Role of Government in Society
Liberalism advocates for limited government intervention, emphasizing individual freedoms, private property rights, and free markets to drive social progress. Socialism supports a more expansive government role in regulating the economy and redistributing wealth to achieve social equality and protect collective interests. The contrasting views reflect fundamental differences in prioritizing personal liberty versus social welfare within governance.
Liberalism vs Socialism: Key Differences
Liberalism emphasizes individual freedom, private property, and market-driven economies, advocating limited government intervention to protect personal rights and promote economic growth. Socialism prioritizes social equality, advocating collective ownership of resources and government control over key industries to reduce wealth disparities and provide universal social services. The key differences lie in their approach to economic management, the role of government, and the balance between individual liberty and social welfare.
Contemporary Debates and Global Impact
Contemporary debates between liberalism and socialism center on the balance between individual freedoms and social equality, with liberalism advocating for free markets and limited government intervention, while socialism emphasizes wealth redistribution and state involvement in social welfare. Globally, liberal policies dominate in capitalist economies promoting innovation and entrepreneurship, whereas socialist frameworks influence regions prioritizing universal healthcare and social safety nets. The impact of these ideologies shapes international trade, economic development strategies, and social justice movements across diverse political landscapes.
Conclusion: Balancing Ideals in Modern Societies
Liberalism emphasizes individual freedoms, private property, and limited government intervention, fostering innovation and personal responsibility, while socialism advocates for wealth redistribution, social equality, and collective ownership to reduce disparities and provide universal access to essential services. Modern societies often seek a pragmatic balance, integrating market-driven economies with social safety nets and regulatory frameworks to address inequality without stifling economic growth. Effective governance hinges on harmonizing these ideals to promote both economic efficiency and social justice in increasingly complex and diverse populations.
Liberalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com