A sunset provision is a legal clause that sets an expiration date for a law or regulation unless further legislative action is taken to extend it. This mechanism ensures that policies are regularly reviewed and adjusted according to current needs and circumstances. Discover how sunset provisions impact your rights and governance throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
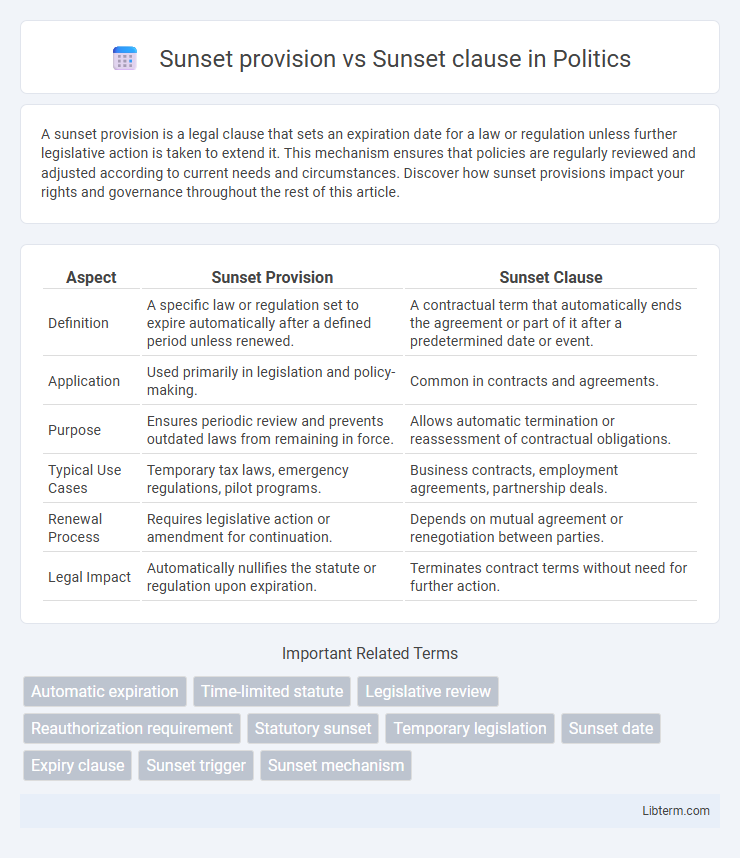
| Aspect | Sunset Provision | Sunset Clause |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A specific law or regulation set to expire automatically after a defined period unless renewed. | A contractual term that automatically ends the agreement or part of it after a predetermined date or event. |
| Application | Used primarily in legislation and policy-making. | Common in contracts and agreements. |
| Purpose | Ensures periodic review and prevents outdated laws from remaining in force. | Allows automatic termination or reassessment of contractual obligations. |
| Typical Use Cases | Temporary tax laws, emergency regulations, pilot programs. | Business contracts, employment agreements, partnership deals. |
| Renewal Process | Requires legislative action or amendment for continuation. | Depends on mutual agreement or renegotiation between parties. |
| Legal Impact | Automatically nullifies the statute or regulation upon expiration. | Terminates contract terms without need for further action. |
Introduction to Sunset Provision and Sunset Clause
Sunset provision and sunset clause both refer to legal or contractual terms that establish an expiration date for a law, regulation, or contract condition, ensuring automatic termination unless renewed. A sunset provision typically appears in legislation to prevent laws from remaining permanently without review, while a sunset clause is commonly included in contracts to specify when certain terms or obligations end. Both mechanisms serve to introduce temporal limits, promoting periodic assessment and adaptation in legal and business contexts.
Defining Sunset Provision
A sunset provision is a specific legal or contractual term that sets an expiration date for a law, regulation, or agreement, ensuring it automatically terminates unless renewed. The key function of a sunset provision is to allow periodic review and evaluation before continuing its enforcement, promoting adaptability in legislative or contractual frameworks. Unlike a general sunset clause, a sunset provision explicitly mandates expiration without requiring action to repeal or amend it.
Understanding Sunset Clause
A Sunset Clause is a legal provision that sets an expiration date for a law, contract, or regulation, ensuring it remains in effect only for a specified period unless renewed. Sunset Provisions function as built-in review mechanisms, promoting accountability by requiring reassessment of the policy's relevance and effectiveness before extension. Understanding a Sunset Clause helps policymakers design temporary measures that avoid indefinite enforcement and encourage periodic evaluation of legislative impact.
Key Differences Between Sunset Provision and Sunset Clause
A sunset provision is a specific legislative measure that automatically terminates a law or regulation after a predetermined period unless further action is taken to extend it, while a sunset clause refers to a contractual term that sets an expiration date for certain obligations or rights within an agreement. The key difference lies in their application; sunset provisions are primarily used in statutory or regulatory contexts, whereas sunset clauses are found in private contracts. Both mechanisms serve to limit the duration of enforceability, but sunset provisions typically require active legislative renewal, whereas sunset clauses depend on contract parties' agreements.
Historical Origins of Sunset Provision and Clause
The historical origins of the sunset provision trace back to ancient legal systems where temporary laws were enacted to address specific circumstances, ensuring automatic expiration after a set period unless renewed. Sunset clauses evolved as a formalized legal mechanism within modern legislative frameworks, particularly in the 20th century, to enhance legislative oversight and prevent outdated regulations from persisting indefinitely. Both concepts share the foundational principle of time-bound validity, but sunset provisions originally emerged from pragmatic governance needs in early civilizations, while sunset clauses reflect contemporary statutory design promoting accountability and adaptability.
Legal Applications of Sunset Provisions
Sunset provisions, often embedded in legislative acts, specify a predetermined expiration date for laws or regulations unless further legislative action extends them, ensuring periodic review and preventing outdated statutes from remaining in effect. Sunset clauses function similarly but are commonly found within contracts, terminating obligations or rights after a set time unless renewed, thus providing legal certainty and flexibility in agreements. Both mechanisms promote accountability and adaptability in legal frameworks by mandating reassessment, reducing regulatory burdens, and aligning policies with current societal needs.
Legislative Use of Sunset Clauses
Sunset provisions and sunset clauses both refer to legal measures that set an expiration date for laws or regulations unless renewed, but they differ primarily in terminology and context. In legislative use, sunset clauses are embedded within statutes to automatically repeal or terminate the law after a specific period, ensuring periodic review and preventing outdated or unnecessary legislation. This mechanism promotes legislative efficiency by requiring lawmakers to reevaluate the law's effectiveness and relevance before extension or permanent enactment.
Advantages of Sunset Provisions vs. Sunset Clauses
Sunset provisions offer clear advantages over sunset clauses by providing automatic termination dates for laws or contracts, reducing the risk of indefinite enforcement and promoting regulatory review. These provisions enhance legislative accountability by requiring periodic reassessment, which ensures that outdated or ineffective measures are revisited systematically. Businesses and policymakers benefit from the predictability and transparency of sunset provisions, promoting informed decision-making and adaptive legal frameworks.
Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
Sunset provision and sunset clause often cause confusion as they both refer to mechanisms that set an expiration date for laws, contracts, or agreements, but a sunset provision is typically embedded in legislation to automatically repeal the law after a specific period unless renewed. A sunset clause often appears in contracts or agreements, delineating the termination of certain conditions or obligations after a predetermined time. Clarifying that a sunset provision applies primarily to statutory laws, whereas a sunset clause governs contractual terms, helps dispel common misconceptions between the two.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Sunset Mechanism
Selecting the appropriate sunset mechanism hinges on the specific legal or contractual context and desired flexibility for termination. Sunset provisions typically offer predetermined expiration dates for laws or regulations, ensuring automatic cessation unless renewed, while sunset clauses provide conditional termination terms within contracts based on agreed criteria. Evaluating the scope, enforcement needs, and risk management goals ensures an effective balance between control and adaptive governance.
Sunset provision Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com