The Tetragrammaton refers to the four-letter Hebrew name of God, YHWH, considered sacred and ineffable in Jewish tradition. Its pronunciation and meaning have been the subject of extensive theological and linguistic studies, symbolizing divine presence and authority. Discover more about the origins, interpretations, and significance of the Tetragrammaton in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
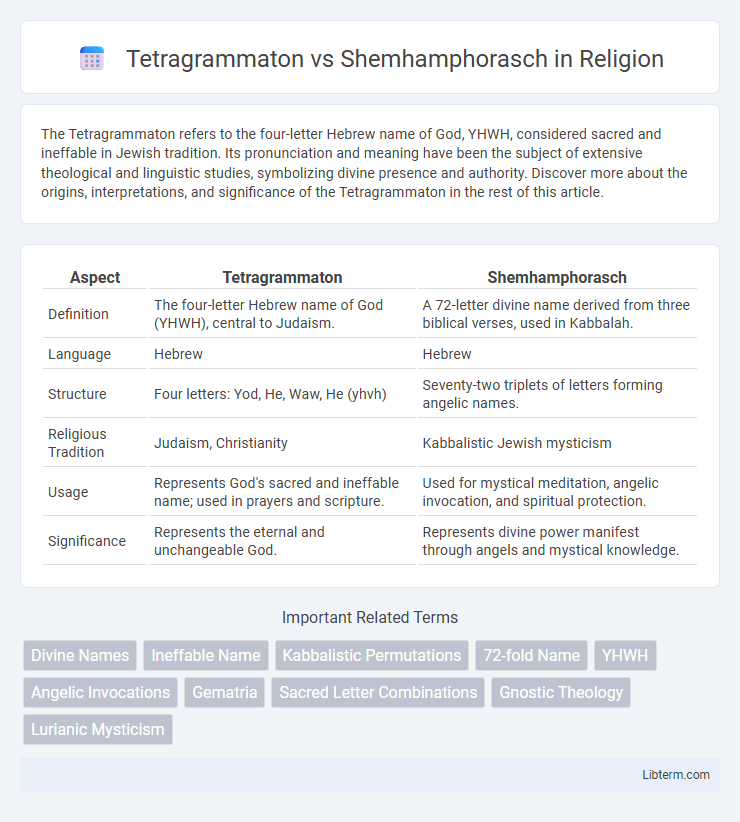
| Aspect | Tetragrammaton | Shemhamphorasch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The four-letter Hebrew name of God (YHWH), central to Judaism. | A 72-letter divine name derived from three biblical verses, used in Kabbalah. |
| Language | Hebrew | Hebrew |
| Structure | Four letters: Yod, He, Waw, He (yhvh) | Seventy-two triplets of letters forming angelic names. |
| Religious Tradition | Judaism, Christianity | Kabbalistic Jewish mysticism |
| Usage | Represents God's sacred and ineffable name; used in prayers and scripture. | Used for mystical meditation, angelic invocation, and spiritual protection. |
| Significance | Represents the eternal and unchangeable God. | Represents divine power manifest through angels and mystical knowledge. |
Introduction to Tetragrammaton and Shemhamphorasch
The Tetragrammaton, represented by the four Hebrew letters YHWH, is the sacred and ineffable name of God in Hebrew tradition, central to Jewish theology and mysticism. The Shemhamphorasch, often translated as the "explicit name," refers to a 72-letter divine name derived from three verses in Exodus, used in Kabbalistic practices for spiritual protection and mystical insights. Both names are foundational in Jewish mysticism, with the Tetragrammaton emphasizing God's unpronounceable essence and the Shemhamphorasch symbolizing divine power channeled through complex angelic hierarchies.
Etymology and Linguistic Origins
The Tetragrammaton, derived from the Greek "tetra" meaning four and "gramma" meaning letter, represents the four-letter Hebrew name of God YHWH, rooted in ancient Semitic languages and pivotal in Judaic tradition. Shemhamphorasch originates from the Hebrew phrase "Shem HaMeforash," meaning "the explicit name," and refers to a 72-letter divine name constructed from three verses in Exodus, reflecting Kabbalistic linguistic mysticism. Both terms highlight distinct etymological pathways: Tetragrammaton emphasizes the four-letter divine name's unpronounceable sanctity, while Shemhamphorasch encapsulates a complex, numerologically and phonologically rich expression in esoteric Jewish theology.
The Tetragrammaton: Meaning and Mysticism
The Tetragrammaton, composed of the four Hebrew letters Yod-Heh-Vav-Heh (yhvh), represents the ineffable name of God in Jewish mysticism and is central to Kabbalistic teachings. This sacred name signifies the divine essence and unity of God, embodying concepts of creation, existence, and eternal presence. Mystics meditate on the Tetragrammaton to access higher spiritual realms and divine wisdom, distinguishing it from the Shemhamphorasch, which refers to the 72-fold name derived from Exodus.
Shemhamphorasch: The Extended Divine Name
Shemhamphorasch, known as the Extended Divine Name, expands beyond the Tetragrammaton (YHWH) by encompassing 72 names derived from three consecutive verses in Exodus 14:19-21. Each name in the Shemhamphorasch corresponds to a unique angelic entity believed to possess distinct spiritual attributes and powers in Kabbalistic tradition. This extended naming system is central to esoteric Jewish mysticism, offering profound insights into divine manifestations and mediating the relationship between the infinite and the finite.
Scriptural and Historical Contexts
The Tetragrammaton, represented by the four Hebrew letters Yod-Heh-Vav-Heh (YHWH), is the sacred and ineffable name of God found extensively in the Hebrew Bible, signifying the eternal and unchanging nature of the divine. The Shemhamphorasch, derived from Kabbalistic tradition, refers to a 72-letter name of God formed from three consecutive verses in Exodus 14:19-21, encapsulating mystical attributes and divine energies beyond the scriptural portrayal of YHWH. Historically, the Tetragrammaton holds central importance in Judaic worship and theology, while the Shemhamphorasch emerges from medieval Jewish mysticism and esoteric interpretations, highlighting different dimensions of divine revelation and interaction.
Usage in Jewish Mysticism and Kabbalah
The Tetragrammaton, representing the four-letter name of God (YHWH), is central to Jewish mysticism and Kabbalah, symbolizing divine essence and unmanifested creative power. The Shemhamphorasch comprises 72 names derived from specific Biblical verses, each associated with distinct angelic forces and spiritual attributes used in mystical practices and rituals. While the Tetragrammaton emphasizes God's ineffable nature, the Shemhamphorasch facilitates focused invocation and interaction with divine energies in esoteric Kabbalistic traditions.
Symbolic Differences and Spiritual Implications
The Tetragrammaton (YHWH) symbolizes the ineffable name of God in Hebrew tradition, embodying divine unity and eternal presence, while the Shemhamphorasch refers to the 72-fold name derived from Exodus, representing specific angelic forces and spiritual attributes. Symbolically, the Tetragrammaton emphasizes God's singular, all-encompassing nature, whereas the Shemhamphorasch serves as a tool for mystical invocation and personalized spiritual influence. Spiritually, the Tetragrammaton underlines divine immanence and transcendence, and the Shemhamphorasch facilitates connection with angelic energies, enhancing protection, wisdom, and transformation in esoteric practices.
Ritual and Magical Applications
The Tetragrammaton, composed of the four Hebrew letters YHWH, serves as a foundational divine name in Jewish mysticism and ritual magic, used for invocation and protection in ceremonial contexts. The Shemhamphorasch, a 72-letter name derived from three verses in Exodus, functions primarily in Western esoteric traditions for summoning angels and achieving specific magical outcomes. Both names are central to ritual practices but differ in their linguistic structure, cultural origins, and specific magical applications within Kabbalistic and Hermetic traditions.
Influence on Western Esoteric Traditions
The Tetragrammaton, representing the sacred four-letter name of God (YHWH) in Hebrew tradition, serves as a foundational symbol in Western esotericism, influencing Kabbalistic and Hermetic teachings through its association with divine manifestation and mystical power. The Shemhamphorasch refers to the 72-fold name of God, derived from three verses in Exodus, and plays a critical role in ritual magic, angelology, and talismanic practices within Western occult traditions. Both concepts deeply inform ceremonial magic, shaping key frameworks in the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn and other esoteric schools by linking divine names to cosmic forces and personal transformation.
Contemporary Interpretations and Debates
Contemporary interpretations of the Tetragrammaton (YHWH) often emphasize its role as the ineffable name of God in Jewish mysticism, while the Shemhamphorasch is regarded as the 72-fold name derived from Exodus, associated with angelic powers and Kabbalistic practices. Debates center on the theological implications of pronouncing or meditating on these names, with some scholars arguing for their spiritual potency in modern mysticism versus others cautioning against appropriation outside traditional contexts. Current discourse also explores the symbolic meanings embedded in these divine names, reflecting shifts in religious, esoteric, and psychological understandings within contemporary spiritual movements.
Tetragrammaton Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com