Consistency is the cornerstone of achieving long-term success in any endeavor, as it builds trust and reinforces positive habits. Maintaining regular effort allows you to overcome obstacles and steadily progress toward your goals. Discover practical strategies to boost your consistency and transform your ambitions into reality by reading the rest of this article.
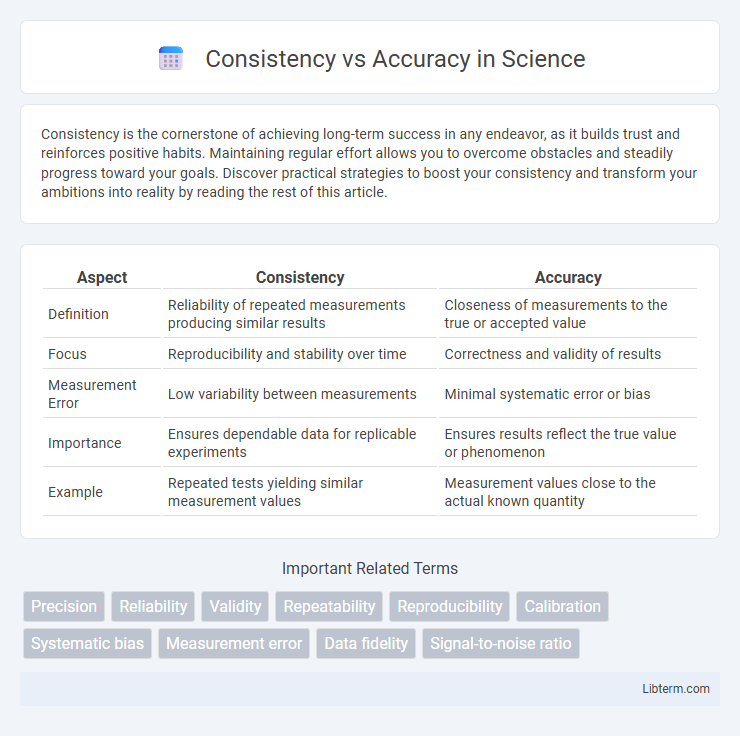
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Consistency | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reliability of repeated measurements producing similar results | Closeness of measurements to the true or accepted value |
| Focus | Reproducibility and stability over time | Correctness and validity of results |
| Measurement Error | Low variability between measurements | Minimal systematic error or bias |
| Importance | Ensures dependable data for replicable experiments | Ensures results reflect the true value or phenomenon |
| Example | Repeated tests yielding similar measurement values | Measurement values close to the actual known quantity |
Understanding Consistency and Accuracy
Consistency measures the reliability of repeated measurements or observations, ensuring similar results under unchanged conditions, while accuracy reflects how close a measurement is to the true or accepted value. Understanding consistency involves assessing the precision and repeatability of data, which reduces random errors, whereas accuracy focuses on minimizing systematic errors to achieve correctness. Distinguishing between these concepts is crucial for quality control, data analysis, and scientific experimentation to ensure valid and dependable outcomes.
Key Differences Between Consistency and Accuracy
Consistency refers to the repeatability of results under unchanged conditions, measuring how reliably a method produces the same outcome. Accuracy indicates how close a measurement or result is to the true or accepted value, reflecting correctness. The key difference lies in consistency focusing on precision and reproducibility, while accuracy emphasizes validity and closeness to the target value.
Why Consistency Matters in Data and Measurement
Consistency in data and measurement ensures reliable and reproducible results, which is crucial for decision-making and trend analysis across various fields. While accuracy reflects how close a measurement is to the true value, consistency guarantees that repeated measurements yield similar results, reducing variability and uncertainty. Maintaining consistency helps identify patterns, detect anomalies, and build confidence in long-term data-driven strategies and scientific research.
The Importance of Accuracy in Reliable Outcomes
Accuracy plays a crucial role in achieving reliable outcomes by ensuring data and results closely represent the true values or facts. High accuracy minimizes errors and false conclusions, which is essential in scientific research, medical diagnostics, and quality control processes. While consistency maintains stability across measurements, it is accuracy that validates the trustworthiness and practical applicability of findings.
Consistency vs Accuracy: Real-world Examples
In medical diagnostics, consistency ensures that different practitioners obtain the same results using a test, while accuracy reflects how closely those results match the true patient condition. In manufacturing, a product measured consistently with minor variation may still be inaccurate if calibration is off, leading to widespread defects. Financial forecasts demonstrate consistency when predictions follow a similar pattern over time, but accuracy is critical to reflecting actual market behavior and informing sound decisions.
Balancing Consistency and Accuracy in Practice
Balancing consistency and accuracy in practice requires understanding that high consistency ensures reliable repeatability of results, while accuracy guarantees correctness relative to a true value or standard. Effective decision-making and data analysis integrate consistent methodologies with continuous validation against accurate benchmarks to minimize systemic errors and improve overall performance. Organizations achieve optimal outcomes by aligning consistent processes with frequent accuracy assessments to adapt dynamically to evolving conditions.
Common Misconceptions About Consistency and Accuracy
Common misconceptions about consistency and accuracy often confuse the two, assuming that a method must be accurate to be consistent or vice versa. Consistency refers to the repeatability of measurements, while accuracy denotes how close a measurement is to the true value; a system can be consistent but inaccurate if it produces the same error repeatedly. Understanding this distinction is crucial in fields like scientific research and quality control, where reliable results depend on both consistent and accurate data.
Impact of Consistency vs Accuracy on Decision-Making
Consistency in data fosters reliable decision-making by ensuring stable, repeatable results that build trust over time. Accuracy directly affects the quality of decisions by providing precise, true-to-reality insights essential for correct conclusions. Balancing consistency and accuracy is crucial, as consistent yet inaccurate data can mislead decisions, while highly accurate but inconsistent data undermines confidence and hinders effective action.
Improving Both Consistency and Accuracy: Strategies
Improving both consistency and accuracy requires implementing standardized processes and continuous training to minimize errors and maintain uniform performance. Leveraging data analytics and feedback loops helps identify discrepancies and refine methods for better precision. Integrating quality control measures with automation tools enhances reliability while ensuring accurate outcomes across repeated tasks.
Conclusion: Choosing Consistency, Accuracy, or Both
Choosing between consistency and accuracy depends on the specific use case and priority of outcomes; consistency ensures reliable performance over time, while accuracy targets correctness in individual instances. In practice, many systems balance both by optimizing algorithms to maintain steady outputs without sacrificing precision. Decision-makers should assess operational goals and constraints to determine the optimal trade-off between consistency, accuracy, or an integrated approach that leverages the strengths of both.
Consistency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com