Polychronic time management involves handling multiple tasks simultaneously, reflecting a flexible approach to scheduling and priorities. This concept contrasts with monochronic cultures, which emphasize completing one task at a time in a linear fashion. Discover how adopting polychronic strategies can enhance your productivity by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
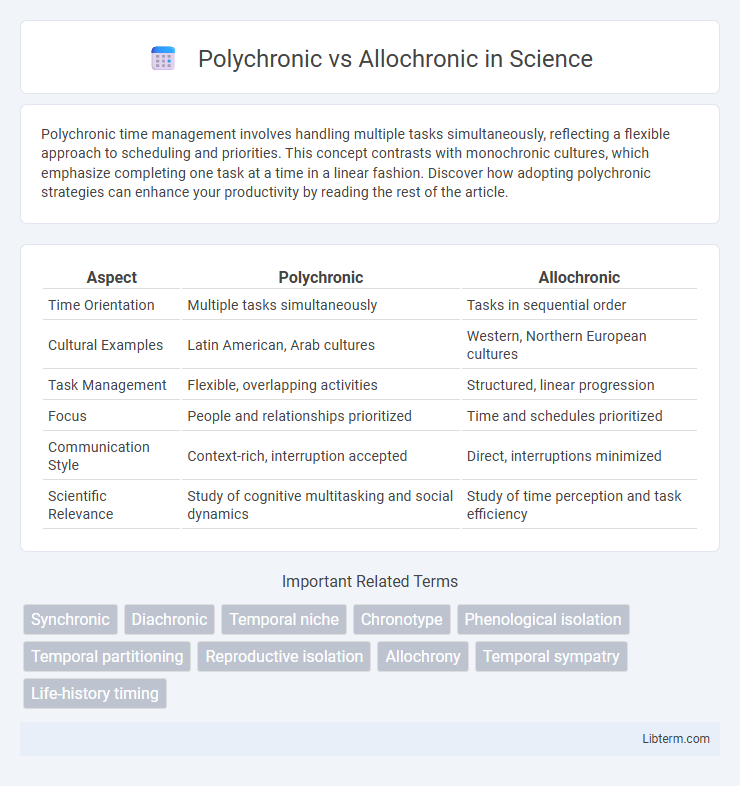
| Aspect | Polychronic | Allochronic |
|---|---|---|
| Time Orientation | Multiple tasks simultaneously | Tasks in sequential order |
| Cultural Examples | Latin American, Arab cultures | Western, Northern European cultures |
| Task Management | Flexible, overlapping activities | Structured, linear progression |
| Focus | People and relationships prioritized | Time and schedules prioritized |
| Communication Style | Context-rich, interruption accepted | Direct, interruptions minimized |
| Scientific Relevance | Study of cognitive multitasking and social dynamics | Study of time perception and task efficiency |
Understanding Polychronic and Allochronic: Definitions and Origins
Polychronic time orientation, rooted in cultural anthropology, emphasizes multitasking and flexible scheduling, prevalent in many Latin American, African, and Middle Eastern societies. Allochronic time, less commonly discussed, refers to a culturally relative perception where time is seen as fluid and less structured compared to monochronic and polychronic frameworks. Understanding these concepts aids in interpreting cultural differences in time management and social interactions, highlighting the diversity of temporal cognition across global communities.
Key Differences Between Polychronic and Allochronic Behaviors
Polychronic behaviors involve multitasking and managing multiple activities simultaneously within flexible time frames, emphasizing relationships over schedules. Allochronic behaviors focus on sequential task completion, adhering to strict schedules and prioritizing punctuality and order. The key difference lies in how time and tasks are organized: polychronic individuals prioritize fluid social interactions, while allochronic individuals value structure and time segmentation.
Cultural Perspectives: Where Polychronic and Allochronic Patterns Dominate
Polychronic time orientation, common in Latin American, Mediterranean, and Middle Eastern cultures, emphasizes multitasking and flexible schedules, prioritizing relationships over strict adherence to clocks. Allochronic time patterns, less prevalent and often found in indigenous or traditional societies, focus on event-based timing dictated by natural cycles or rituals rather than linear hours. Understanding these cultural perspectives is crucial for effective communication and collaboration across global contexts, where differing time concepts influence social interactions and business practices.
Impact on Communication Styles and Social Interactions
Polychronic cultures, which prioritize multitasking and flexible scheduling, foster communication styles that emphasize relationships, context, and indirect cues, often leading to more fluid and spontaneous social interactions. Allochronic perspectives, centered on strict time adherence and sequential task completion, promote direct, time-sensitive communication that values punctuality and clear agendas, influencing social interactions to be more structured and goal-oriented. Understanding these temporal orientations is crucial for improving cross-cultural communication and minimizing misunderstandings in diverse social environments.
Time Management: Polychronic vs Allochronic Approaches
Polychronic time management emphasizes multitasking and flexible scheduling, allowing individuals to handle multiple tasks simultaneously and prioritize relational interactions over strict adherence to deadlines. In contrast, allochronic time management follows a linear, sequential approach where tasks are completed one at a time, with a strong focus on punctuality and structured planning. Organizations adopting polychronic methods benefit from adaptability and responsiveness, while those using allochronic approaches enhance efficiency through precise time allocation and task completion.
Workplace Dynamics: Productivity and Collaboration
Polychronic workplace dynamics prioritize multitasking and flexible schedules, enhancing collaboration through overlapping tasks and fluid communication among team members. Allochronic environments emphasize sequential task management and strict time adherence, promoting productivity via focused, uninterrupted work phases and clear deadlines. Balancing polychronic and allochronic approaches can optimize both productivity and collaboration by aligning team workflows with diverse temporal preferences.
Advantages of Polychronic Behavior in Modern Society
Polychronic behavior enhances multitasking abilities, allowing individuals to manage multiple tasks and social interactions simultaneously, which increases productivity in fast-paced modern environments. This approach fosters stronger interpersonal relationships by prioritizing human connections over rigid schedules, improving teamwork and communication in diverse settings. Embracing polychronic time orientation supports adaptability and flexibility, crucial for navigating the complexities and interruptions of contemporary work and social life.
Challenges Faced by Allochronic Individuals in Polychronic Environments
Allochronic individuals, who prefer completing tasks sequentially, face significant challenges in polychronic environments characterized by multitasking and simultaneous activities. These environments demand constant attention shifts, often causing stress and reduced productivity for allochronic people who thrive on structure and focus. The clash between their time management style and the flexible, overlapping scheduling common in polychronic settings leads to misunderstandings and inefficiency.
Adapting and Navigating Mixed Chronemic Cultures
Adapting and navigating mixed chronemic cultures requires understanding the fundamental differences between polychronic and monochronic time orientations. Polychronic cultures prioritize multitasking, flexible schedules, and relational interactions, whereas monochronic cultures emphasize punctuality, linear time management, and task completion. Effective cross-cultural communication hinges on recognizing these temporal preferences and adjusting behavior to accommodate diverse time perceptions, ensuring smoother interpersonal and professional engagements.
Future Trends: Integrating Polychronic and Allochronic Values
Future trends indicate a growing integration of polychronic and allochronic time orientation values, fostering adaptability in multicultural work environments and global communication strategies. Businesses are increasingly leveraging polychronic flexibility alongside allochronic scheduling rigor to optimize productivity and enhance cross-cultural collaboration. Emerging technological tools enable seamless synchronization of these differing temporal approaches, driving innovation in time management practices worldwide.
Polychronic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com