Intelligent design posits that certain features of the universe and living organisms are best explained by an intelligent cause rather than undirected processes like natural selection. This perspective challenges conventional evolutionary theory by highlighting complex biological structures that seem purposefully engineered. Explore the full article to understand how intelligent design shapes debates in science and philosophy.
Table of Comparison
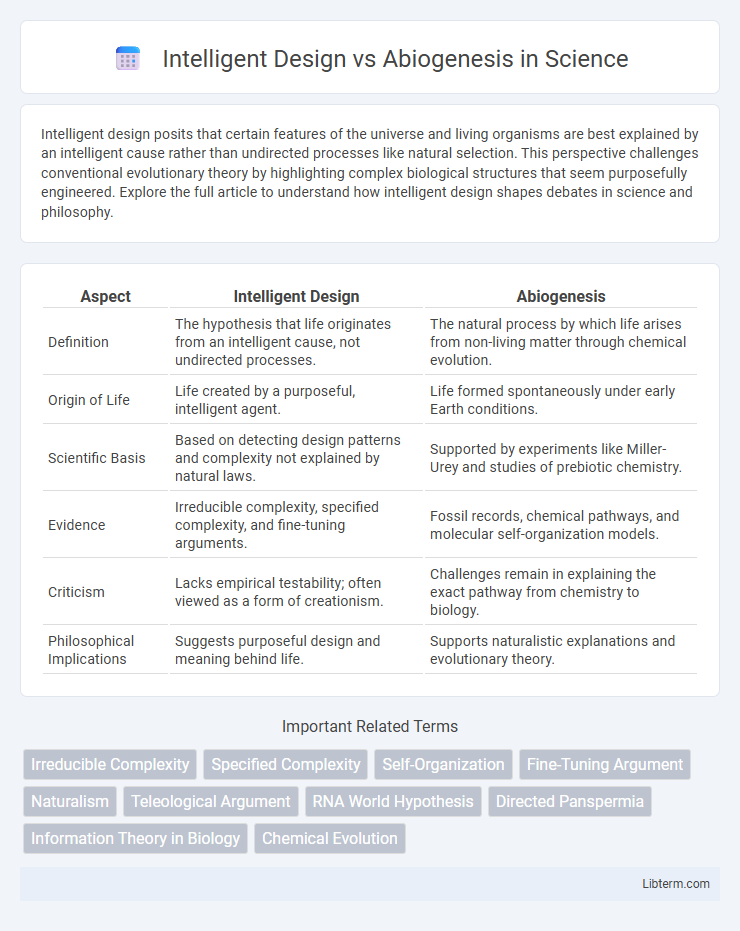
| Aspect | Intelligent Design | Abiogenesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The hypothesis that life originates from an intelligent cause, not undirected processes. | The natural process by which life arises from non-living matter through chemical evolution. |
| Origin of Life | Life created by a purposeful, intelligent agent. | Life formed spontaneously under early Earth conditions. |
| Scientific Basis | Based on detecting design patterns and complexity not explained by natural laws. | Supported by experiments like Miller-Urey and studies of prebiotic chemistry. |
| Evidence | Irreducible complexity, specified complexity, and fine-tuning arguments. | Fossil records, chemical pathways, and molecular self-organization models. |
| Criticism | Lacks empirical testability; often viewed as a form of creationism. | Challenges remain in explaining the exact pathway from chemistry to biology. |
| Philosophical Implications | Suggests purposeful design and meaning behind life. | Supports naturalistic explanations and evolutionary theory. |
Introduction to Origins: Intelligent Design vs Abiogenesis
Intelligent Design posits that certain features of the universe and living organisms are best explained by an intelligent cause rather than undirected natural processes, emphasizing complexity and specified information. Abiogenesis investigates the natural process by which life arose from non-living matter through chemical evolution on early Earth, supported by experimental evidence in prebiotic chemistry. The debate centers on origins of life theories, contrasting purposeful creation with naturalistic explanations in biological and cosmological contexts.
Defining Intelligent Design: Core Principles and Claims
Intelligent Design posits that certain features of the universe and living organisms are best explained by an intelligent cause rather than undirected processes like natural selection or chemical evolution. Core principles include irreducible complexity, specified complexity, and the assertion that biological information systems exhibit hallmarks of purposeful design. Proponents claim that these features cannot be adequately explained by abiogenesis, which hypothesizes life arising from non-living matter through natural chemical processes.
Understanding Abiogenesis: Scientific Foundations
Abiogenesis refers to the natural process through which life arises from non-living matter, supported by extensive research in chemistry and molecular biology demonstrating how simple organic molecules can gradually form complex self-replicating systems. Experimental evidence such as the Miller-Urey experiment highlights the potential for amino acids and other life-building blocks to originate under prebiotic Earth conditions. This scientific foundation contrasts with Intelligent Design by emphasizing natural mechanisms and empirical observations rather than supernatural causation.
Historical Context: Evolution of Both Theories
Intelligent Design emerged in the late 20th century as a response to the perceived gaps in abiogenesis and Darwinian evolution, emphasizing purposeful creation by an intelligent cause. Abiogenesis, rooted in 19th-century scientific inquiry, explores the natural emergence of life from non-living matter, with key milestones including Alexander Oparin's primordial soup hypothesis and Stanley Miller's 1953 experiment simulating early Earth conditions. The historical evolution of both theories reflects ongoing debates between scientific naturalism and theological perspectives regarding the origins of life on Earth.
Key Arguments Supporting Intelligent Design
Intelligent Design argues that complex biological structures exhibit specified complexity and irreducible complexity, which cannot be adequately explained by random mutations and natural selection alone. Proponents highlight the information-rich structures in DNA and molecular machines within cells as evidence of purposeful design. This perspective emphasizes that certain biochemical systems demonstrate an intricate arrangement that biological evolution by abiogenesis fails to sufficiently account for.
Major Evidence for Abiogenesis
Abiogenesis is supported by major evidence such as the Miller-Urey experiment, which demonstrated the spontaneous formation of amino acids from simple gases under simulated early Earth conditions. Geological findings of ancient microfossils and stromatolites provide physical proof of early life forms arising naturally over 3.5 billion years ago. Molecular biology reveals that RNA molecules can self-replicate and catalyze reactions, supporting the RNA world hypothesis as a plausible pathway for life's origins without intelligent intervention.
Common Criticisms and Counterarguments
Critics of Intelligent Design argue it lacks empirical support and relies on gaps in scientific knowledge as evidence, while proponents counter that abiogenesis cannot fully explain the origin of complex biological information. Abiogenesis faces criticism for the improbability of life arising spontaneously from non-living matter under prebiotic conditions, with Intelligent Design advocates emphasizing the perceived inadequacy of naturalistic explanations for molecular complexity. The debate centers on whether natural processes alone suffice to explain life's emergence or if an intelligent cause is a necessary inference based on current scientific limitations.
Scientific Consensus: Where Do Experts Stand?
The scientific consensus overwhelmingly supports abiogenesis as the origin of life, grounded in extensive empirical research and observable natural processes. Intelligent Design lacks widespread acceptance in the scientific community due to its reliance on supernatural explanations that cannot be tested or falsified. Experts emphasize that theories based on testable hypotheses and repeatable experiments, such as abiogenesis, form the foundation of modern biological sciences.
Philosophical and Theological Implications
The debate between Intelligent Design and Abiogenesis raises profound philosophical and theological implications regarding the origin and complexity of life, challenging naturalistic explanations with the assertion of purposeful creation by an intelligent cause. Intelligent Design argues for evidence of deliberate guidance in biological systems, invoking questions about consciousness and intentionality beyond empirical science. Abiogenesis, as a naturalistic explanation, prompts reevaluation of traditional theological doctrines on creation, emphasizing evolutionary processes and chemical origins that exclude supernatural intervention.
Future Directions: Research, Debate, and Education
Future research in Intelligent Design (ID) versus Abiogenesis emphasizes interdisciplinary studies integrating molecular biology, cosmology, and information theory to clarify origins of life. Debates focus on epistemological frameworks and methodological naturalism guiding scientific inquiry, encouraging educational curricula to include critical discussions on both perspectives. Advancements in synthetic biology and astrobiology offer empirical avenues to test hypotheses, shaping informed public discourse and policy decisions.
Intelligent Design Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com