Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used to synthesize functional gene products like proteins, essential for cell function and development. Understanding gene regulation helps you grasp how traits are inherited and how genetic disorders occur. Explore the rest of the article to dive deeper into the mechanisms governing gene expression and its impact on health.
Table of Comparison
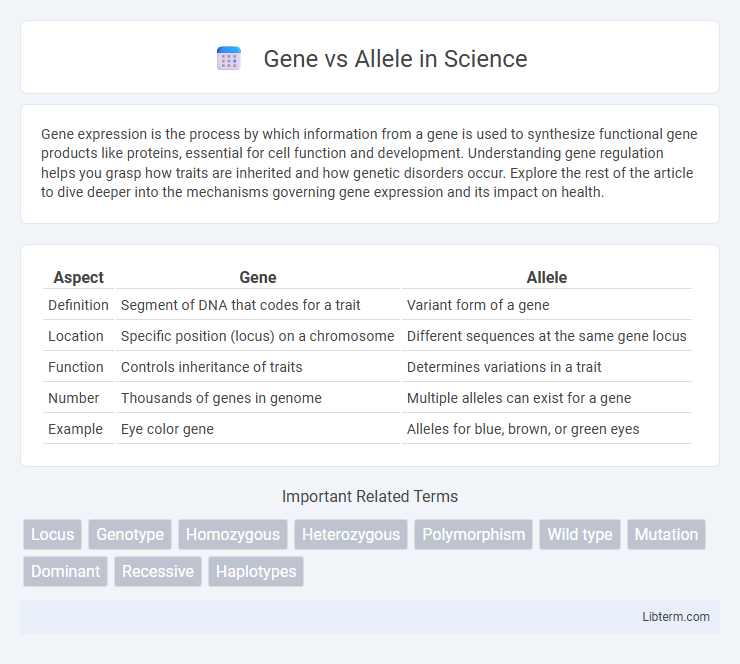
| Aspect | Gene | Allele |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Segment of DNA that codes for a trait | Variant form of a gene |
| Location | Specific position (locus) on a chromosome | Different sequences at the same gene locus |
| Function | Controls inheritance of traits | Determines variations in a trait |
| Number | Thousands of genes in genome | Multiple alleles can exist for a gene |
| Example | Eye color gene | Alleles for blue, brown, or green eyes |
Understanding Genes and Alleles: A Brief Overview
Genes are segments of DNA that encode specific proteins or functions, serving as the fundamental units of heredity. Alleles are variant forms of a gene found at the same locus on homologous chromosomes, responsible for genetic diversity and variations in traits. Understanding the relationship between genes and alleles is crucial for grasping inheritance patterns and genetic expression.
Defining Genes: The Blueprint of Life
Genes are segments of DNA that serve as the blueprint of life, encoding instructions for the synthesis of proteins essential for cellular functions and organism development. Each gene resides at a specific locus on a chromosome and determines hereditary traits by guiding the production of particular proteins. Alleles are variant forms of a gene that arise through mutations and exist at the same genetic locus, contributing to genetic diversity and influencing phenotypic differences within a population.
What Are Alleles? Variations Within Genes
Alleles are different versions of the same gene, representing variations at specific loci on chromosomes that contribute to genetic diversity within a population. Each allele can encode for distinct traits or influence the expression of a gene, resulting in phenotypic differences among individuals. Understanding the role of alleles is essential in genetics, as they determine inherited characteristics and variations in biological functions.
Gene Structure and Function in Genetics
Genes are segments of DNA composed of exons, introns, promoters, and regulatory sequences that direct the synthesis of proteins and functional RNA molecules essential for cellular processes. Alleles represent variant forms of a gene sequence at a specific locus that lead to different phenotypic expressions by altering the gene's coding or regulatory regions. The structural differences in alleles impact gene function by modifying protein structure, gene expression levels, or splicing patterns, thereby contributing to genetic diversity and heredity.
How Alleles Influence Traits and Variation
Alleles are different versions of a gene that occupy the same position on a chromosome and contribute to genetic variation by coding for alternative traits or characteristics. The specific combination of alleles inherited from parents influences an organism's phenotype, determining variations such as eye color, blood type, or susceptibility to diseases. Allelic diversity within populations drives evolutionary adaptation by introducing variability in traits that can be favored or disfavored by environmental pressures.
Key Differences Between Genes and Alleles
Genes are distinct sequences of DNA that code for specific traits, while alleles are different versions or variants of a gene found at the same locus on homologous chromosomes. Each gene can have multiple alleles, which contribute to the diversity of phenotypes within a population. Alleles influence the expression of traits through dominant, recessive, or codominant inheritance patterns, distinguishing their role from the fundamental identity of the gene itself.
Inheritance Patterns: Genes, Alleles, and Heredity
Genes are segments of DNA that determine specific traits, while alleles are the different versions of a gene located at the same locus on homologous chromosomes. Inheritance patterns are influenced by dominant and recessive alleles, with homozygous or heterozygous combinations affecting phenotypic expression. Mendelian genetics explains how alleles segregate and assort independently, shaping heredity through predictable transmission of traits from parents to offspring.
Dominant and Recessive Alleles: The Basics
Genes are segments of DNA that code for specific traits, while alleles are different versions of a gene that determine variations in those traits. Dominant alleles express their traits even when only one copy is present, whereas recessive alleles require two copies to manifest their characteristics. Understanding dominant and recessive allele interactions is essential in predicting inheritance patterns and trait expression.
Real-World Examples of Genes and Alleles
Genes are segments of DNA that code for specific traits, such as the gene responsible for eye color or blood type in humans. Alleles are different versions of a gene, like the allele for blue eyes versus the allele for brown eyes within the same eye color gene. For example, the cystic fibrosis gene has multiple alleles, some causing the disease while others result in normal lung function.
The Role of Genes and Alleles in Genetic Disorders
Genes are specific sequences of DNA that encode instructions for proteins and determine inherited traits, while alleles are different versions of a gene that vary at a particular locus. The role of genes and alleles in genetic disorders involves mutations or variations that can disrupt normal gene function, leading to inherited diseases such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, or Huntington's disease. Understanding the specific allelic variations helps in diagnosing genetic disorders, predicting disease risk, and developing targeted therapies.
Gene Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com