Expression is the art of conveying emotions, thoughts, or ideas through language, art, or body movement, allowing individuals to communicate uniquely and authentically. Mastering your expression can enhance personal connections and professional interactions, fostering clarity and understanding. Explore the rest of the article to discover powerful techniques to refine your expression and make your message resonate.
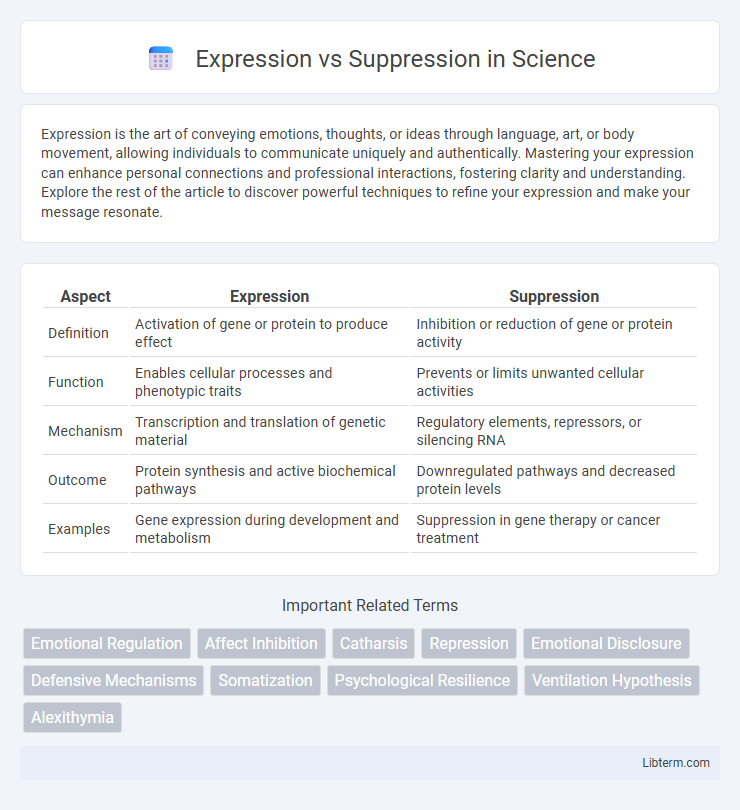
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Expression | Suppression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Activation of gene or protein to produce effect | Inhibition or reduction of gene or protein activity |
| Function | Enables cellular processes and phenotypic traits | Prevents or limits unwanted cellular activities |
| Mechanism | Transcription and translation of genetic material | Regulatory elements, repressors, or silencing RNA |
| Outcome | Protein synthesis and active biochemical pathways | Downregulated pathways and decreased protein levels |
| Examples | Gene expression during development and metabolism | Suppression in gene therapy or cancer treatment |
Understanding Expression and Suppression
Understanding expression involves recognizing how individuals convey emotions through verbal and nonverbal cues, reflecting authentic feelings that impact psychological well-being. Suppression refers to the conscious effort to inhibit emotional responses, often leading to increased stress and decreased emotional clarity. Research indicates that balanced expression supports healthier relationships and emotional regulation, while excessive suppression may contribute to anxiety and depressive symptoms.
The Psychology Behind Expression
The psychology behind expression reveals that verbalizing emotions facilitates cognitive processing, promoting mental clarity and emotional relief. Research indicates that expressing feelings activates neural pathways linked to empathy and emotional regulation, which can reduce stress and improve psychological well-being. Suppressing emotions, conversely, often leads to increased physiological arousal and long-term negative impacts on mental health, including anxiety and depression.
The Hidden Costs of Suppression
Suppressing emotions leads to increased physiological stress, higher risk of cardiovascular disease, and weakened immune response. Expression of feelings promotes mental clarity, reduces anxiety, and enhances interpersonal relationships by fostering authentic communication. Chronic emotional suppression contributes to internalized anger, depression, and diminished overall well-being, underscoring the hidden costs often overlooked in psychological health.
Emotional Health: Expression vs Suppression
Expressing emotions supports emotional health by reducing stress, enhancing mood, and strengthening relationships through authentic communication. Suppression of emotions often leads to increased psychological distress, higher risk of anxiety and depression, and impaired social connections. Emotional expression facilitates resilience and overall well-being, while suppression can contribute to emotional dysregulation and physical health issues.
Impacts on Relationships
Expression fosters open communication and emotional intimacy, strengthening trust and understanding between partners. Suppression of feelings often leads to misunderstandings, increased stress, and emotional distance, weakening relational bonds. Consistent emotional expression enhances conflict resolution and overall relationship satisfaction.
Physical Effects of Suppressed Emotions
Suppressed emotions trigger increased autonomic nervous system activity, leading to elevated heart rate and blood pressure. Chronic emotional suppression is linked to heightened cortisol levels, which contribute to systemic inflammation and impaired immune function. This prolonged physiological stress response raises the risk of cardiovascular diseases, gastrointestinal issues, and weakened overall health.
Cultural Influences on Emotional Expression
Cultural influences significantly shape the ways individuals express or suppress emotions, with collectivist societies often promoting emotional suppression to maintain social harmony, while individualistic cultures typically encourage open emotional expression to assert personal identity. Research indicates that in East Asian cultures, emotional restraint is valued to avoid disrupting group cohesion, whereas Western cultures prioritize expressing feelings as a means of authenticity and self-assertion. These cultural norms impact psychological well-being, as misalignment between personal emotional tendencies and societal expectations can lead to increased stress and emotional distress.
Benefits of Healthy Self-Expression
Healthy self-expression improves emotional well-being by allowing individuals to articulate feelings clearly, reducing stress and preventing emotional buildup. It fosters authentic communication, which strengthens relationships through trust and understanding. Engaging in expressive behaviors like journaling or creative arts enhances self-awareness and promotes psychological resilience.
Techniques for Managing Suppressed Emotions
Techniques for managing suppressed emotions involve mindful expression methods such as journaling, which facilitates emotional clarity and reduces psychological stress. Cognitive-behavioral strategies help individuals identify and reframe negative thought patterns tied to emotional suppression, promoting healthier coping mechanisms. Incorporating physical activities like yoga or deep-breathing exercises can release stored tension, enhancing emotional regulation and overall mental well-being.
Finding Balance: When to Express and When to Hold Back
Navigating emotional expression versus suppression requires understanding context and emotional impact to find balance. Expressing emotions can foster genuine connections and reduce internal stress, while strategic suppression helps maintain professionalism and avoid unnecessary conflict. Making conscious decisions based on timing, audience, and emotional intensity optimizes mental health and interpersonal relationships.
Expression Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com