Interdisciplinary approaches combine knowledge and methods from multiple disciplines to solve complex problems and foster innovation. This integration encourages creative thinking and broadens perspectives, enhancing research quality and practical outcomes. Discover how embracing interdisciplinary strategies can transform your projects by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
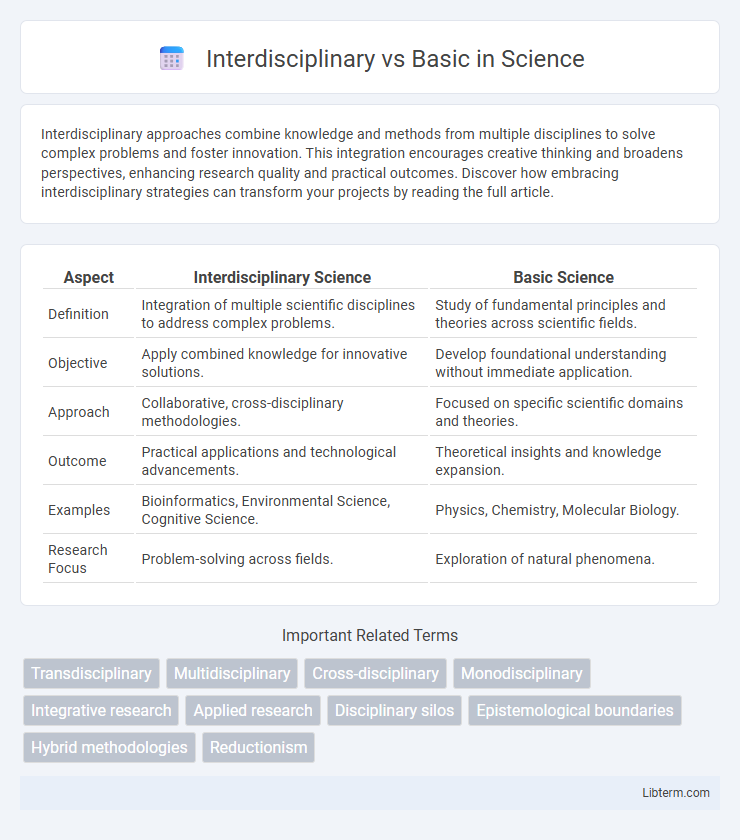
| Aspect | Interdisciplinary Science | Basic Science |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of multiple scientific disciplines to address complex problems. | Study of fundamental principles and theories across scientific fields. |
| Objective | Apply combined knowledge for innovative solutions. | Develop foundational understanding without immediate application. |
| Approach | Collaborative, cross-disciplinary methodologies. | Focused on specific scientific domains and theories. |
| Outcome | Practical applications and technological advancements. | Theoretical insights and knowledge expansion. |
| Examples | Bioinformatics, Environmental Science, Cognitive Science. | Physics, Chemistry, Molecular Biology. |
| Research Focus | Problem-solving across fields. | Exploration of natural phenomena. |
Introduction to Interdisciplinary and Basic Approaches
Interdisciplinary approaches integrate knowledge and methods from multiple disciplines to solve complex problems that cannot be addressed by one field alone. Basic approaches focus on fundamental principles and theories within a single discipline to build a deep understanding of core concepts. Introduction to interdisciplinary methods highlights collaboration, synthesis, and innovation, while basic approaches emphasize foundational learning and specialized expertise.
Defining Interdisciplinary Studies
Interdisciplinary studies integrate methods and perspectives from multiple academic disciplines to address complex problems that cannot be understood through a single field alone. Unlike basic studies, which focus on foundational knowledge within a specific discipline, interdisciplinary research combines theories, concepts, and methodologies to create comprehensive solutions. This approach fosters innovation by bridging gaps between fields such as science, technology, humanities, and social sciences.
Understanding Basic (Disciplinary) Research
Basic (disciplinary) research focuses on generating foundational knowledge within a specific academic field by exploring fundamental principles, theories, and concepts. It aims to deepen understanding of core disciplinary frameworks without immediate practical application, providing a theoretical basis for future innovations. This research type is essential for advancing specialized knowledge, serving as the groundwork for interdisciplinary studies that integrate insights across multiple fields.
Key Differences Between Interdisciplinary and Basic Research
Interdisciplinary research integrates methods, concepts, and theories from multiple disciplines to address complex problems, while basic research focuses on fundamental principles within a single field without immediate practical application. Key differences include interdisciplinary research's emphasis on collaboration across fields, broader scope, and practical problem-solving orientation versus basic research's pursuit of theoretical knowledge and deep understanding within a narrow scientific domain. Interdisciplinary projects often produce innovative solutions by synthesizing diverse perspectives, whereas basic research builds foundational knowledge that supports long-term scientific advancement.
Benefits of Interdisciplinary Approaches
Interdisciplinary approaches foster innovation by integrating knowledge from multiple fields to solve complex problems more effectively than basic, single-discipline methods. This collaboration enhances creativity and leads to comprehensive solutions, benefiting sectors like healthcare, environmental science, and technology. Organizations adopting interdisciplinary strategies often experience accelerated research breakthroughs and improved practical outcomes.
Advantages of Basic Research Methods
Basic research methods offer deep theoretical insights that drive scientific innovation by exploring fundamental principles without immediate commercial objectives. These methods enable the development of generalizable knowledge applicable across various fields, fostering long-term advancements in technology, medicine, and social sciences. Emphasizing empirical rigor and controlled experimentation, basic research provides a strong foundation for interdisciplinary studies and applied research breakthroughs.
Challenges in Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Interdisciplinary collaboration faces challenges such as communication barriers due to differing terminologies, variations in research methodologies, and conflicting disciplinary priorities that impede cohesive teamwork. Integrating diverse perspectives often leads to difficulties in establishing common goals, coordinating efforts, and synthesizing findings across fields like biology, engineering, and social sciences. Overcoming these obstacles requires developing shared vocabularies, fostering mutual respect, and implementing structured frameworks to align interdisciplinary objectives and workflows effectively.
Limitations of Basic Research
Basic research often encounters limitations in its direct applicability to real-world problems, as it primarily seeks to expand foundational knowledge without immediate practical outcomes. The lack of interdisciplinary integration restricts its ability to address complex, multifaceted issues that span multiple fields. Consequently, the narrow focus of basic research can delay innovation and the development of comprehensive solutions in applied sciences.
Real-World Applications: Interdisciplinary vs Basic
Interdisciplinary research integrates methods and knowledge from multiple disciplines to address complex real-world problems, enhancing practical applications in fields like healthcare, environmental science, and technology development. Basic research, focused on generating fundamental knowledge, often serves as the foundation for future interdisciplinary innovations but may have limited immediate real-world impact. Combining both approaches accelerates the translation of theoretical insights into effective solutions for societal challenges.
Choosing the Right Approach for Research Success
Selecting between interdisciplinary and basic research hinges on your project's goals, desired impact, and available resources. Interdisciplinary research integrates methods and knowledge from multiple fields to tackle complex problems and drive innovation, while basic research focuses on fundamental scientific principles to expand understanding within a specific discipline. Aligning your approach with clear objectives ensures targeted outcomes, whether aiming for groundbreaking applications or foundational knowledge advancement.
Interdisciplinary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com