Diachronic analysis examines the development and evolution of language, culture, or phenomena over time, highlighting changes and historical progressions. This approach contrasts with synchronic analysis, which studies a subject at a specific point. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of diachronic methods and their applications.
Table of Comparison
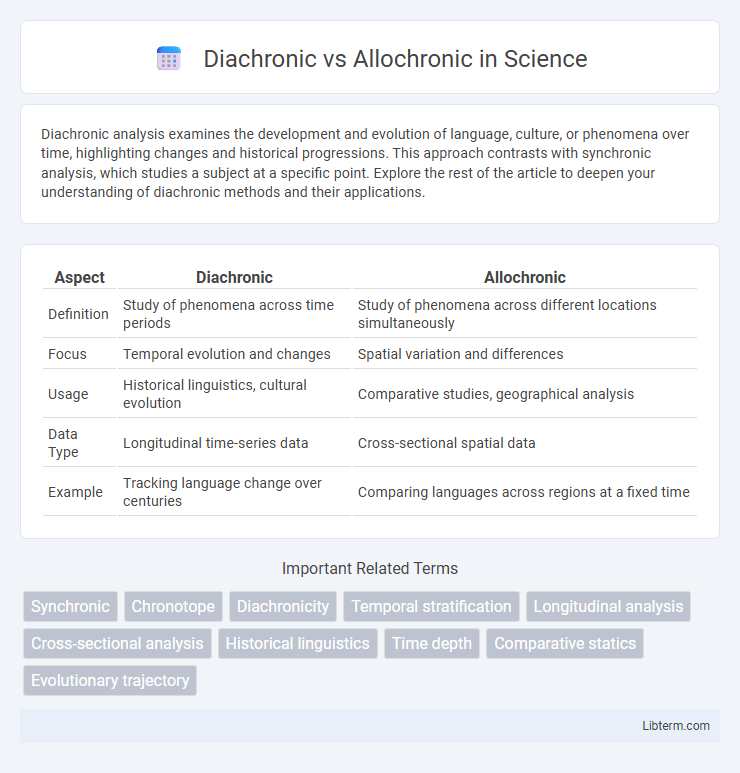
| Aspect | Diachronic | Allochronic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of phenomena across time periods | Study of phenomena across different locations simultaneously |
| Focus | Temporal evolution and changes | Spatial variation and differences |
| Usage | Historical linguistics, cultural evolution | Comparative studies, geographical analysis |
| Data Type | Longitudinal time-series data | Cross-sectional spatial data |
| Example | Tracking language change over centuries | Comparing languages across regions at a fixed time |
Introduction to Diachronic and Allochronic
Diachronic analysis examines phenomena through time, focusing on how languages, cultures, or events evolve and change historically. Allochronic study contrasts this by analyzing different subjects or groups existing simultaneously but with distinct characteristics or temporal frameworks. Understanding these approaches is essential for disciplines like linguistics, anthropology, and history to differentiate between temporal development and synchronization of diverse elements.
Defining Diachronic Analysis
Diachronic analysis examines linguistic or cultural phenomena across different periods of time, focusing on their historical development and evolution. It tracks changes and transformations within a language, society, or concept over time, highlighting patterns and shifts. This temporal perspective contrasts with synchrony, which studies systems at a specific moment, making diachronic analysis essential for understanding long-term progressions and origins.
Understanding Allochronic Perspectives
Allochronic perspectives emphasize changes and developments occurring across different points in time within cultures or languages, highlighting temporal variability rather than spatial differences. This approach allows for a deeper understanding of historical processes and transformations by examining sequences and patterns over extended periods. Researchers analyzing allochronic data uncover how cultural or linguistic phenomena evolve distinctively in diverse temporal contexts, offering valuable insights into dynamic change.
Key Differences between Diachronic and Allochronic Approaches
The diachronic approach studies phenomena through historical development and changes over time, emphasizing temporal progression and evolution. The allochronic approach compares different cultures or societies at a specific point in time, highlighting cross-sectional differences rather than chronological sequences. Key differences lie in diachronic research's focus on longitudinal change versus allochronic analysis' emphasis on spatial or cultural variation at one moment.
Applications of Diachronic Methods
Diachronic methods are extensively applied in historical linguistics to trace language evolution over time, enabling the reconstruction of proto-languages and the study of phonetic, semantic, and syntactic changes. In archaeology, diachronic analysis helps identify cultural transformations and societal developments by examining stratified artifacts and historical records across different periods. These temporal studies enhance understanding of long-term processes in fields such as anthropology, paleontology, and literary analysis, providing insights into historical continuity and change.
Uses of Allochronic Approaches
Allochronic approaches are primarily used to analyze phenomena by comparing different regions or societies at the same point in time, enabling cross-sectional studies of cultural, social, or linguistic variations. These methods facilitate understanding of spatial diversity and contemporaneous differences, crucial in fields like anthropology, sociology, and linguistics for revealing how similar processes manifest differently across locales. Employing allochronic analysis supports policy-making and targeted interventions by highlighting regional disparities and facilitating comparative assessments.
Advantages and Limitations of Diachronic Study
Diachronic study enables researchers to analyze changes and developments in language, culture, or phenomena over extended periods, offering deep insights into evolution and historical context. Its advantage lies in revealing patterns and causes behind transformations, contributing to comprehensive understanding across time. Limitations include potential difficulties in data availability and interpretation biases due to incomplete records or shifting analytical frameworks.
Strengths and Drawbacks of Allochronic Analysis
Allochronic analysis excels at identifying cultural or societal changes over extended periods by comparing different groups or stages, offering a dynamic perspective on evolution. Its strength lies in revealing patterns of transformation and adaptation that are often missed in static snapshots. However, this approach can face drawbacks such as temporal biases, difficulties in ensuring data comparability, and challenges arising from varying contextual influences between time-separated samples.
Diachronic vs Allochronic: Comparative Case Studies
Diachronic and allochronic approaches offer distinct frameworks for comparative case studies, where diachronic analysis examines changes within a single entity across different time periods, emphasizing historical development and temporal evolution. Allochronic comparison, in contrast, investigates different entities at the same temporal point, highlighting spatial or cultural differences without temporal variation. Integrating diachronic and allochronic perspectives enhances understanding by contextualizing temporal dynamics alongside concurrent diversity in comparative research.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Analytical Approach
Selecting the appropriate analytical approach depends on whether the focus is on changes over time within the same cultural context or differences across cultures at a single time point. Diachronic analysis excels in tracing historical developments and evolution, providing insight into temporal dynamics. Allochronic analysis offers valuable cross-cultural comparisons by examining simultaneous variations, ideal for identifying cultural diversity and structural differences.
Diachronic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com