Community and society form the backbone of human interaction, influencing culture, values, and social norms. Your role within these groups shapes identity and fosters cooperation, leading to collective growth and well-being. Explore the rest of this article to understand how community dynamics impact individual and societal development.
Table of Comparison
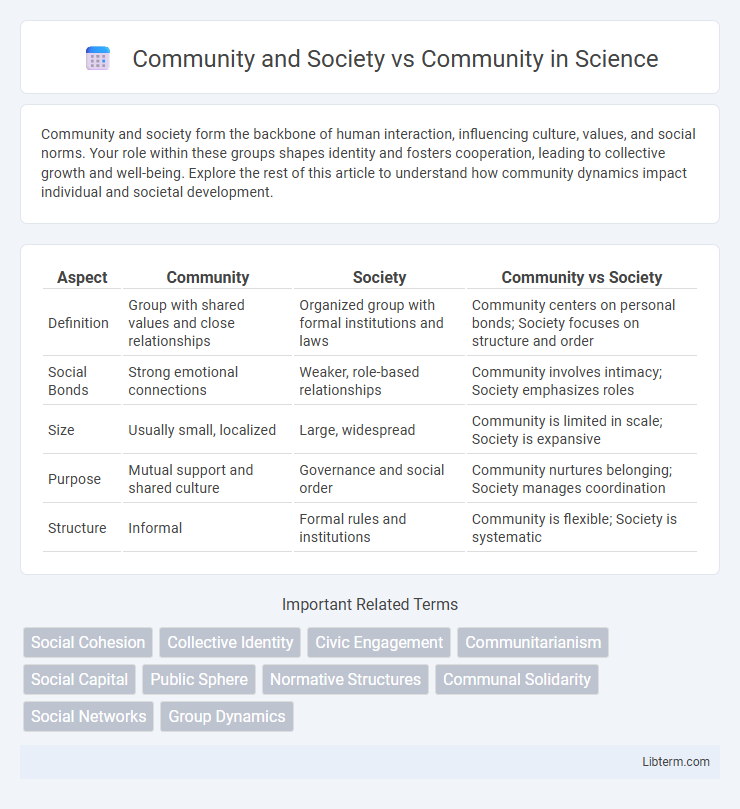
| Aspect | Community | Society | Community vs Society |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Group with shared values and close relationships | Organized group with formal institutions and laws | Community centers on personal bonds; Society focuses on structure and order |
| Social Bonds | Strong emotional connections | Weaker, role-based relationships | Community involves intimacy; Society emphasizes roles |
| Size | Usually small, localized | Large, widespread | Community is limited in scale; Society is expansive |
| Purpose | Mutual support and shared culture | Governance and social order | Community nurtures belonging; Society manages coordination |
| Structure | Informal | Formal rules and institutions | Community is flexible; Society is systematic |
Defining Community and Society: Key Differences
Community is defined by close social bonds, shared values, and direct interactions among members, fostering a sense of belonging and mutual support. Society encompasses a larger, more complex structure organized by institutions, laws, and systems that regulate relationships and social order across diverse populations. The key difference lies in the intimacy and scale of connections--community involves personal relationships while society functions through formalized roles and collective norms.
The Structure of Community vs Society
The structure of community centers on close-knit relationships, shared values, and strong social cohesion among members who often interact personally. Society, in contrast, is characterized by a more complex and impersonal organization with diverse institutions and formal roles that regulate large populations. Communities emphasize intimate social bonds, whereas societies rely on systemic frameworks and governance to maintain order and facilitate cooperation.
Social Bonds: Community Connection vs Societal Organization
Social bonds in a community emphasize personal connections, trust, and shared values that foster a sense of belonging and mutual support among members. In contrast, societal organization focuses on structured relationships and institutional frameworks that govern larger populations through laws, policies, and formal roles. Understanding these distinctions clarifies how community fosters intimate social ties while society maintains order and collective functionality.
Roles and Responsibilities within Community and Society
Roles and responsibilities within a community focus on immediate, localized interactions such as mutual support, shared norms, and cooperation among members. In contrast, society encompasses broader institutional responsibilities including governance, law enforcement, and social welfare aimed at maintaining order and addressing systemic issues. Community roles prioritize interpersonal relationships and collective well-being, while societal roles emphasize structured systems and policy implementation.
Communication Patterns: Close-Knit vs Wide-Reaching
Close-knit communities exhibit dense, frequent communication patterns fostering strong interpersonal bonds and shared norms, enhancing social cohesion and mutual support. In contrast, wide-reaching communities rely on broader, less frequent interactions that facilitate diverse information exchange and connectivity across varied social groups. These differing communication patterns shape the structure and function of social networks, influencing collective identity and resource mobilization within communities and societies.
Sense of Identity: Belonging in Communities vs Societies
A strong sense of identity emerges more naturally in communities due to close interpersonal relationships and shared experiences that foster belonging and mutual support. Societies, being larger and more diverse, offer a broader social framework where identity is often shaped by cultural, legal, or institutional affiliations rather than intimate ties. The distinction between communities and societies highlights how localized connections reinforce individual identity, while societies create a collective identity based on common norms and values.
Cultural Values: Community Traditions vs Societal Norms
Community traditions embody localized cultural values passed through generations, creating a shared identity and sense of belonging among members. Societal norms encompass broader, formalized rules and expectations that regulate behavior across diverse populations, often influenced by law, policy, and cultural pluralism. The interplay between community traditions and societal norms reflects tensions and accommodations between intimate cultural practices and generalized social frameworks.
Power Dynamics and Leadership in Community vs Society
Power dynamics in communities often center on localized, participatory leadership where members have direct influence and accountability, fostering collaborative decision-making processes. In contrast, societies typically exhibit hierarchical power structures with formalized leadership roles that govern large populations through institutional frameworks and centralized authority. This distinction impacts how authority is exercised, negotiated, and challenged within smaller community settings versus broader societal contexts.
Challenges: Small-Scale Community Issues vs Societal Problems
Small-scale community issues often involve localized challenges such as resource allocation, social cohesion, and direct conflict resolution, which require immediate and personalized solutions. Societal problems, in contrast, encompass broader systemic challenges like inequality, public health crises, and economic disparities that demand large-scale policy interventions and coordinated efforts across multiple sectors. Addressing small community issues effectively contributes to mitigating larger societal problems by fostering resilience and engagement at the grassroots level.
Evolving Relationships: Community Integration within Society
Community integration within society reflects the dynamic interplay between localized social groups and broader societal structures, shaping evolving relationships through shared values, norms, and common goals. As communities adapt to societal changes, they foster social cohesion, inclusivity, and collective identity, enhancing both individual well-being and societal resilience. The continuous negotiation between community autonomy and societal influence drives the transformation of social networks, enabling sustainable integration and collaborative development.
Community and Society Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com