Efficient project management drives timely completion and maximizes resource utilization, ensuring that goals align with strategic objectives. Understanding key phases such as initiation, planning, execution, and closure enhances your ability to deliver successful outcomes. Explore the rest of the article to master essential project management techniques and tools.
Table of Comparison
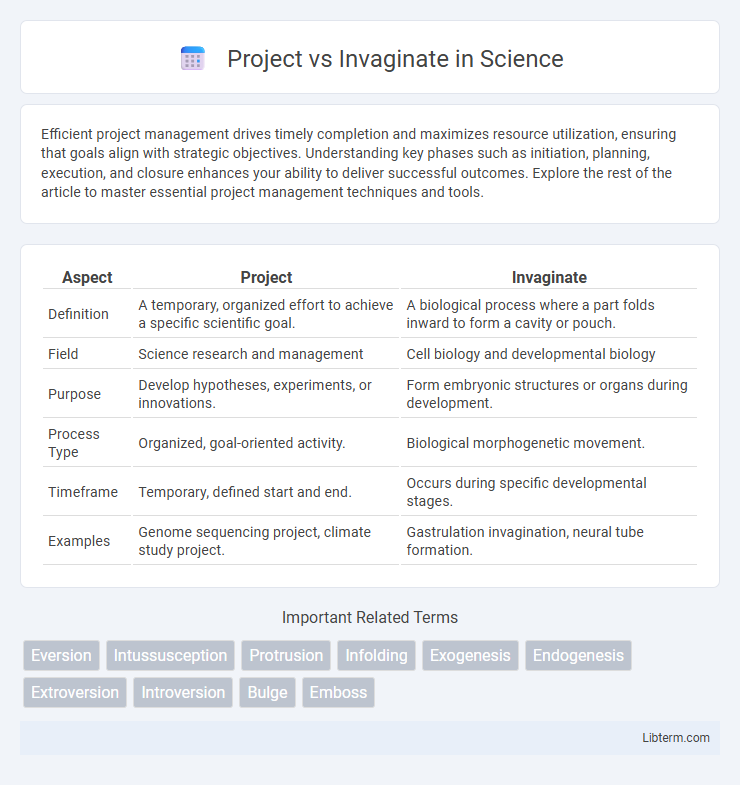
| Aspect | Project | Invaginate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A temporary, organized effort to achieve a specific scientific goal. | A biological process where a part folds inward to form a cavity or pouch. |
| Field | Science research and management | Cell biology and developmental biology |
| Purpose | Develop hypotheses, experiments, or innovations. | Form embryonic structures or organs during development. |
| Process Type | Organized, goal-oriented activity. | Biological morphogenetic movement. |
| Timeframe | Temporary, defined start and end. | Occurs during specific developmental stages. |
| Examples | Genome sequencing project, climate study project. | Gastrulation invagination, neural tube formation. |
Understanding "Project" and "Invaginate": Definitions and Differences
Project" refers to a planned set of tasks aimed at achieving a specific goal, often with defined timelines and resources, commonly used in business, engineering, and software development contexts. "Invaginate" is a biological term describing the process where one part of a structure folds inward to form a pouch or cavity, frequently observed in embryology and anatomy. The primary difference lies in their domains: "Project" is a management and organizational concept, while "Invaginate" describes a physical morphological process.
Historical Origins of the Terms "Project" and "Invaginate
The term "project" originates from the Latin word "projectum," meaning "something thrown forward," reflecting its historical use in planning and vision. "Invaginate" derives from the Latin "invaginatus," meaning "to enfold or envelop," historically used in biological contexts to describe structures folded inward. Understanding these etymologies highlights how "project" emphasizes outward planning, while "invaginate" focuses on inward folding processes.
Applications of "Project" in Science and Technology
Project in science and technology refers to a planned set of tasks or initiatives aimed at achieving specific research, engineering, or development goals. Common applications include managing large-scale scientific experiments, software development, and technology innovation, where systematic coordination of resources and timelines is critical. Project methodologies such as Agile and Waterfall optimize collaboration and delivery in fields like biotechnology, aerospace, and information technology.
The Role of "Invaginate" in Biological Processes
Invaginate plays a critical role in biological processes by facilitating the inward folding of cell membranes, which is essential for cellular mechanisms like endocytosis and gastrulation. This membrane invagination allows cells to internalize molecules, form vesicles, and initiate complex developmental pathways. Understanding the function of invaginate helps clarify how cells regulate nutrient uptake, signaling, and tissue morphogenesis.
Visualizing "Project" vs "Invaginate": Key Illustrations
Visualizing "Project" involves depicting outward growth or expansion, often shown through diagrams representing objectives, timelines, and deliverables. In contrast, "Invaginate" is illustrated by inward folding or indentation, common in biological diagrams highlighting cell membrane or tissue structures. Key illustrations emphasize "Project" as expansive and forward-moving, while "Invaginate" captures a contracting, inward motion.
Comparative Analysis: Functions and Mechanisms
Project and Invaginate differ significantly in their biological functions and underlying mechanisms. Project involves the extension or growth of cellular structures facilitating exploration or connection, while Invaginate refers to the inward folding of membranes to enable processes like endocytosis or compartmentalization. The mechanism of Project relies on cytoskeletal dynamics promoting outward protrusions, whereas Invaginate depends on membrane curvature changes driven by protein interactions and lipid composition.
Importance in Medical and Engineering Fields
Projective techniques and invagination both play crucial roles in medical and engineering fields by enhancing diagnostic accuracy and structural analysis. In medicine, projective methods are essential for psychological assessment and imaging interpretation, while invagination is critical for understanding anatomical folding processes and tissue engineering applications. Engineering leverages projective geometry for precise modeling and design, whereas invagination principles inform the development of flexible materials and bio-inspired structures.
Examples of "Project" and "Invaginate" in Real-World Contexts
Projecting architectural blueprints involves creating detailed, scaled drawings that visualize buildings before construction, ensuring precise planning and execution. In biology, invaginate describes the folding of an embryonic tissue layer inward to form complex structures like the neural tube, essential for proper development. Similarly, in technology, project management software projects timelines and resources, while invagination techniques improve microfluidic device designs by creating intricate surface features.
Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
Project and Invaginate are often confused due to their overlapping themes of involvement and progression, but Project primarily refers to a planned undertaking with specific goals, while Invaginate describes a process of folding inward, often in biological contexts. A common misconception is that Invaginate can be used interchangeably with Project in general project management discussions, which is inaccurate because Invaginate is not a term related to task organization or execution. Clarifying these distinctions enhances precise communication, particularly in academic, medical, and professional settings where their meanings are context-specific.
Future Trends and Research Directions
Project and invaginate processes are increasingly studied for their roles in tissue development and repair, with future trends emphasizing the integration of advanced imaging techniques and computational modeling to better understand cellular dynamics. Emerging research focuses on the molecular signaling pathways that regulate these mechanisms, aiming to manipulate them for regenerative medicine and cancer therapy. Innovations in biomaterials and gene editing are expected to drive significant advancements in controlling project extension and invagination during morphogenesis.
Project Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com