Divergent explores a dystopian society divided into factions based on human virtues, where the protagonist discovers she does not fit neatly into any category. The storyline delves into themes of identity, choice, and rebellion against conformity, captivating readers with its thrilling plot and complex characters. Dive into the rest of the article to uncover the deeper layers of this compelling narrative and its impact on young adult literature.
Table of Comparison
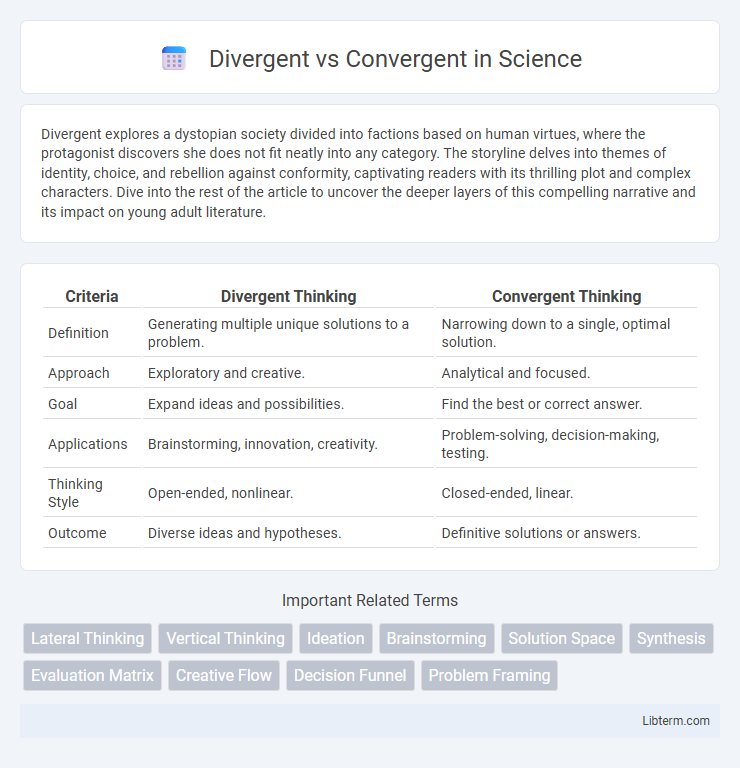
| Criteria | Divergent Thinking | Convergent Thinking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generating multiple unique solutions to a problem. | Narrowing down to a single, optimal solution. |
| Approach | Exploratory and creative. | Analytical and focused. |
| Goal | Expand ideas and possibilities. | Find the best or correct answer. |
| Applications | Brainstorming, innovation, creativity. | Problem-solving, decision-making, testing. |
| Thinking Style | Open-ended, nonlinear. | Closed-ended, linear. |
| Outcome | Diverse ideas and hypotheses. | Definitive solutions or answers. |
Understanding Divergent and Convergent Thinking
Divergent thinking involves generating multiple, unique solutions or ideas from a single starting point, promoting creativity and exploration. Convergent thinking narrows these options to identify the best or most effective solution by focusing on logic and accuracy. Understanding both processes is crucial for problem-solving, as divergent thinking fuels idea generation while convergent thinking refines and implements those ideas.
Key Differences Between Divergent and Convergent Approaches
Divergent thinking generates multiple, creative solutions by exploring many possible options, while convergent thinking narrows down those possibilities to identify the single best answer. Divergent methods emphasize innovation and open-ended exploration, whereas convergent approaches prioritize logic, accuracy, and decision-making based on available information. Key differences include the objective--divergent aims for variety and novelty, convergent focuses on synthesis and solution selection.
Historical Origins of Divergent and Convergent Theories
Divergent thinking traces its origins to Joy Paul Guilford's research in the 1950s, emphasizing creativity and the generation of multiple solutions from a single problem. Convergent thinking, rooted in traditional logical and problem-solving theories from early cognitive psychology, focuses on narrowing down multiple possibilities to find a single correct answer. Both theories have significantly influenced educational psychology and cognitive science by shaping modern approaches to creative versus analytical thinking processes.
Applications in Problem-Solving
Divergent thinking enhances problem-solving by generating diverse ideas and exploring multiple possibilities, essential for brainstorming and innovation processes. Convergent thinking refines these ideas by evaluating and selecting the most effective solutions, critical in decision-making and implementation phases. Integrating both approaches optimizes creative problem-solving, balancing originality with practicality across various fields such as design, engineering, and business strategy.
Impact on Creativity and Innovation
Divergent thinking drives creativity by generating multiple unique ideas, while convergent thinking refines those ideas to practical solutions, directly influencing innovation outcomes. Industries leveraging both approaches benefit from a balanced workflow that promotes idea diversity and efficient problem-solving. Studies show teams utilizing divergent and convergent methods achieve higher innovation rates and more original product development.
Advantages of Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking fosters creativity by encouraging the generation of multiple unique solutions and ideas, enhancing problem-solving potential in complex scenarios. It promotes open-mindedness and innovation by allowing for the exploration of diverse perspectives without immediate judgment or limitations. This approach is particularly valuable in brainstorming sessions and creative industries where novel ideas and adaptability are critical to success.
Strengths of Convergent Thinking
Convergent thinking excels in delivering precise solutions by narrowing down multiple ideas into a single, optimal answer, making it invaluable for problem-solving tasks that require accuracy and efficiency. Its strength lies in leveraging logic, data analysis, and existing knowledge to evaluate alternatives quickly and systematically. This method is particularly effective in scientific research, standardized testing, and situations demanding clear, evidence-based decisions.
Common Misconceptions
Divergent and convergent thinking are often misunderstood as mutually exclusive, but they actually complement each other in the creative process. A common misconception is that divergent thinking is purely about randomness or chaos, whereas it systematically generates multiple solutions by exploring different perspectives. Convergent thinking is mistakenly seen as limiting or rigid, but it involves critical evaluation and synthesis to refine ideas and select the most effective solutions.
Integrating Both Approaches in Practice
Integrating divergent and convergent thinking enhances problem-solving by encouraging expansive idea generation followed by focused evaluation and selection. Practical application often involves brainstorming sessions to produce diverse possibilities and structured analysis techniques to refine and implement the best solutions. Combining these approaches fosters innovation while ensuring feasibility and effectiveness in decision-making processes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Goals
Divergent thinking fosters creativity by generating numerous unique ideas, making it ideal for brainstorming and exploring new possibilities. Convergent thinking narrows options to identify the best solution, focusing on logic and efficiency, which suits decision-making and problem-solving tasks. Selecting the right approach depends on your goals: use divergent methods for innovation and idea expansion, and convergent methods to evaluate choices and implement practical solutions.
Divergent Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com