Ex vivo techniques involve studying biological processes outside the living organism, often using tissues or cells in controlled environments to gain precise insights. These methods provide valuable data on cellular behavior and drug responses without the complexity of whole-body interactions. Explore the rest of the article to discover how ex vivo approaches are transforming biomedical research and your understanding of disease mechanisms.
Table of Comparison
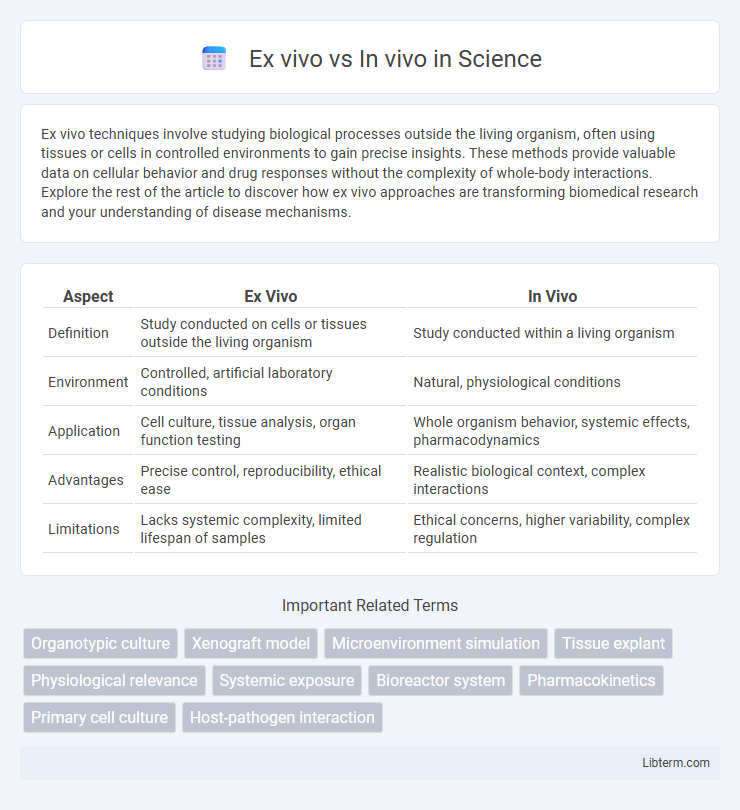
| Aspect | Ex Vivo | In Vivo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study conducted on cells or tissues outside the living organism | Study conducted within a living organism |
| Environment | Controlled, artificial laboratory conditions | Natural, physiological conditions |
| Application | Cell culture, tissue analysis, organ function testing | Whole organism behavior, systemic effects, pharmacodynamics |
| Advantages | Precise control, reproducibility, ethical ease | Realistic biological context, complex interactions |
| Limitations | Lacks systemic complexity, limited lifespan of samples | Ethical concerns, higher variability, complex regulation |
Introduction to Ex Vivo and In Vivo Methods
Ex vivo methods involve the examination of cells, tissues, or organs outside their original biological context, allowing controlled experimental manipulation while preserving physiological relevance. In vivo methods study biological processes within living organisms, maintaining complex interactions and systemic responses that are critical for accurate pathophysiological insights. Both approaches complement each other by providing distinct advantages in biomedical research, with ex vivo offering precise control and in vivo yielding holistic understanding.
Defining Ex Vivo: Techniques and Applications
Ex vivo techniques involve studying biological samples outside their native organism while maintaining the natural cellular environment, allowing detailed analysis of tissues, organs, or cells under controlled conditions. Common ex vivo methods include tissue culture, organ perfusion, and isolated organ systems, enabling precise manipulation and observation of physiological processes. These approaches are crucial in drug testing, toxicology studies, and regenerative medicine, bridging the gap between in vitro experiments and in vivo dynamics.
Understanding In Vivo: Procedures and Significance
In vivo procedures involve studying biological processes directly within living organisms, allowing observation of complex interactions in their natural environment. These methods are crucial for understanding physiological responses, drug effects, and disease progression with high relevance to human health. The significance of in vivo studies lies in their ability to provide comprehensive insights that in vitro or ex vivo models cannot fully replicate.
Key Differences Between Ex Vivo and In Vivo Studies
Ex vivo studies involve analyzing biological processes outside the living organism, often using isolated tissues or organs, which allows precise control over experimental conditions and direct observation of cellular responses. In vivo studies are conducted within living organisms, providing insights into complex systemic interactions, metabolism, and physiological responses that cannot be replicated ex vivo. Key differences include environmental context, with ex vivo offering simplified, controlled settings and in vivo maintaining the natural biological environment, impacting data relevancy and translational potential.
Advantages of Ex Vivo Approaches
Ex vivo approaches allow precise control of experimental conditions, enhancing reproducibility and reducing variability compared to in vivo studies. These methods enable direct access to tissues or cells, facilitating detailed cellular and molecular analyses without systemic influences. Ex vivo techniques also reduce ethical concerns by minimizing animal usage and improving the relevance of human-derived samples in biomedical research.
Benefits of In Vivo Experiments
In vivo experiments provide critical insights into complex biological systems by allowing researchers to study physiological processes within a living organism, ensuring accurate representation of interactions between tissues and organs. These studies facilitate the observation of real-time responses to treatments or interventions under natural conditions, which are often unattainable in ex vivo settings. Moreover, in vivo models enable comprehensive safety and efficacy assessments crucial for drug development and translational research.
Limitations of Ex Vivo Research
Ex vivo research faces limitations such as the inability to fully replicate the complex interactions and systemic environment present in living organisms, which can lead to incomplete or misleading biological responses. The lack of physiological factors like blood flow, hormonal regulation, and immune system dynamics restricts the extrapolation of results to in vivo conditions. Consequently, ex vivo models often require validation through in vivo studies to confirm the relevance and accuracy of findings.
Challenges in In Vivo Methodologies
In vivo methodologies face significant challenges including limited control over experimental variables and ethical constraints related to animal welfare. The complexity of living organisms introduces variability that often complicates data interpretation and reproducibility. Moreover, in vivo studies can be resource-intensive, requiring specialized equipment and prolonged timelines for observing biological effects.
Choosing Between Ex Vivo and In Vivo: Factors to Consider
Choosing between ex vivo and in vivo methods depends on the specific research goals, experimental control, and ethical considerations. Ex vivo techniques allow precise manipulation of biological tissues outside the organism, providing detailed cellular and molecular insights with reduced systemic variability. In vivo studies offer comprehensive physiological context, enabling observation of complex interactions within a living organism but require stringent ethical approval and consideration of animal welfare.
Future Trends in Ex Vivo and In Vivo Research
Future trends in ex vivo and in vivo research emphasize advanced organ-on-a-chip technologies and 3D bioprinting for more precise disease modeling and drug testing. Integration of AI-driven data analysis and real-time imaging enhances predictive accuracy and reduces reliance on animal models. Personalized medicine benefits from patient-derived ex vivo cultures and genetically engineered in vivo models, accelerating therapeutic discoveries and tailored treatments.
Ex vivo Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com