Acquired skills and knowledge form the foundation for personal and professional growth, enabling you to adapt to changing environments and seize new opportunities. Understanding how to effectively acquire and apply new information can significantly enhance your success in various aspects of life. Explore the full article to discover strategies that will empower your learning journey.
Table of Comparison
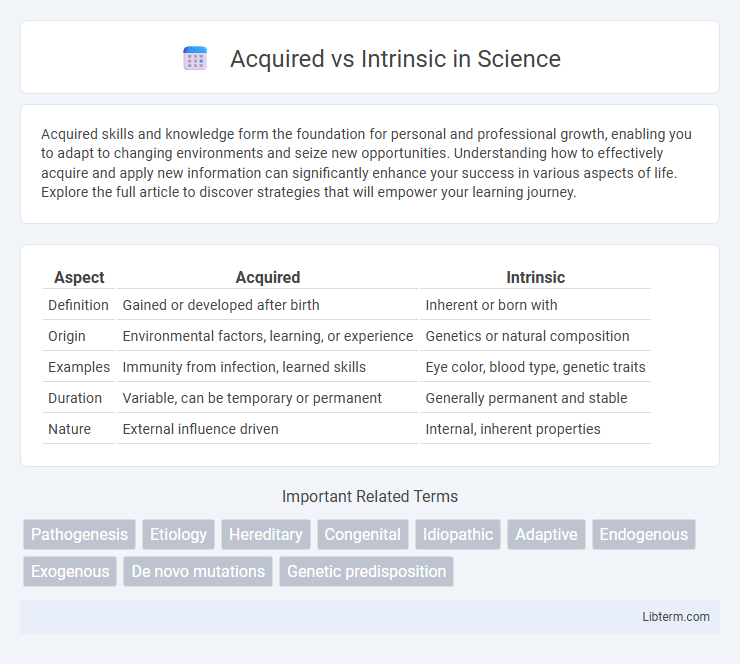
| Aspect | Acquired | Intrinsic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gained or developed after birth | Inherent or born with |
| Origin | Environmental factors, learning, or experience | Genetics or natural composition |
| Examples | Immunity from infection, learned skills | Eye color, blood type, genetic traits |
| Duration | Variable, can be temporary or permanent | Generally permanent and stable |
| Nature | External influence driven | Internal, inherent properties |
Introduction to Acquired vs Intrinsic
Acquired traits develop through environmental influences, experiences, or learned behaviors, shaping an individual's characteristics after birth. Intrinsic traits are inherent qualities determined by genetic makeup, present from birth and influencing natural abilities or predispositions. Understanding the distinction between acquired and intrinsic traits is essential for fields such as genetics, psychology, and developmental biology.
Defining Acquired Characteristics
Acquired characteristics refer to traits or features that an organism develops during its lifetime due to environmental influences, learning, or personal experiences rather than through genetic inheritance. These modifications can include alterations in behavior, physical adaptations from exercise, or skills gained through practice. Understanding acquired characteristics is crucial for studying phenotypic plasticity and the impacts of non-genetic factors on an organism's development.
Understanding Intrinsic Traits
Intrinsic traits refer to inherent characteristics present from birth, shaped by genetics and biological factors. These traits influence behavior, personality, and cognitive abilities without external influence or learning. Understanding intrinsic traits helps distinguish natural predispositions from acquired skills or habits developed through experience and environment.
Key Differences Between Acquired and Intrinsic
Acquired traits are characteristics gained through environmental influence or experience, while intrinsic traits are innate, genetically inherited features present at birth. Acquired traits can change over an individual's lifetime, whereas intrinsic traits remain consistent regardless of external factors. Understanding these key differences helps distinguish between nature-driven and nurture-driven aspects of development.
Origins and Influences: Nature vs Nurture
Acquired traits develop through environmental exposure and experiences, shaped primarily by upbringing, culture, and personal interactions, demonstrating the influence of nurture. Intrinsic traits originate from genetic inheritance and biological factors, highlighting the role of nature in determining inherent characteristics. Understanding the balance between acquired and intrinsic origins is essential in fields like psychology and behavioral genetics to analyze human development comprehensively.
Real-World Examples of Acquired vs Intrinsic
Acquired traits, like language skills learned through education or musical ability developed via practice, contrast with intrinsic traits such as eye color or genetic predisposition to certain diseases. For instance, a person born with a natural resistance to a specific illness represents an intrinsic trait, while someone who builds immunity after exposure or vaccination demonstrates an acquired characteristic. Real-world examples highlight that athletes may develop physical endurance through training (acquired), whereas their natural body composition or muscle fiber type remains intrinsic.
Impact on Personal Development
Acquired traits, developed through experience and learning, shape personal development by enhancing skills, knowledge, and emotional resilience over time. Intrinsic traits, rooted in genetics and inherent personality, influence natural tendencies and predispositions that guide behavior and motivation from birth. The interaction between acquired and intrinsic traits determines the overall trajectory of individual growth and adaptability.
Role in Learning and Adaptation
Acquired traits develop through environmental interactions and experience, playing a pivotal role in adaptive learning by allowing organisms to respond dynamically to changes. Intrinsic traits, encoded genetically, provide a foundational framework for behavior and physiological responses, guiding initial learning capacities and adaptability. The interplay between acquired experiences and intrinsic predispositions shapes effective learning processes and successful adaptation to new environments.
Relevance in Various Fields (Psychology, Biology)
Acquired traits stem from environmental influences and learning experiences, playing a critical role in psychology by shaping behavior and cognitive development through conditioning and socialization. In biology, intrinsic traits are genetically inherited characteristics essential for survival and adaptation, influencing an organism's phenotype and evolutionary fitness. Understanding the relevance of acquired versus intrinsic traits aids in fields like behavioral genetics and developmental psychology by distinguishing between nature and nurture factors impacting human growth and species evolution.
Conclusion: Integrating Acquired and Intrinsic
Integrating acquired and intrinsic factors enhances overall effectiveness by combining learned skills with innate abilities, creating a well-rounded approach to personal and professional growth. This synergy allows individuals to leverage their natural talents while continuously developing new competencies through experience and education. Emphasizing both elements fosters adaptability, resilience, and sustained success across various domains.
Acquired Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com