Environmental sustainability is essential for preserving natural resources and maintaining ecological balance. Implementing eco-friendly practices reduces pollution and conserves energy, benefiting the planet and future generations. Discover practical strategies to enhance your environmental impact by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
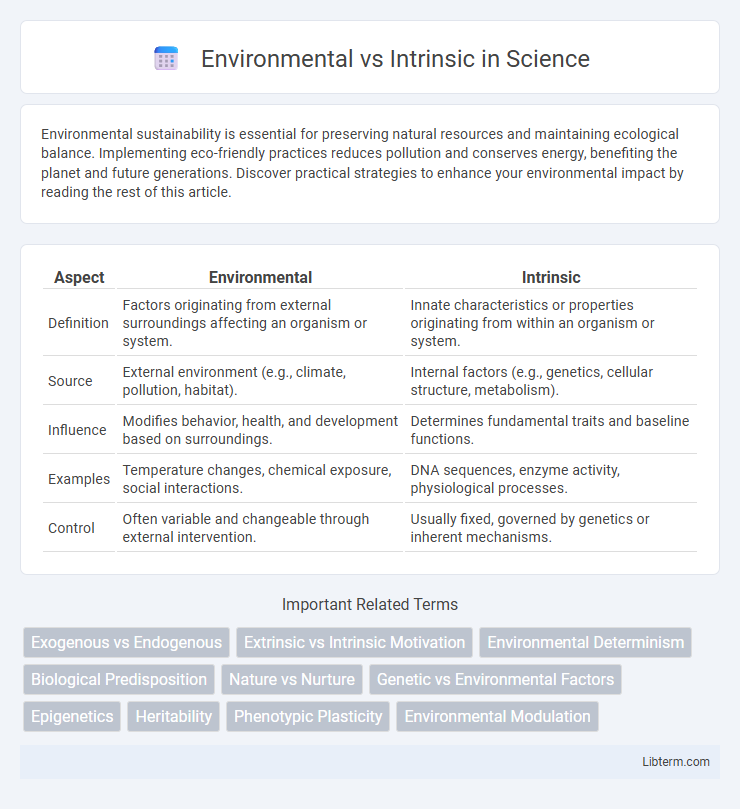
| Aspect | Environmental | Intrinsic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Factors originating from external surroundings affecting an organism or system. | Innate characteristics or properties originating from within an organism or system. |
| Source | External environment (e.g., climate, pollution, habitat). | Internal factors (e.g., genetics, cellular structure, metabolism). |
| Influence | Modifies behavior, health, and development based on surroundings. | Determines fundamental traits and baseline functions. |
| Examples | Temperature changes, chemical exposure, social interactions. | DNA sequences, enzyme activity, physiological processes. |
| Control | Often variable and changeable through external intervention. | Usually fixed, governed by genetics or inherent mechanisms. |
Understanding Environmental vs Intrinsic Factors
Environmental factors encompass external influences such as climate, pollution, and social conditions that shape individual behavior and health outcomes, while intrinsic factors refer to internal characteristics including genetics, metabolism, and psychological traits. Understanding the interplay between environmental and intrinsic factors enables more precise risk assessments and targeted interventions in fields like medicine, psychology, and public health. Research highlights that integrating both factors provides a comprehensive approach to addressing complex issues such as chronic diseases and developmental disorders.
Defining Environmental Influences
Environmental influences refer to external factors such as climate, culture, and socioeconomic conditions that shape an individual's development and behavior. These influences interact dynamically with intrinsic factors like genetics and biology to determine physical, cognitive, and emotional outcomes. Understanding environmental factors helps isolate the impact of nurture in contrast to innate traits in psychological and developmental studies.
Exploring Intrinsic Characteristics
Exploring intrinsic characteristics reveals fundamental properties inherent to a material or system, independent of external factors or environmental influences. Intrinsic qualities such as atomic structure, chemical composition, and molecular bonding directly determine performance, stability, and reactivity. Understanding these core attributes enables precise prediction of behavior under varied conditions and guides innovation in material science and biological applications.
Key Differences Between Environmental and Intrinsic Variables
Environmental variables refer to external factors influencing a system, such as temperature, humidity, and light, while intrinsic variables originate within the system, including genetic traits or internal biochemical processes. Environmental variables are often dynamic and subject to external changes, whereas intrinsic variables tend to be stable and inherent to the organism or system. Understanding the distinction between these variables is crucial for accurate modeling and analysis in fields like ecology, biology, and system engineering.
The Role of Genetics in Intrinsic Factors
Genetics plays a crucial role in intrinsic factors by determining an individual's biological makeup, including susceptibility to certain diseases and physiological traits. Inherent genetic variations influence metabolic processes, immune system function, and cellular aging, which cannot be altered by environmental changes. Understanding genetic contributions helps differentiate intrinsic aging and health risks from those shaped by external environmental exposures.
How Environment Shapes Outcomes
Environmental factors such as socioeconomic status, cultural norms, and access to education significantly influence individual outcomes by shaping behavior, opportunities, and cognitive development. Studies in psychology and sociology highlight that exposure to enriched environments during critical developmental periods leads to enhanced intellectual and emotional growth compared to deprived settings. Gene-environment interactions further demonstrate that while intrinsic genetics provide potential, environmental contexts determine the extent to which these traits manifest and develop.
Case Studies Highlighting Environmental vs Intrinsic Impacts
Case studies on environmental vs intrinsic impacts reveal that environmental factors such as pollution and habitat destruction significantly alter species behavior and ecosystem dynamics, while intrinsic factors like genetic variation and metabolic rates drive individual organism resilience and adaptation. Research in urban ecology demonstrates that pollutant exposure leads to measurable changes in wildlife health, contrasting with intrinsic impacts observed in species-specific genetic traits influencing survival rates under stress. Longitudinal studies combining environmental stressors and intrinsic biological responses offer comprehensive insights into adaptive mechanisms across diverse ecosystems.
Interplay Between Environmental and Intrinsic Elements
The interplay between environmental and intrinsic elements significantly influences human behavior and development, with environmental factors such as culture, social interactions, and surroundings shaping intrinsic traits like cognition and personality. Intrinsic factors, including genetic predispositions and innate abilities, interact dynamically with environmental stimuli, creating a complex feedback loop that determines individual outcomes. Understanding this bidirectional relationship is crucial in fields like psychology, neuroscience, and education to optimize growth and adaptation strategies.
Implications for Personal Development
Environmental factors shape personal development by influencing behavior, attitudes, and skills through external conditions such as family, culture, and education. Intrinsic factors, including genetic predispositions and inherent personality traits, determine innate potential and resilience, impacting self-motivation and emotional regulation. Understanding the balance between environmental stimuli and intrinsic characteristics is crucial for tailoring effective personal growth strategies and fostering holistic self-improvement.
Future Directions in Research on Environmental vs Intrinsic
Future research on environmental versus intrinsic factors will increasingly leverage advanced neuroimaging and epigenetic techniques to delineate their complex interplay in shaping human behavior and health outcomes. Emphasis on longitudinal cohort studies will enhance understanding of how early-life environmental exposures interact with genetic predispositions over time. Integrating multi-omics data with machine learning models promises to unravel personalized intervention strategies tailored to individual environmental and intrinsic profiles.
Environmental Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com