Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different structures, leading to distinct chemical and physical properties. Understanding isomers is crucial in fields like chemistry and pharmacology, where the arrangement of atoms affects a compound's behavior and effectiveness. Explore this article to uncover the fascinating types and significance of isomers in your scientific studies.
Table of Comparison
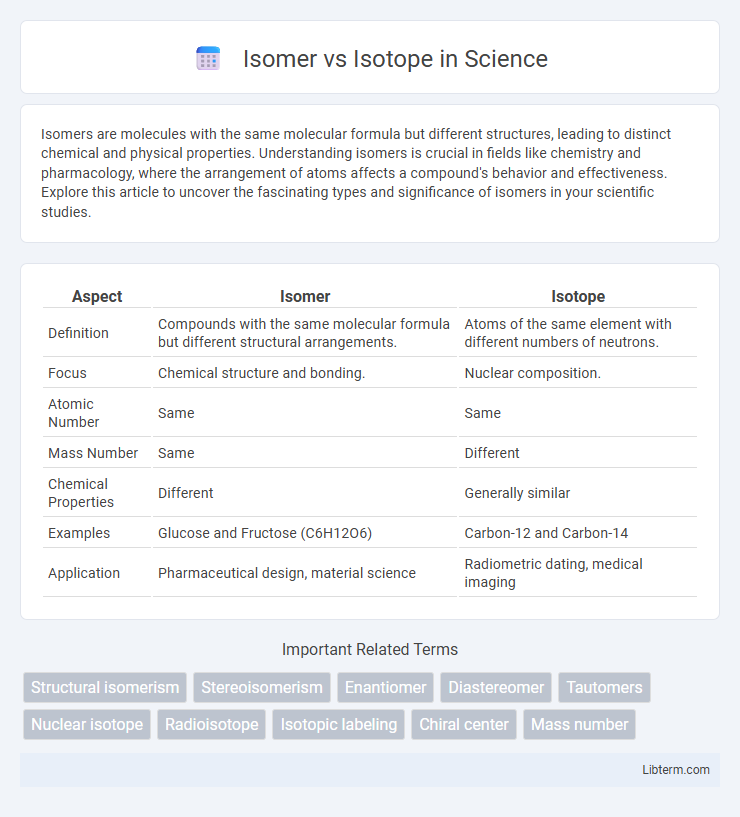
| Aspect | Isomer | Isotope |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. | Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. |
| Focus | Chemical structure and bonding. | Nuclear composition. |
| Atomic Number | Same | Same |
| Mass Number | Same | Different |
| Chemical Properties | Different | Generally similar |
| Examples | Glucose and Fructose (C6H12O6) | Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 |
| Application | Pharmaceutical design, material science | Radiometric dating, medical imaging |
Introduction to Isomers and Isotopes
Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements, resulting in distinct physical and chemical properties. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have identical atomic numbers but different neutron counts, leading to variations in atomic mass. Understanding isomers and isotopes is crucial for applications in chemistry, physics, and medical diagnostics.
Defining Isomers: Key Concepts
Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements, resulting in distinct physical and chemical properties. They include structural isomers, which differ in the connectivity of atoms, and stereoisomers, which have the same connectivity but differ in spatial orientation. This fundamental concept in chemistry highlights how atomic arrangement influences molecular behavior despite identical atomic composition.
Understanding Isotopes: Core Principles
Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element that share the same number of protons but differ in neutron count, resulting in different atomic masses. These nuclear differences influence isotopic stability and radioactive properties, with applications in radiometric dating, medical imaging, and nuclear energy. Understanding isotopes involves recognizing their role in atomic structure and their distinct physical and chemical behaviors compared to isomers, which are molecules with the same molecular formula but different arrangements.
Types of Isomers in Chemistry
Isomers in chemistry are molecules with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms, classified mainly into structural isomers and stereoisomers; structural isomers include chain, position, and functional group isomers, while stereoisomers comprise enantiomers and diastereomers. Isotopes, in contrast, are variants of a single chemical element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, impacting atomic mass but not chemical behavior. Understanding isomer types is crucial for drug design and material science, where molecular geometry influences function and reactivity.
Types of Isotopes: Stable vs Radioactive
Isotopes are variants of a chemical element with the same number of protons but different neutron counts, classified into stable and radioactive types based on nuclear stability. Stable isotopes, such as Carbon-12 and Oxygen-16, do not undergo radioactive decay and remain constant over time, making them useful in environmental and geological studies. Radioactive isotopes, like Carbon-14 and Uranium-238, emit radiation as they decay to more stable forms, widely applied in medical imaging, radiometric dating, and nuclear energy production.
Structural Differences: Isomer vs Isotope
Isomers exhibit structural differences through variations in the arrangement of atoms within the same molecular formula, resulting in distinct compounds with unique chemical properties. Isotopes differ structurally in the number of neutrons within the atomic nucleus, maintaining identical atomic numbers but varying atomic masses. These fundamental distinctions impact molecular behavior for isomers and nuclear characteristics for isotopes.
Chemical Properties and Reactivity
Isomers exhibit different chemical properties and reactivity due to variations in the arrangement of atoms within the same molecular formula, affecting their functional groups and spatial orientation. Isotopes, possessing identical atomic numbers but differing neutron counts, maintain nearly identical chemical behavior because their electron configurations remain unchanged. The slight differences in isotopes primarily influence physical properties and nuclear stability rather than chemical reactions.
Applications in Science and Industry
Isomers play a crucial role in pharmaceuticals, as different isomeric forms of a compound can exhibit distinct biological activities and drug efficacy, impacting drug design and development. Isotopes are extensively utilized in medical diagnostics and treatment, such as radioactive isotopes in cancer radiotherapy and stable isotopes in metabolic tracing. Both isomers and isotopes are vital in scientific research and industrial applications, from material science to environmental studies, enabling precise analysis and innovation.
Common Examples: Isomers and Isotopes
Isomers and isotopes differ fundamentally in chemical structure and atomic composition; isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms, exemplified by glucose and fructose, while isotopes are variants of the same element with differing neutron numbers, such as Carbon-12 and Carbon-14. Common isomers include structural isomers like butanol and isobutanol, and stereoisomers like cis-2-butene and trans-2-butene, which influence chemical properties without changing elemental composition. Common isotopes, including Uranium-235 and Uranium-238, vary in nuclear properties and stability, playing crucial roles in fields like radiometric dating and nuclear energy.
Summary: Distinguishing Isomer vs Isotope
Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements, affecting their chemical properties and behavior. Isotopes are variants of elements with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, influencing atomic mass and nuclear stability. Understanding the distinction is crucial in chemistry and physics for interpreting molecular interactions and atomic characteristics.
Isomer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com