Unilineal kinship systems trace descent exclusively through either the male or female line, shaping social structure and inheritance patterns. This approach deeply influences family roles, inheritance rights, and cultural identity within a community. Explore the rest of the article to understand how unilineal descent impacts societies worldwide and your own cultural heritage.
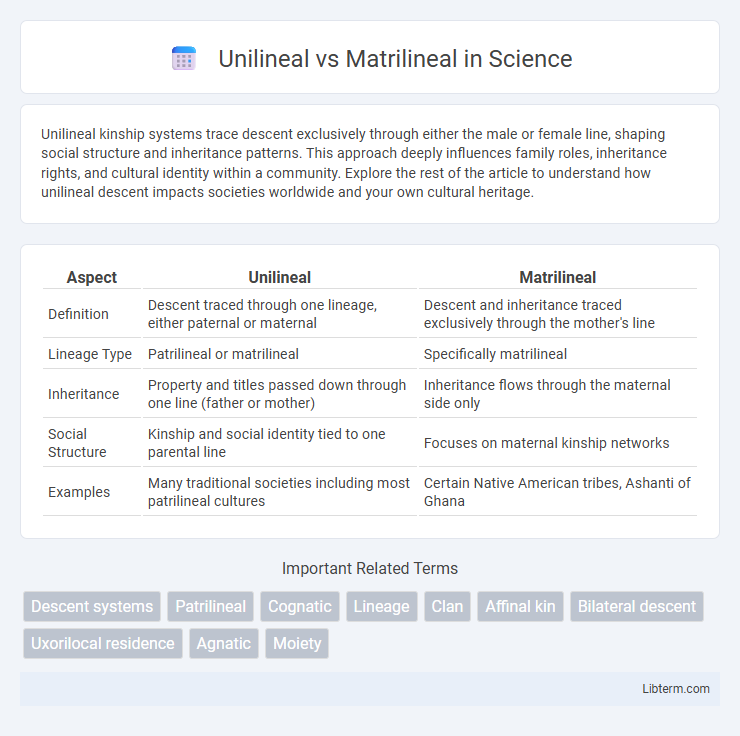
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Unilineal | Matrilineal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Descent traced through one lineage, either paternal or maternal | Descent and inheritance traced exclusively through the mother's line |
| Lineage Type | Patrilineal or matrilineal | Specifically matrilineal |
| Inheritance | Property and titles passed down through one line (father or mother) | Inheritance flows through the maternal side only |
| Social Structure | Kinship and social identity tied to one parental line | Focuses on maternal kinship networks |
| Examples | Many traditional societies including most patrilineal cultures | Certain Native American tribes, Ashanti of Ghana |
Introduction to Kinship Systems
Unilineal kinship systems trace descent exclusively through one parent's lineage, either patrilineal (father's line) or matrilineal (mother's line), shaping inheritance, social identity, and familial roles. Matrilineal systems emphasize maternal ancestry, often conferring lineage continuity, property rights, and clan membership through the mother's side. Understanding these kinship patterns reveals fundamental variations in cultural organization, social structure, and lineage-based responsibilities across societies.
Defining Unilineal Descent
Unilineal descent defines lineage through one gender line, either paternal (patrilineal) or maternal (matrilineal), tracing inheritance, clan membership, and social identity exclusively. Patrilineal descent links individuals to their father's lineage, while matrilineal descent connects them to their mother's lineage, influencing kinship ties and property transmission. This system shapes social structures by emphasizing a single ancestral line for cultural and legal purposes.
Understanding Matrilineal Descent
Matrilineal descent traces lineage exclusively through the mother's line, emphasizing inheritance, social status, and clan membership passed down maternally. This system contrasts with unilineal descent, which can be either matrilineal or patrilineal, but matrilineal societies specifically prioritize maternal ancestry for determining kinship and property rights. Anthropological studies reveal matrilineal descent as a critical structure in societies like the Hopi and the Akan, where women play central roles in lineage continuity and family identity.
Key Differences Between Unilineal and Matrilineal
Unilineal descent traces lineage exclusively through one gender, either paternal (patrilineal) or maternal (matrilineal), whereas matrilineal descent specifically follows the maternal line. The key difference lies in unilineal systems encompassing both patrilineal and matrilineal descent types, while matrilineal descent is a subset focusing solely on inheritance, lineage, and kinship through the mother's side. Matrilineal societies often emphasize maternal kinship roles, property inheritance, and social identity, contrasting with the broader practice of unilineal descent which can prioritize either parental line.
Advantages of Unilineal Structures
Unilineal kinship structures, which trace descent through either the paternal (patrilineal) or maternal (matrilineal) line exclusively, offer clear advantages in terms of inheritance clarity and social organization. Patrilineal systems often provide stronger political alliances and property continuity, while matrilineal systems can enhance maternal support networks and stability in lineage identity. These streamlined lineage frameworks reduce conflicts over heritage and succession, ensuring cohesive family roles and resource management.
Cultural Examples of Matrilineality
Matrilineal societies trace descent and inheritance through the mother's lineage, common among the Akan of Ghana, where property and titles pass through female ancestors. The Minangkabau of Indonesia exemplify matrilineality, with women owning ancestral land and playing key roles in family and community decision-making. Among the Navajo in North America, clan membership and social identity follow the mother's line, shaping kinship bonds and cultural practices.
Social Roles and Gender Dynamics
Unilineal descent systems, whether patrilineal or matrilineal, structure social roles and gender dynamics by tracing lineage exclusively through one gender, which often determines inheritance, residence, and authority within the community. In patrilineal societies, men typically hold dominant social roles and property rights, reinforcing patriarchal gender dynamics, while matrilineal systems grant women greater control over land, resources, and familial decision-making, shifting power dynamics more favorably toward females. These descent patterns deeply influence kinship obligations, leadership roles, and the distribution of social power, shaping gender-specific expectations and community organization.
Inheritance and Lineage Patterns
Unilineal inheritance and lineage patterns trace descent exclusively through one gender, with unilineal systems divided into patrilineal (father's line) and matrilineal (mother's line) groups. In patrilineal societies, inheritance and family name pass through the male lineage, often granting property and social status to sons, whereas matrilineal systems emphasize inheritance through the female line, allocating rights and resources typically to daughters or maternal relatives. These distinct patterns shape social organization, defining kinship roles, succession, and the distribution of wealth within communities.
Impact on Family Organization
Unilineal descent systems, including patrilineal and matrilineal, significantly shape family organization by determining lineage, inheritance, and residence patterns. In matrilineal societies, lineage and inheritance pass through the mother's line, often resulting in extended maternal kin networks and matrilocal residence, where husbands live with their wives' families. This contrasts with unilineal patrilineal systems, where descent and property typically follow the father's line, promoting patrilocal residence and emphasizing the father's lineage in family structure.
Contemporary Relevance and Changes
Contemporary societies exhibit significant shifts in unilineal and matrilineal descent systems, reflecting evolving social values and gender roles. Urbanization, globalization, and legal reforms increasingly challenge traditional unilineal lineage patterns, promoting more egalitarian kinship recognition. Matrilineal systems gain renewed relevance in contexts prioritizing women's inheritance rights and social status, adapting to modern family structures and cultural dynamics.
Unilineal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com