Metamorphosis represents a profound transformation in form, structure, or character, often observed in the life cycles of insects, amphibians, or symbolic human experiences. This process highlights nature's ability to adapt and evolve, showcasing stunning changes from one stage to another, such as a caterpillar becoming a butterfly. Dive deeper into the fascinating stages and significance of metamorphosis in the full article.
Table of Comparison
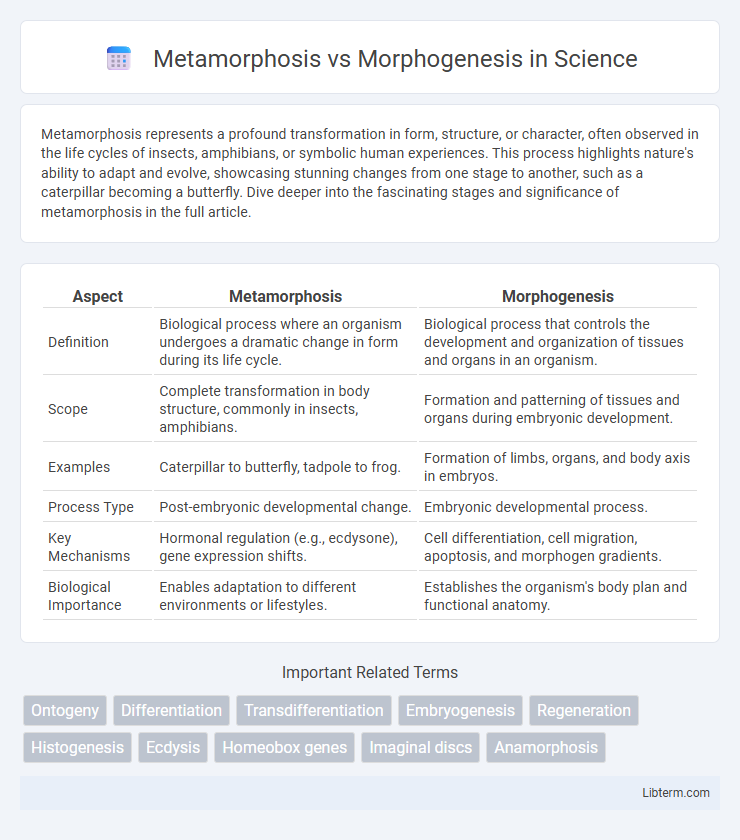
| Aspect | Metamorphosis | Morphogenesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Biological process where an organism undergoes a dramatic change in form during its life cycle. | Biological process that controls the development and organization of tissues and organs in an organism. |
| Scope | Complete transformation in body structure, commonly in insects, amphibians. | Formation and patterning of tissues and organs during embryonic development. |
| Examples | Caterpillar to butterfly, tadpole to frog. | Formation of limbs, organs, and body axis in embryos. |
| Process Type | Post-embryonic developmental change. | Embryonic developmental process. |
| Key Mechanisms | Hormonal regulation (e.g., ecdysone), gene expression shifts. | Cell differentiation, cell migration, apoptosis, and morphogen gradients. |
| Biological Importance | Enables adaptation to different environments or lifestyles. | Establishes the organism's body plan and functional anatomy. |
Introduction to Metamorphosis and Morphogenesis
Metamorphosis is a biological process where an organism undergoes a complete or partial physical transformation after birth or hatching, commonly seen in insects like butterflies and amphibians like frogs. Morphogenesis refers to the biological mechanism that controls the shape and structure formation of tissues and organs during embryonic development. Both processes are fundamental to developmental biology, with metamorphosis emphasizing postnatal physical changes and morphogenesis focusing on the organized cellular development that forms an organism's body plan.
Defining Metamorphosis: Key Concepts
Metamorphosis is a biological process involving a distinct and often rapid transformation in an organism's body structure through specific developmental stages, commonly observed in insects like butterflies and amphibians such as frogs. Key concepts defining metamorphosis include complete and incomplete metamorphosis, where complete metamorphosis consists of four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult, while incomplete metamorphosis involves three stages: egg, nymph, and adult. This process is regulated by hormonal changes that trigger cellular differentiation and morphological remodeling essential for transitioning from juvenile to mature forms.
Understanding Morphogenesis: Core Principles
Morphogenesis is the biological process that controls the shape and structure formation of tissues and organs during development, driven by genetic and molecular signaling pathways such as Wnt, Hedgehog, and Notch. It involves cellular behaviors including proliferation, differentiation, migration, and apoptosis, orchestrated in a spatial and temporal manner to produce complex anatomical forms. Unlike metamorphosis, which is a dramatic transformation between life stages, morphogenesis specifically refers to the continuous shaping and organization of cells within a developing organism.
Biological Processes Involved in Metamorphosis
Metamorphosis involves a series of complex biological processes such as hormonal regulation, cellular differentiation, and programmed cell death that transform an organism from juvenile to adult form, commonly seen in insects and amphibians. Ecdysone and juvenile hormone are key regulators triggering molting and tissue remodeling during metamorphosis. Unlike morphogenesis, which primarily refers to the development of an organism's shape through cell proliferation and movement, metamorphosis encompasses systemic physiological changes leading to a distinct morphological transition.
Mechanisms and Stages of Morphogenesis
Morphogenesis involves the coordinated cell growth, differentiation, and spatial organization that shape tissues and organs during embryonic development, primarily regulated by genetic and molecular signals like morphogens and transcription factors. This process includes stages such as gastrulation, where the three germ layers form, and organogenesis, during which these layers develop into specialized structures. In contrast, metamorphosis entails a dramatic transformation after initial development, involving programmed hormonal changes that reconfigure the organism's morphology from larval to adult forms.
Comparative Analysis: Metamorphosis vs Morphogenesis
Metamorphosis involves a distinct, often rapid transformation in an organism's life cycle, such as the transition from larva to adult in insects, characterized by drastic morphological and physiological changes. Morphogenesis refers to the biological process that governs the organized growth and spatial distribution of cells and tissues during embryonic development, shaping an organism's form and structure. Comparative analysis highlights that while metamorphosis alters an organism's developmental stages, morphogenesis focuses on the cellular and tissue-level mechanisms driving shape and structure formation within those stages.
Evolutionary Significance of Metamorphosis and Morphogenesis
Metamorphosis and morphogenesis play crucial roles in evolutionary adaptations by enabling organisms to occupy distinct ecological niches during different life stages, thus reducing intraspecific competition. Metamorphosis facilitates significant morphological and physiological transformations, allowing species like amphibians and insects to exploit diverse habitats and enhance survival rates. Morphogenesis governs the developmental processes that shape organismal form and complexity, driving evolutionary innovations through genetic and cellular patterning mechanisms.
Case Studies: Examples Across Species
Metamorphosis in insects like butterflies involves a complete transformation from larva to adult, exemplified by the monarch butterfly's transition from caterpillar to winged adult, showcasing drastic morphological and physiological changes. Morphogenesis, observed in vertebrates such as zebrafish embryos, entails the regulated formation of tissues and organs through cellular processes like differentiation and proliferation, demonstrating controlled growth patterns rather than a complete life stage shift. Case studies highlight that metamorphosis typically occurs in species with distinct life stages, while morphogenesis is fundamental to the developmental biology of all multicellular organisms.
Molecular and Genetic Regulation
Metamorphosis and morphogenesis are regulated by distinct molecular and genetic pathways, with metamorphosis primarily controlled by hormone-driven gene expression changes involving ecdysone and juvenile hormone in insects. Morphogenesis depends on a complex network of signaling molecules such as Wnt, Hedgehog, and BMP pathways that guide cellular differentiation, tissue patterning, and organ formation. Both processes rely on transcription factors and epigenetic modifications to finely tune gene expression during developmental transitions and tissue remodeling.
Applications and Future Research Directions
Metamorphosis applications primarily target developmental biology, pest control, and robotics, leveraging the transformation processes to inform biomimetic designs and adaptive systems. Morphogenesis research drives advances in tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, and synthetic biology by elucidating how spatial cell organization shapes organismal structures. Future research directions emphasize integrating multi-omics data and computational modeling to enhance control over these biological phenomena, enabling breakthroughs in medical therapies and biofabrication technologies.
Metamorphosis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com