Metamorphosis represents a profound biological transformation where an organism undergoes a dramatic change in form or structure during its lifecycle. This process is essential for species like butterflies and amphibians, enabling them to transition from immature stages to fully developed adults. Discover how understanding metamorphosis can reveal the incredible adaptability of life in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
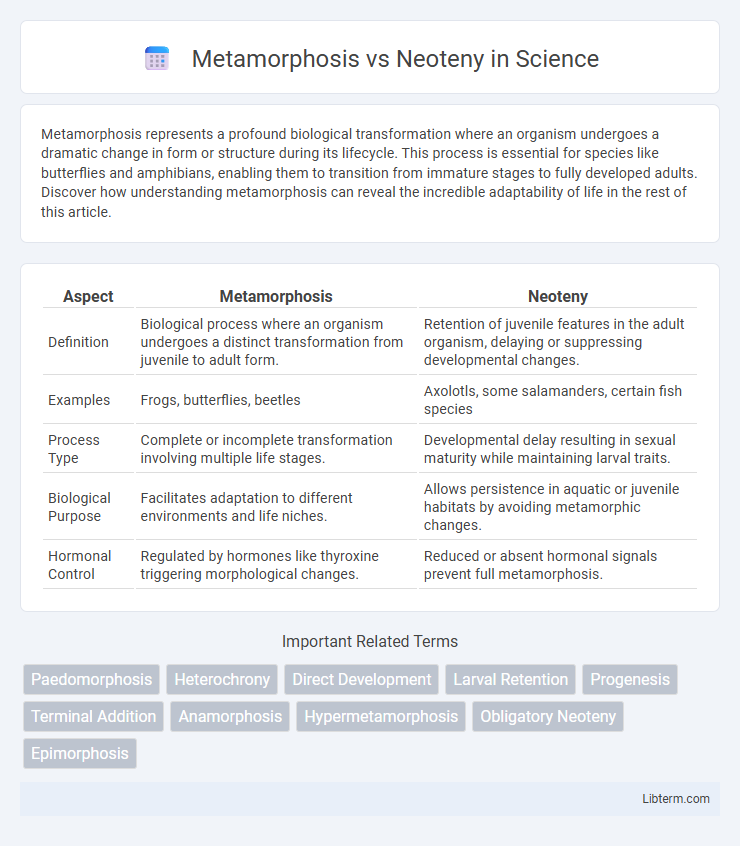
| Aspect | Metamorphosis | Neoteny |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Biological process where an organism undergoes a distinct transformation from juvenile to adult form. | Retention of juvenile features in the adult organism, delaying or suppressing developmental changes. |
| Examples | Frogs, butterflies, beetles | Axolotls, some salamanders, certain fish species |
| Process Type | Complete or incomplete transformation involving multiple life stages. | Developmental delay resulting in sexual maturity while maintaining larval traits. |
| Biological Purpose | Facilitates adaptation to different environments and life niches. | Allows persistence in aquatic or juvenile habitats by avoiding metamorphic changes. |
| Hormonal Control | Regulated by hormones like thyroxine triggering morphological changes. | Reduced or absent hormonal signals prevent full metamorphosis. |
Introduction to Metamorphosis and Neoteny
Metamorphosis is a biological process where an organism undergoes a dramatic transformation from larval to adult form, commonly seen in insects like butterflies and amphibians such as frogs. Neoteny refers to the retention of juvenile traits into adulthood, allowing certain species, like the axolotl, to remain in a larval state while achieving sexual maturity. These contrasting developmental strategies highlight different evolutionary adaptations for growth and survival in animals.
Defining Metamorphosis: Stages and Processes
Metamorphosis is a biological process involving distinct stages such as egg, larva, pupa, and adult, characterized by significant morphological and physiological changes. This process enables organisms like butterflies and amphibians to transition from immature larval forms to fully developed adults with different structures and functions. The key stages include embryonic development, larval growth, pupation or transformation, and emergence as a mature organism, distinct from neoteny where juvenile traits are retained in the adult.
Understanding Neoteny: Characteristics and Examples
Neoteny is an evolutionary process where an organism retains juvenile traits into its adult stage, contrasting with metamorphosis, which involves distinct developmental changes from larva to adult. Key characteristics of neoteny include delayed or slowed somatic development and the maintenance of larval features such as gills and aquatic lifestyle, commonly observed in species like the axolotl and certain salamanders. Understanding neoteny helps explain adaptive strategies in evolution, where retention of juvenile traits offers survival advantages in stable environments.
Evolutionary Significance of Metamorphosis
Metamorphosis drives evolutionary success by enabling distinct larval and adult stages to exploit different ecological niches, reducing intraspecific competition and enhancing survival rates. This developmental process promotes biodiversity and adaptation through dramatic morphological transformations, allowing species to respond swiftly to environmental changes. Metamorphosis contributes to evolutionary innovation by facilitating complex life cycles, increasing reproductive potential, and boosting dispersal capabilities.
Evolutionary Role of Neoteny in Species Adaptation
Neoteny plays a critical evolutionary role by allowing species to retain juvenile characteristics into adulthood, facilitating rapid adaptation to changing environments without the need for extensive morphological changes. This developmental strategy often results in increased plasticity and extended periods of growth and learning, enhancing survival and reproductive success in diverse ecological niches. In contrast to complete metamorphosis, neoteny enables species like axolotls to exploit aquatic habitats continuously, demonstrating its adaptive advantage by maintaining larval traits that confer specific environmental benefits.
Key Differences Between Metamorphosis and Neoteny
Metamorphosis involves a complete physical transformation from juvenile to adult stages, such as caterpillars turning into butterflies, whereas neoteny is the retention of juvenile traits into the adult form, exemplified by axolotls maintaining gills. Key differences include the timing and extent of development; metamorphosis features distinct morphological changes triggered by hormones like ecdysone, while neoteny results from delayed or suppressed hormonal processes leading to sexual maturity without full metamorphic transition. These biological strategies impact survival, reproduction, and ecological adaptability across various species.
Biological Mechanisms Underlying Each Process
Metamorphosis involves complex hormonal regulation, primarily through fluctuations in ecdysone and juvenile hormone levels, triggering dramatic morphological and physiological transformations in insects and amphibians. Neoteny is characterized by the retention of juvenile features into adulthood due to altered endocrine pathways, particularly mutations or reductions in thyroid hormone activity that delay or inhibit normal developmental progression. These distinct biological mechanisms underscore how differential hormone signaling pathways control growth patterns and life cycle transitions in various species.
Ecological Impacts on Developmental Strategies
Metamorphosis and neoteny represent contrasting developmental strategies that significantly influence ecological dynamics; metamorphosis allows organisms like amphibians to exploit multiple habitats by undergoing drastic morphological changes, thereby reducing intraspecific competition and enhancing resource utilization across aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. Neoteny, where organisms retain juvenile traits into adulthood as observed in some salamander species, fosters adaptation to stable, specialized niches often with high aquatic dependence, affecting local food webs and predator-prey relationships. These developmental strategies shape population distribution, ecosystem connectivity, and evolutionary trajectories by altering life cycle duration, habitat requirements, and resilience to environmental changes.
Notable Species Exhibiting Metamorphosis vs Neoteny
Notable species exhibiting metamorphosis include the Monarch butterfly (Danaus plexippus), which undergoes complete metamorphosis with distinct larval, pupal, and adult stages, and the common frog (Rana temporaria), transforming from tadpole to adult through complex morphological changes. In contrast, neoteny is prominently observed in the axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum), which retains juvenile aquatic features and gills throughout its life cycle while achieving sexual maturity. Some salamanders like the tiger salamander (Ambystoma tigrinum) may display facultative neoteny, depending on environmental conditions.
Implications for Research and Conservation
Metamorphosis and neoteny represent distinct developmental strategies with significant implications for research and conservation by influencing species' adaptability and population dynamics. Understanding metamorphosis, which involves complete transformation, aids in studying ecological roles and life cycle vulnerabilities, while neoteny, the retention of juvenile traits in adults, provides insights into evolutionary adaptations and genetic regulation. Conservation efforts benefit from recognizing these differences to develop targeted strategies that support species with variable developmental modes in changing environments.
Metamorphosis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com