Unilineal descent traces family lineage through a single line, either paternal or maternal, shaping social identity and inheritance patterns. This system influences kinship structures and cultural traditions, impacting how communities organize themselves and relate to ancestry. Explore the rest of the article to understand how unilineal descent affects social dynamics and your sense of heritage.
Table of Comparison
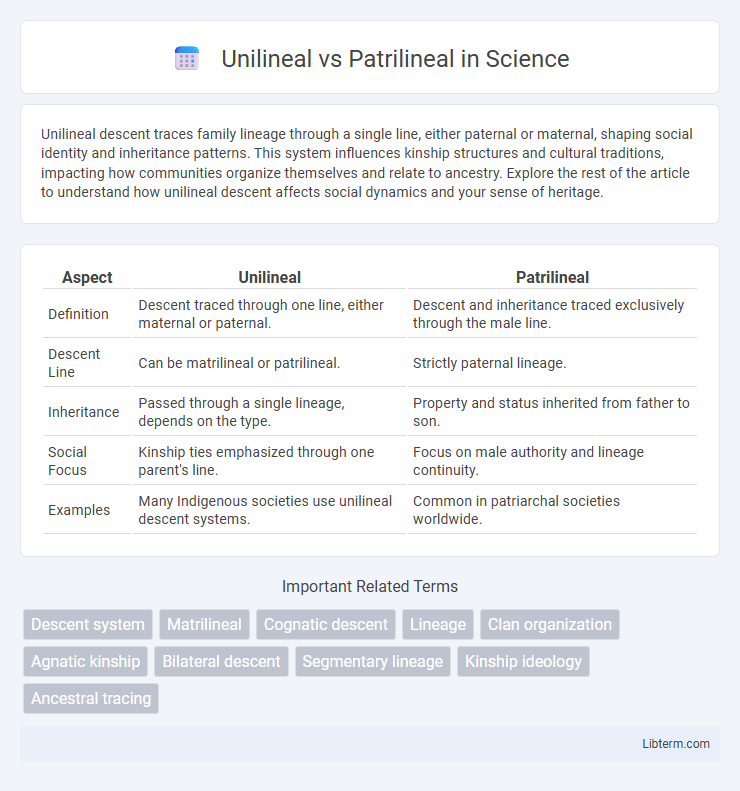
| Aspect | Unilineal | Patrilineal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Descent traced through one line, either maternal or paternal. | Descent and inheritance traced exclusively through the male line. |
| Descent Line | Can be matrilineal or patrilineal. | Strictly paternal lineage. |
| Inheritance | Passed through a single lineage, depends on the type. | Property and status inherited from father to son. |
| Social Focus | Kinship ties emphasized through one parent's line. | Focus on male authority and lineage continuity. |
| Examples | Many Indigenous societies use unilineal descent systems. | Common in patriarchal societies worldwide. |
Introduction to Unilineal and Patrilineal Descent
Unilineal descent systems trace lineage exclusively through one gender, either paternal or maternal, defining inheritance, identity, and social roles within a society. Patrilineal descent specifically follows the male line, where individuals belong to their father's lineage, inheriting property, status, and family name through paternal ancestors. These systems shape kinship structures, influence inheritance rules, and affect social organization across diverse cultures worldwide.
Defining Unilineal Descent
Unilineal descent refers to tracing kinship through a single lineage, either maternal or paternal, which establishes inheritance, social status, and family ties. Patrilineal descent specifically follows the male line, where lineage, property, and clan membership are inherited from the father. Unilineal systems simplify genealogical identity by emphasizing one ancestral line, contrasting with bilateral descent that considers both parents equally.
Understanding Patrilineal Descent
Patrilineal descent traces lineage exclusively through the male line, establishing inheritance, family name, and social status from father to son. This system shapes kinship patterns, property rights, and succession in many cultures worldwide, emphasizing male ancestry for defining identity and familial obligations. Understanding patrilineal descent reveals how societies organize themselves around paternal lineage, influencing social structure and cultural continuity.
Key Differences Between Unilineal and Patrilineal Systems
Unilineal systems trace descent exclusively through one gender line, either matrilineal or patrilineal, emphasizing lineage and inheritance rights through that gender. Patrilineal systems, a subset of unilineal descent, specifically follow the male line for inheritance, family name, and social identity. The key difference lies in unilineal systems' potential matrilineal aspect, while patrilineal systems strictly prioritize male lineage transmission.
Cultural Examples of Unilineal Descent
Unilineal descent systems trace lineage exclusively through one parent's line, either maternal (matrilineal) or paternal (patrilineal), shaping inheritance and social identity. Indigenous groups such as the Navajo in North America practice matrilineal descent, where clan membership and property pass through the mother's lineage. In contrast, many traditional societies like the Igbo of Nigeria follow a patrilineal system, emphasizing father-to-son transmission of family name and inheritance.
Societal Role of Patrilineal Descent
Patrilineal descent shapes societal roles by tracing lineage and inheritance through the male line, reinforcing male authority and kinship bonds within clans or families. This system often determines succession, property rights, and familial responsibilities, consolidating power among male descendants. Patrilineal societies typically emphasize paternal ancestry to maintain social structure and continuity across generations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each System
Unilineal descent systems, including patrilineal and matrilineal lines, streamline inheritance and social identity by tracing lineage through a single gender line, strengthening group cohesion and clarifying property rights. Patrilineal systems specifically prioritize male lineage for inheritance and familial ties, often reinforcing patriarchal structures but providing stability in lineage continuity and resource control. Both systems may limit individual flexibility in kinship relations and can marginalize members who fall outside the designated lineage, potentially leading to social exclusion or disputes over inheritance.
Impact on Inheritance and Family Structure
Unilineal descent systems, including patrilineal and matrilineal, define inheritance and family structure by tracing lineage through a single gender line, profoundly influencing property rights and kinship roles. Patrilineal descent specifically channels inheritance, family name, and social status from father to son, reinforcing male authority and lineage continuity within patriarchal societies. This system often shapes familial alliances, residence patterns, and succession customs, with profound effects on wealth distribution and social organization.
Modern Trends in Descent Systems
Modern trends in descent systems reveal a shift from strict unilineal or patrilineal frameworks toward more flexible and bilateral kinship models. Increasing globalization and social mobility encourage recognition of both maternal and paternal lineages, challenging traditional patrilineal dominance found in many cultures. Contemporary societies often integrate legal and social reforms promoting gender equality that influence descent practices and inheritance rights.
Conclusion: Significance of Descent Patterns
Unilineal and patrilineal descent patterns significantly shape kinship, inheritance, and social identity by determining lineage through either one parent or specifically the father's line. Patrilineal descent influences property rights and societal roles predominantly in patriarchal cultures, reinforcing male lineage continuity. Understanding these patterns is crucial for analyzing cultural organization, familial obligations, and gender dynamics across different societies.
Unilineal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com