Deterministic systems operate with predictable outcomes based on initial conditions, ensuring consistent and reproducible results every time. This concept is fundamental in fields such as computer science, mathematics, and physics, where processes must avoid randomness to guarantee accuracy. Explore the rest of the article to discover how deterministic principles impact your daily technology and decision-making processes.
Table of Comparison
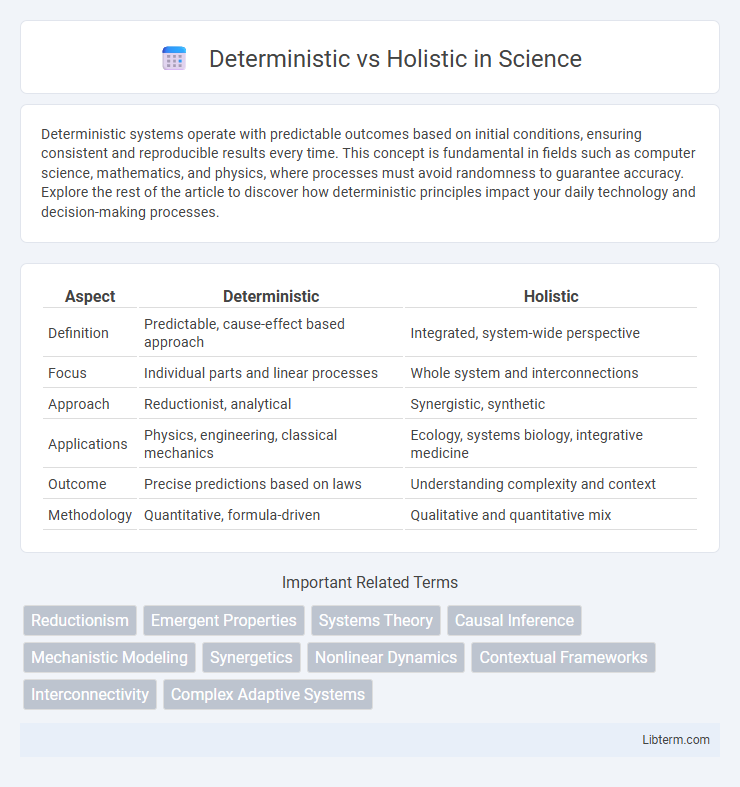
| Aspect | Deterministic | Holistic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Predictable, cause-effect based approach | Integrated, system-wide perspective |
| Focus | Individual parts and linear processes | Whole system and interconnections |
| Approach | Reductionist, analytical | Synergistic, synthetic |
| Applications | Physics, engineering, classical mechanics | Ecology, systems biology, integrative medicine |
| Outcome | Precise predictions based on laws | Understanding complexity and context |
| Methodology | Quantitative, formula-driven | Qualitative and quantitative mix |
Introduction to Deterministic and Holistic Approaches
Deterministic approaches rely on fixed rules and clear cause-and-effect relationships to produce predictable outcomes, making them essential in fields such as engineering and computer science. Holistic approaches consider the entire system, including interdependencies and complex interactions, which is crucial in disciplines like ecology and psychology. Emphasizing system-wide perspectives, holistic methods address multifaceted problems that deterministic models may oversimplify.
Defining Deterministic Methodology
Deterministic methodology relies on fixed, predictable processes where outcomes are strictly determined by initial conditions and predefined rules. This approach emphasizes measurable data, structured models, and reproducible results, often used in scientific experiments and algorithmic computations. It contrasts with holistic methodology by focusing on linear cause-effect relationships rather than interconnected systems and emergent properties.
What Is Holistic Perspective?
A holistic perspective emphasizes the interconnectedness of systems and views phenomena as integrated wholes rather than isolated parts, contrasting with deterministic approaches that focus on cause-and-effect relationships. It considers multiple dimensions, including physical, emotional, social, and environmental factors, to understand complex situations comprehensively. This approach is widely applied in fields like healthcare, education, and environmental science to promote balanced, sustainable outcomes.
Key Differences Between Deterministic and Holistic Views
Deterministic views emphasize cause-and-effect relationships, predicting outcomes based on specific initial conditions using fixed rules or models. Holistic perspectives consider systems as interconnected wholes, prioritizing the integration of multiple factors and the context surrounding phenomena rather than isolated variables. The key difference lies in determinism's linear, reductionist approach versus holism's comprehensive, systemic understanding of complex interactions.
Advantages of Deterministic Analysis
Deterministic analysis offers precise, reproducible results by using fixed input values and predefined assumptions, ensuring consistent outcomes in engineering and risk assessment applications. Its computational efficiency enables faster decision-making compared to probabilistic methods, reducing complexity without compromising essential accuracy. This approach facilitates clear interpretation and straightforward validation, making it advantageous for regulatory compliance and safety-critical evaluations.
Benefits of Holistic Thinking
Holistic thinking enhances problem-solving by integrating diverse perspectives and recognizing complex, interconnected systems, leading to more sustainable and innovative solutions. This cognitive approach improves decision-making effectiveness in dynamic environments by considering long-term impacts and multiple variables simultaneously. Organizations adopting holistic frameworks experience increased adaptability, resilience, and alignment with overall strategic goals.
Limitations of Deterministic Approach
The deterministic approach often struggles with handling complex systems due to its reliance on predefined rules and fixed variables, resulting in limited adaptability and rigid predictions. This method fails to incorporate uncertainty and variability inherent in real-world scenarios, reducing its effectiveness in dynamic environments. Consequently, deterministic models can provide overly simplistic solutions that overlook nuanced interactions and emergent phenomena captured by holistic approaches.
Challenges in Holistic Application
Holistic application faces significant challenges such as managing complex, interconnected variables that resist straightforward measurement and predictability found in deterministic models. Integrating diverse data sources while maintaining coherence requires advanced computational techniques and robust frameworks to ensure accurate interpretation. Addressing the ambiguity and subjectivity inherent in holistic approaches demands adaptive strategies that can evolve with dynamic system behaviors and contextual changes.
Real-World Examples: Deterministic vs Holistic
Deterministic approaches, such as assembly line manufacturing, rely on fixed, predictable processes ensuring consistent output, exemplified by automotive production systems. Holistic methods, like integrated urban planning, consider multiple variables including social, environmental, and economic factors to create sustainable communities. Real-world scenarios highlight that while deterministic models excel in controlled production environments, holistic strategies are essential for managing complex, interdependent systems.
Choosing the Right Approach: Context Matters
Choosing the right approach between deterministic and holistic methods depends on the specific context and objectives of a project or analysis. Deterministic approaches offer precise, rule-based outcomes ideal for well-defined systems like engineering or software development, while holistic methods provide broader, integrative insights suited for complex, adaptive environments such as organizational development or ecosystem management. Evaluating the nature of data, uncertainty levels, and desired comprehensiveness ensures alignment with the best-suited approach for optimal decision-making.
Deterministic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com