Abstraction simplifies complex systems by focusing on essential features while hiding irrelevant details, enabling clearer understanding and efficient problem-solving. This concept is fundamental in fields such as computer science, art, and philosophy, where it aids in managing information overload. Explore the rest of the article to discover how abstraction can enhance your analytical and creative skills.
Table of Comparison
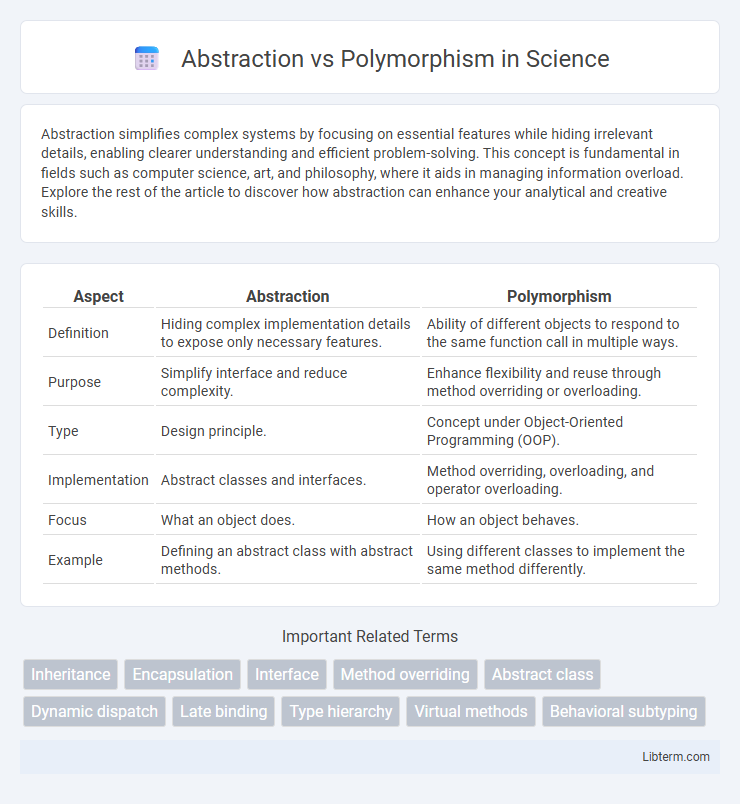
| Aspect | Abstraction | Polymorphism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiding complex implementation details to expose only necessary features. | Ability of different objects to respond to the same function call in multiple ways. |
| Purpose | Simplify interface and reduce complexity. | Enhance flexibility and reuse through method overriding or overloading. |
| Type | Design principle. | Concept under Object-Oriented Programming (OOP). |
| Implementation | Abstract classes and interfaces. | Method overriding, overloading, and operator overloading. |
| Focus | What an object does. | How an object behaves. |
| Example | Defining an abstract class with abstract methods. | Using different classes to implement the same method differently. |
Understanding Abstraction in Programming
Abstraction in programming simplifies complex systems by hiding unnecessary details and exposing only essential features, enabling developers to manage complexity efficiently. It allows the creation of abstract classes and interfaces that define a blueprint for other classes, promoting modularity and code reusability. Understanding abstraction helps in designing flexible software architectures where implementation details can change without affecting the overall system behavior.
Defining Polymorphism in OOP
Polymorphism in object-oriented programming (OOP) refers to the ability of different classes to be treated as instances of the same class through a common interface, enabling one interface to control access to a variety of underlying forms (data types). It allows methods to operate differently based on the object class that invokes them, promoting flexibility and extensibility in code through method overriding and dynamic binding. Polymorphism is distinct from abstraction, which focuses on hiding complex implementation details and exposing only essential features of an object.
Core Differences Between Abstraction and Polymorphism
Abstraction hides complex implementation details by exposing only essential features through abstract classes or interfaces, emphasizing the "what" over the "how" in object-oriented programming. Polymorphism enables objects of different classes to be treated as instances of a common superclass, allowing methods to perform differently based on the object's actual class at runtime. While abstraction deals with design and structure to reduce complexity, polymorphism focuses on behavior flexibility and method overriding to achieve dynamic method dispatch.
Advantages of Using Abstraction
Abstraction simplifies complex systems by exposing only essential features, reducing development time and improving code maintainability. It enhances security by hiding implementation details, preventing unintended interactions and vulnerabilities. Leveraging abstraction facilitates easier code updates and promotes reusable components, leading to more efficient software design.
Benefits of Implementing Polymorphism
Polymorphism enhances software flexibility by allowing objects of different classes to be treated as instances of a common superclass, facilitating code reusability and scalability. It simplifies code maintenance and improves readability by enabling a single interface to represent different data types, reducing the need for multiple conditional statements. Implementing polymorphism leads to more dynamic and extensible systems by supporting method overriding and dynamic binding, essential for effective object-oriented design.
Real-World Examples of Abstraction
Abstraction simplifies complex systems by hiding unnecessary details while highlighting essential features, exemplified in real-world examples such as vehicle controls where drivers interact with a steering wheel without understanding engine mechanics. Polymorphism allows objects of different classes to be treated as instances of a common superclass, enabling methods like "start()" to operate uniquely on a car, bike, or truck. The abstraction in devices like smartphones abstracts various internal processes, allowing users to perform complex tasks effortlessly.
Practical Applications of Polymorphism
Polymorphism enables objects of different classes to be treated as instances of a common superclass, allowing for flexible and reusable code in software development. It is widely applied in designing user interfaces where multiple components respond to the same method call, and in implementing callback mechanisms that enhance system modularity. Practical uses include overriding methods in subclasses to provide specific behaviors while maintaining consistent interfaces across diverse object types.
Abstraction vs Polymorphism: Code Comparisons
Abstraction hides complex implementation details by defining abstract classes or interfaces, allowing developers to focus on essential features without exposing inner workings. Polymorphism enables objects of different classes to be treated as instances of the same superclass, typically using method overriding to execute class-specific behavior dynamically at runtime. Code comparisons often highlight abstraction through abstract methods or interfaces requiring implementation, while polymorphism demonstrates method calls on superclass references resolving to subclass implementations during execution.
Choosing Between Abstraction and Polymorphism
Choosing between abstraction and polymorphism depends on the design goals of software development; abstraction emphasizes defining clear interfaces and hiding complex implementation details, facilitating maintainability and modularity. Polymorphism allows objects of different classes to be treated uniformly through a common interface, promoting flexibility and extensibility by enabling method overriding and dynamic behavior. Effective use of abstraction establishes a strong foundation for code architecture, while polymorphism enhances runtime adaptability and code reusability in object-oriented programming.
Best Practices for Combining Abstraction and Polymorphism
Combining abstraction and polymorphism effectively requires designing clear interfaces that define abstract methods, ensuring consistent implementation across subclasses to promote code reusability and scalability. Use abstraction to hide complex implementation details while leveraging polymorphism to enable dynamic method binding, allowing behavior to vary seamlessly at runtime. Prioritize maintaining low coupling and high cohesion by adhering to SOLID principles, particularly the Open/Closed Principle, which supports extending functionality without modifying existing code.
Abstraction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com