Mutable data structures allow you to modify elements after creation, enabling dynamic and flexible programming. Understanding mutable types like lists and dictionaries is essential for efficient memory management and performance in your code. Explore the full article to learn how manipulating mutable objects can improve your programming skills.
Table of Comparison
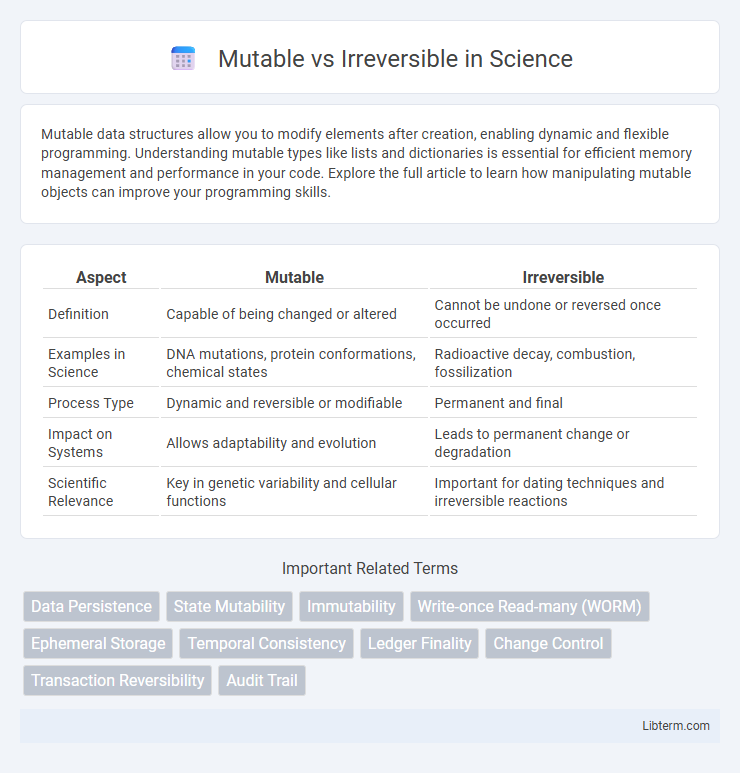
| Aspect | Mutable | Irreversible |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Capable of being changed or altered | Cannot be undone or reversed once occurred |
| Examples in Science | DNA mutations, protein conformations, chemical states | Radioactive decay, combustion, fossilization |
| Process Type | Dynamic and reversible or modifiable | Permanent and final |
| Impact on Systems | Allows adaptability and evolution | Leads to permanent change or degradation |
| Scientific Relevance | Key in genetic variability and cellular functions | Important for dating techniques and irreversible reactions |
Introduction to Mutability and Irreversibility
Mutability refers to the ability of an object or data structure to be changed after its creation, with examples including lists and dictionaries in programming languages like Python. Irreversibility describes entities or processes that cannot be undone or restored to their original state once altered, such as cryptographic hash functions or certain chemical reactions. Understanding mutability and irreversibility is essential for designing efficient algorithms, managing data integrity, and ensuring predictable behavior in software development.
Defining Mutable and Irreversible Concepts
Mutable concepts allow changes and modifications over time, adapting based on new information or conditions. Irreversible concepts are fixed and cannot be altered once established, preserving their original state permanently. Understanding the distinction between mutable and irreversible is crucial in fields like programming, data management, and decision-making processes.
Key Differences Between Mutable and Irreversible
Mutable objects allow modification after creation, enabling changes to their state or content throughout their lifecycle. Irreversible entities, by contrast, cannot be altered once established, ensuring data integrity and consistent state over time. This distinction impacts programming choices, memory management, and system design, where mutable data structures offer flexibility, while irreversible ones provide stability and predictability.
Common Use Cases for Mutability
Mutable objects, such as lists and dictionaries in Python or ArrayLists in Java, are ideal for scenarios requiring frequent updates and modifications. They enable efficient data manipulation in applications like real-time data processing, user input handling, and dynamic content generation. Choosing mutable structures enhances performance when data states change frequently without the need to create new instances.
Where Irreversibility Matters Most
Irreversibility matters most in data security and blockchain technology where immutable records prevent fraud and ensure trust. Mutable systems are preferred in dynamic environments like software development for flexibility and quick updates. Critical sectors such as finance and healthcare rely heavily on irreversible data to maintain integrity and compliance with regulatory standards.
Benefits of Mutable Systems
Mutable systems provide flexibility by allowing data to be updated or modified, which enhances adaptability in dynamic environments. This capability supports real-time decision-making and efficient error correction, reducing downtime and improving overall system performance. Organizations leveraging mutable architectures benefit from streamlined workflows and accelerated innovation cycles.
Advantages of Irreversible Approaches
Irreversible approaches offer enhanced security by preventing unauthorized modifications, ensuring data integrity and trustworthiness in sensitive applications such as blockchain technology and cryptographic hashing. These methods reduce risks of data tampering and enhance auditability, which is crucial for compliance in regulated industries like finance and healthcare. Furthermore, irreversible processes simplify system state management by eliminating ambiguity in data versions, leading to more predictable and reliable outcomes.
Challenges of Mutability
Mutable data structures introduce challenges such as increased risk of unintended side effects, making debugging and testing more complex. Concurrency issues arise because mutable states require careful synchronization to avoid race conditions in multi-threaded environments. Ensuring consistency and managing state changes demand rigorous design patterns, often leading to higher maintenance overhead compared to immutable data structures.
Limitations of Irreversible Systems
Irreversible systems face significant limitations due to their inability to adapt or modify past actions, which restricts flexibility and error correction in dynamic environments. These systems often result in permanent changes that cannot be undone, leading to potential data loss or system failures if mistakes occur. Such constraints make irreversible designs less suitable for applications requiring frequent updates, iterative processes, or real-time adjustments.
Choosing Between Mutable and Irreversible Solutions
Choosing between mutable and irreversible solutions depends on the specific use case and system requirements. Mutable solutions allow data to be modified after creation, offering flexibility for frequent updates and dynamic environments, while irreversible solutions ensure immutability, enhancing security, auditability, and consistency, especially in blockchain and compliance contexts. Assessing factors such as performance needs, data integrity, and regulatory compliance helps determine the optimal choice for software design and data management.
Mutable Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com