Quantitative analysis involves the systematic examination of numerical data to identify patterns, relationships, and trends that inform decision-making processes. Techniques such as statistical modeling, data mining, and predictive analytics enhance the accuracy and reliability of these insights. Explore the rest of the article to discover how quantitative methods can optimize your business strategies.
Table of Comparison
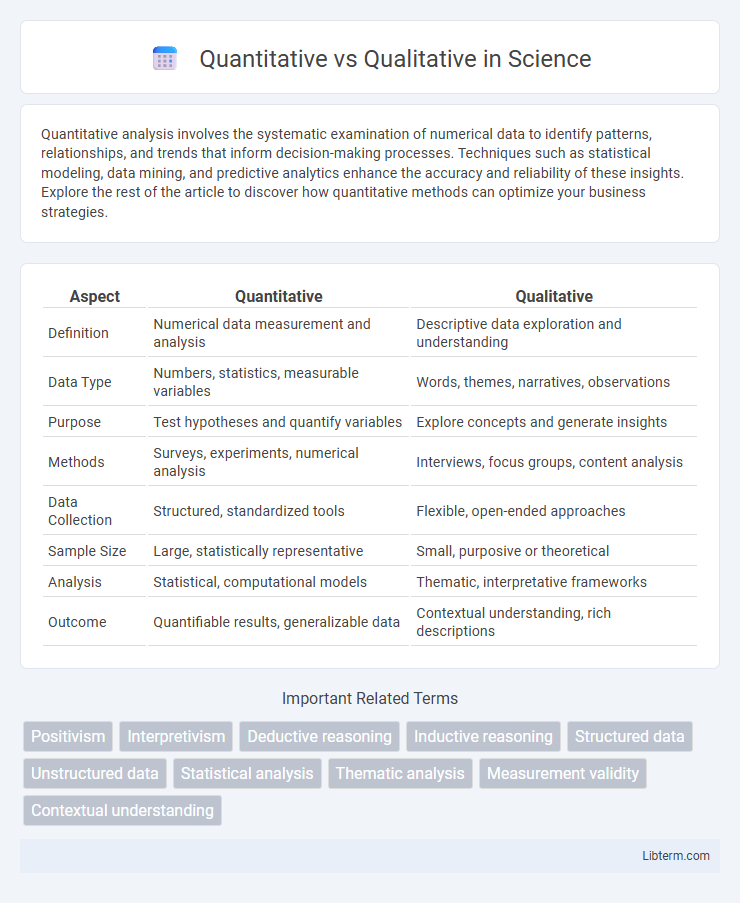
| Aspect | Quantitative | Qualitative |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Numerical data measurement and analysis | Descriptive data exploration and understanding |
| Data Type | Numbers, statistics, measurable variables | Words, themes, narratives, observations |
| Purpose | Test hypotheses and quantify variables | Explore concepts and generate insights |
| Methods | Surveys, experiments, numerical analysis | Interviews, focus groups, content analysis |
| Data Collection | Structured, standardized tools | Flexible, open-ended approaches |
| Sample Size | Large, statistically representative | Small, purposive or theoretical |
| Analysis | Statistical, computational models | Thematic, interpretative frameworks |
| Outcome | Quantifiable results, generalizable data | Contextual understanding, rich descriptions |
Understanding Quantitative and Qualitative Research
Quantitative research systematically collects and analyzes numerical data to identify patterns, test hypotheses, and make predictions, using statistical tools for reliability and validity. Qualitative research explores human experiences and social phenomena through non-numerical data like interviews, observations, and thematic analysis to gain in-depth understanding. Understanding quantitative and qualitative methods is crucial for selecting the appropriate research design, ensuring accurate data interpretation, and addressing specific research questions effectively.
Key Differences Between Quantitative and Qualitative Methods
Quantitative methods involve numerical data analysis, emphasizing measurable variables and statistical techniques to identify patterns and test hypotheses. Qualitative methods focus on understanding phenomena through non-numerical data such as interviews, observations, and textual analysis, providing in-depth insights into context and meaning. Key differences include data type, analysis approach, and research objectives, with quantitative aiming for generalizability and qualitative targeting detailed, contextual understanding.
When to Use Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is most effective when the goal is to collect measurable data to identify patterns, test hypotheses, or quantify variables across large populations. It is ideal for studies requiring statistical analysis, such as surveys, experiments, and numerical data comparisons, providing objective and generalizable results. Use quantitative research when precise measurement, scalability, and structured data collection are essential for making data-driven decisions or validating theoretical models.
When to Use Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is ideal when exploring complex phenomena, understanding motivations, and gaining in-depth insights into human behaviors and experiences. It is best used in the early stages of research to generate hypotheses, discover patterns, or clarify ambiguous problems through interviews, focus groups, and case studies. This approach excels when context, meaning, and subjective perspectives are crucial to inform decision-making and develop rich, detailed data.
Data Collection Techniques: Quantitative vs Qualitative
Quantitative data collection techniques include surveys, questionnaires, and structured observations that produce numerical data for statistical analysis. Qualitative data collection relies on interviews, focus groups, and open-ended observations to capture detailed, descriptive insights. Choosing between quantitative and qualitative methods depends on research objectives, with quantitative focusing on measurable, generalizable data and qualitative emphasizing context and depth.
Analyzing Quantitative Data
Analyzing quantitative data involves statistical techniques such as regression analysis, hypothesis testing, and descriptive statistics to uncover patterns and relationships within numerical datasets. This process ensures objectivity by focusing on measurable variables, enabling precise comparisons and trend identification across large sample sizes. Effective quantitative data analysis supports evidence-based decision-making and predictive modeling in fields like economics, healthcare, and social sciences.
Analyzing Qualitative Data
Analyzing qualitative data involves interpreting non-numerical information such as interviews, focus groups, and open-ended survey responses to uncover patterns, themes, and insights. Techniques like thematic analysis, content analysis, and narrative analysis help researchers grasp complex human experiences, social contexts, and motivations. Qualitative data analysis enhances understanding of subjective phenomena and complements quantitative methods by providing depth and context.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Approach
Quantitative research excels in providing measurable and statistically analyzable data, enabling objective comparisons and generalizations from large sample sizes, but it often lacks depth in understanding context or participant perspectives. Qualitative research offers rich, detailed insights into behaviors and motivations through methods like interviews and observations, yet it may suffer from smaller sample sizes and challenges in replicability and generalization. Balancing these approaches depends on the research goals, as quantitative methods suit hypothesis testing and trend analysis, while qualitative methods are ideal for exploring complex phenomena and generating theories.
Combining Quantitative and Qualitative Methods
Combining quantitative and qualitative methods enhances research by leveraging numerical data's precision alongside rich, contextual insights. This mixed-methods approach allows for comprehensive analysis, validating statistical trends with in-depth understanding of participant experiences. Integrating surveys, experiments, interviews, and focus groups increases the robustness, reliability, and relevance of findings across diverse disciplines such as social sciences, healthcare, and market research.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Research
Choosing the right research method depends on the research objectives and the type of data needed. Quantitative methods provide statistical, numerical data ideal for testing hypotheses and measuring variables, while qualitative methods offer deeper insights through textual or visual data to explore meanings and experiences. Researchers should evaluate factors such as sample size, data collection techniques, and analysis goals to select the most effective approach for their specific study.
Quantitative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com