Exploration drives human curiosity and the quest for knowledge, uncovering new territories and expanding our understanding of the world and beyond. It fuels innovation, shapes history, and inspires groundbreaking discoveries that redefine possibilities. Dive into the rest of this article to uncover how exploration continues to impact your life and shape the future.
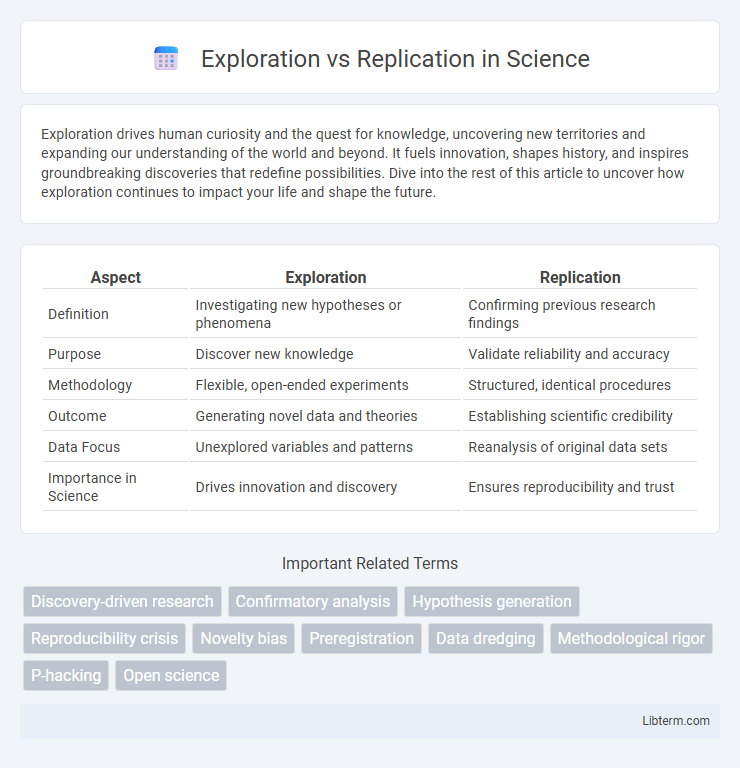
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Exploration | Replication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investigating new hypotheses or phenomena | Confirming previous research findings |
| Purpose | Discover new knowledge | Validate reliability and accuracy |
| Methodology | Flexible, open-ended experiments | Structured, identical procedures |
| Outcome | Generating novel data and theories | Establishing scientific credibility |
| Data Focus | Unexplored variables and patterns | Reanalysis of original data sets |
| Importance in Science | Drives innovation and discovery | Ensures reproducibility and trust |
Understanding Exploration and Replication
Understanding exploration involves investigating new ideas, hypotheses, or methods to generate innovative insights and expand knowledge boundaries. Replication emphasizes the process of repeating experiments or studies to verify results and ensure reliability and validity in research findings. Both exploration and replication are critical for scientific progress, with exploration driving discovery and replication reinforcing trust in evidence.
The Importance of Exploration in Research
Exploration in research drives the discovery of novel phenomena and deepens understanding by investigating uncharted areas and formulating new hypotheses. This process fosters innovation and lays the groundwork for subsequent replication studies that confirm and generalize findings. Prioritizing exploration accelerates scientific progress and enables researchers to address complex, emerging questions across diverse disciplines.
The Role of Replication in Scientific Progress
Replication reinforces scientific progress by verifying the reliability and validity of original research findings. It serves as a critical mechanism to identify errors, confirm results across diverse populations or settings, and build robust, evidence-based knowledge. By ensuring reproducibility, replication strengthens theories and supports cumulative advancements in various scientific disciplines.
Key Differences Between Exploration and Replication
Exploration involves investigating new hypotheses or phenomena to generate novel insights, while replication focuses on confirming the reliability and validity of existing findings through repeated studies. Exploration prioritizes flexibility and discovery, often employing diverse methods and datasets, whereas replication emphasizes methodological consistency and precise reproducibility. Key differences include the purpose--innovation versus verification--and the outcome, with exploration producing potential new theories and replication strengthening empirical evidence.
Benefits of Pursuing Exploration
Pursuing exploration drives innovation by uncovering new knowledge and novel solutions that can differentiate businesses in competitive markets. It enables organizations to adapt to changing environments and identify emerging opportunities before competitors. Exploration fosters creativity and strategic flexibility, critical for long-term growth and sustainability.
Strengths of Emphasizing Replication
Emphasizing replication enhances the reliability and validity of scientific findings by confirming results across multiple studies and diverse contexts. It strengthens the evidence base, reducing the likelihood of false positives and increasing confidence in generalizability. Replication efforts also contribute to cumulative knowledge, facilitating the refinement of theories and methodologies in research fields.
Balancing Exploration and Replication in Research
Balancing exploration and replication in research ensures scientific progress through innovative discovery while validating existing knowledge. Exploration drives novel hypotheses and experimental designs, uncovering uncharted phenomena, whereas replication confirms reliability and generalizability of findings across diverse contexts. Strategic allocation of resources between these approaches optimizes research impact and fosters cumulative knowledge growth.
Challenges Faced in Exploration and Replication
Exploration faces challenges such as unpredictable outcomes, limited prior knowledge, and high resource consumption due to the need for innovation and discovery in uncharted areas. Replication struggles with reproducibility issues, variations in experimental conditions, and inconsistent data quality that hinder verifying original findings. Both exploration and replication require rigorous methodologies to address uncertainties and ensure reliable, scalable results in research and development.
Impact of Exploration and Replication on Innovation
Exploration drives breakthrough innovation by encouraging experimentation with novel ideas, technologies, and processes, creating new knowledge and opportunities for growth. Replication enhances innovation efficiency by refining successful innovations, ensuring reliability, and enabling scalable implementation across markets or industries. Balancing exploration and replication maximizes innovation impact, fostering both creative discovery and practical application.
Future Directions for Exploration and Replication
Future directions for exploration emphasize adaptive learning algorithms that dynamically adjust to new data patterns, enhancing model generalization and robustness. Replication efforts are increasingly focusing on standardized protocols and open data repositories to verify reproducibility across diverse contexts and datasets. Integrating these approaches will advance reliable innovation by balancing novel discovery with empirical validation.
Exploration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com