Antibiotics are powerful medications designed to fight bacterial infections by killing or inhibiting bacteria growth. Misuse or overuse of antibiotics can lead to resistance, making infections harder to treat. Learn how to use antibiotics effectively and protect your health by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
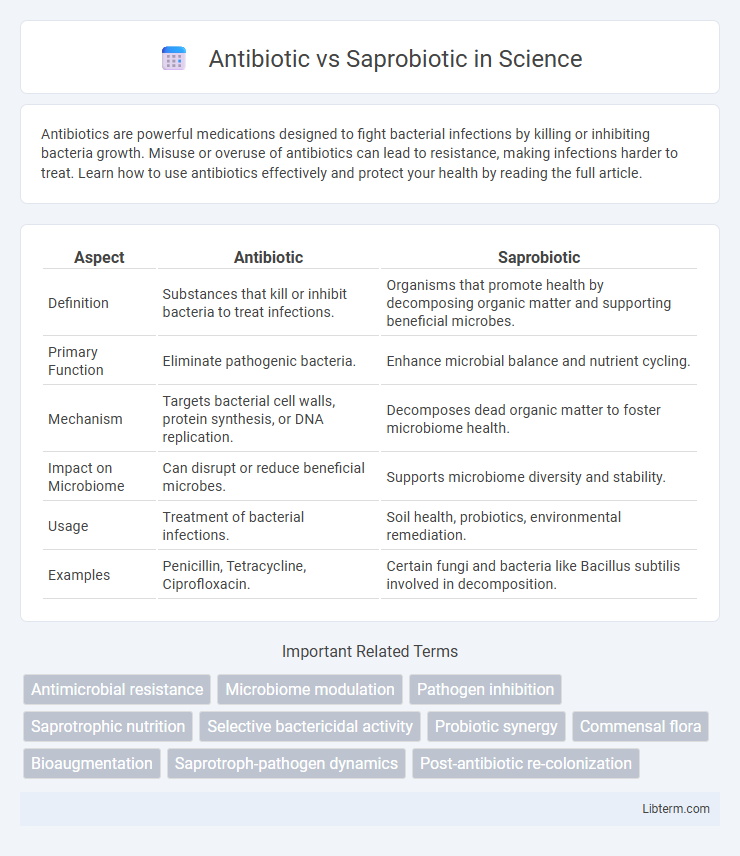
| Aspect | Antibiotic | Saprobiotic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Substances that kill or inhibit bacteria to treat infections. | Organisms that promote health by decomposing organic matter and supporting beneficial microbes. |
| Primary Function | Eliminate pathogenic bacteria. | Enhance microbial balance and nutrient cycling. |
| Mechanism | Targets bacterial cell walls, protein synthesis, or DNA replication. | Decomposes dead organic matter to foster microbiome health. |
| Impact on Microbiome | Can disrupt or reduce beneficial microbes. | Supports microbiome diversity and stability. |
| Usage | Treatment of bacterial infections. | Soil health, probiotics, environmental remediation. |
| Examples | Penicillin, Tetracycline, Ciprofloxacin. | Certain fungi and bacteria like Bacillus subtilis involved in decomposition. |
Understanding Antibiotics: Definition and Mechanism
Antibiotics are powerful antimicrobial agents designed to combat bacterial infections by targeting specific cellular functions such as cell wall synthesis, protein production, or DNA replication. These drugs selectively inhibit or kill pathogenic bacteria, disrupting their growth and reproduction processes. Unlike saprobiotics, which harness beneficial microbes for ecological balance, antibiotics focus on eradicating harmful bacterial strains to restore health.
What Are Saprobiotics? An Overview
Saprobiotics are beneficial microorganisms that help restore and maintain the natural balance of the gut microbiome by consuming harmful pathogens and supporting healthy bacteria growth. Unlike antibiotics, which broadly kill bacteria and can disrupt gut flora, saprobiotics promote a symbiotic environment essential for digestive health and immune function. These microbes enhance nutrient absorption and improve gut barrier integrity, providing a targeted approach to microbiome management.
Key Differences Between Antibiotics and Saprobiotics
Antibiotics are chemical substances that kill or inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria, targeting harmful microorganisms to treat infections. Saprobiotics, on the other hand, promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, enhancing gut microbiota balance and supporting digestive health. The key difference lies in their function: antibiotics eliminate harmful bacteria, whereas saprobiotics encourage beneficial bacteria proliferation for improved microbiome diversity.
Mode of Action: Antibiotics vs Saprobiotics
Antibiotics function by targeting and inhibiting essential bacterial processes such as cell wall synthesis, protein production, or DNA replication, leading to the death or growth suppression of pathogenic bacteria. Saprobiotics, in contrast, promote the growth of beneficial microbial communities by supplying substrates or creating an environment favorable to non-pathogenic microbes, thereby indirectly inhibiting harmful bacteria through competitive exclusion and microbial balance restoration. The mode of action of antibiotics is direct microbial killing or inhibition, whereas saprobiotics emphasize ecosystem modulation to enhance host microbiome health.
Benefits and Limitations of Antibiotics
Antibiotics effectively target and eliminate harmful bacterial infections, providing rapid relief and preventing the spread of disease; however, their overuse can lead to antibiotic resistance, reducing efficacy and complicating treatment. They do not differentiate between beneficial and harmful bacteria, potentially disrupting the microbiome and causing side effects such as gastrointestinal issues. Despite limitations, antibiotics remain critical in managing bacterial infections but require prudent use to maintain their long-term benefits.
Health Advantages of Saprobiotics
Saprobiotics promote gut health by enhancing the beneficial microbiota without causing antibiotic resistance, unlike antibiotics that can disrupt microbial balance and lead to resistant strains. These organisms support immune function and improve nutrient absorption, contributing to overall well-being. Saprobiotics offer a sustainable approach to maintaining health through natural microbial synergy, reducing the risk of side effects associated with antibiotic use.
Impact on Gut Microbiome: Comparative Analysis
Antibiotics disrupt the gut microbiome by indiscriminately killing both harmful and beneficial bacteria, leading to reduced microbial diversity and potential dysbiosis. In contrast, saprobiotics support gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria through nutrient provision and competitive exclusion of pathogens. Comparative studies reveal that while antibiotics can cause short- and long-term microbiome imbalance, saprobiotics enhance microbial resilience and diversity, fostering a more stable gut ecosystem.
Safety and Side Effects: What to Consider
Antibiotics, designed to eliminate harmful bacteria, often carry risks such as gastrointestinal issues, allergic reactions, and antibiotic resistance due to their broad-spectrum action. Saprobiotics, which support beneficial microbial balance, generally present fewer side effects and are considered safer for long-term use, enhancing immune function and gut health. When choosing between antibiotics and saprobiotics, it is crucial to evaluate the severity of infection, potential adverse reactions, and the impact on microbiome diversity to ensure optimal safety and therapeutic outcomes.
Applications in Modern Medicine
Antibiotics play a critical role in modern medicine by targeting bacterial infections through the inhibition of cell wall synthesis, protein production, or DNA replication, thereby effectively treating conditions such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, and sepsis. Saprobiotics, leveraging beneficial non-pathogenic microorganisms, are increasingly applied in gut microbiota restoration therapies, enhancing immune function and preventing dysbiosis-related diseases like inflammatory bowel syndrome and antibiotic-associated diarrhea. The complementary use of antibiotics and saprobiotics optimizes patient outcomes by combining pathogen eradication with microbiome support, reducing the risk of secondary infections and promoting faster recovery.
Future Trends: Integrating Antibiotics and Saprobiotics
Future trends in healthcare emphasize integrating antibiotics and saprobiotics to enhance treatment efficacy and reduce antibiotic resistance. Combining targeted antibiotics with saprobiotics can restore and maintain healthy microbiomes, promoting overall patient recovery. Research continues to explore optimized dosing and synergistic effects to balance pathogen elimination with beneficial microbiota support.
Antibiotic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com