Understanding irregular patterns is crucial for mastering language nuances and avoiding common mistakes. Irregular verbs and forms often deviate from standard rules, making them challenging but essential for fluent communication. Discover how to master these exceptions and improve your language skills by reading the full article.
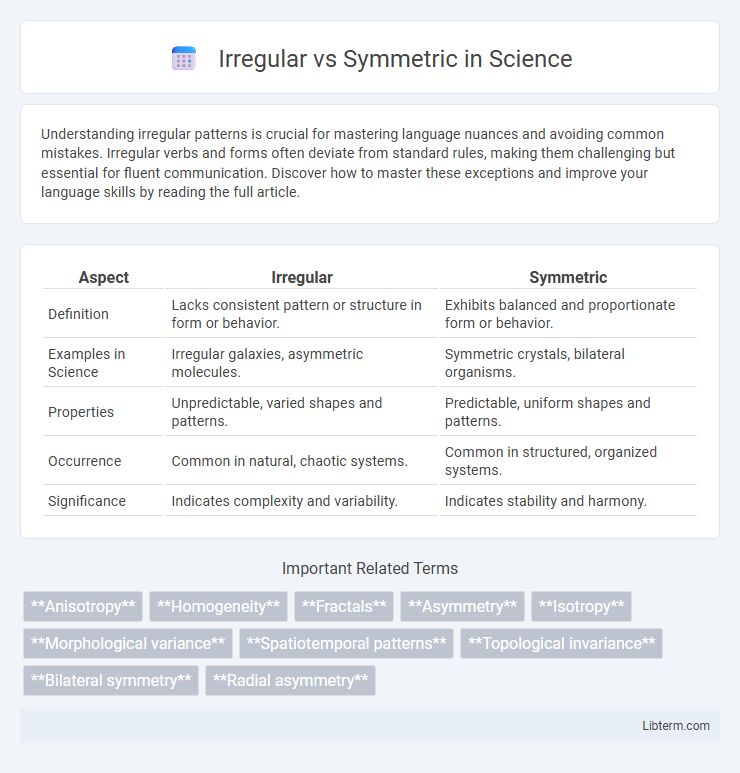
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Irregular | Symmetric |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lacks consistent pattern or structure in form or behavior. | Exhibits balanced and proportionate form or behavior. |
| Examples in Science | Irregular galaxies, asymmetric molecules. | Symmetric crystals, bilateral organisms. |
| Properties | Unpredictable, varied shapes and patterns. | Predictable, uniform shapes and patterns. |
| Occurrence | Common in natural, chaotic systems. | Common in structured, organized systems. |
| Significance | Indicates complexity and variability. | Indicates stability and harmony. |
Introduction to Irregular and Symmetric Structures
Irregular structures deviate from conventional geometric patterns, featuring unpredictable shapes and varying component arrangements, impacting their load distribution and stability. Symmetric structures exhibit balanced and mirror-image configurations, promoting uniform stress distribution and ease of analysis in engineering design. Understanding the fundamental differences between irregular and symmetric structures guides effective architectural planning and structural integrity assessment.
Defining Irregular Structures
Irregular structures are characterized by non-uniform shapes, unpredictable load paths, and asymmetric configurations that challenge traditional design methods. These structures often exhibit discontinuities or complex geometries that lead to uneven stress distribution and require advanced analytical techniques for accurate assessment. Understanding the irregularity is crucial for ensuring structural stability, especially in seismic zones where dynamic responses differ significantly from symmetric counterparts.
Understanding Symmetric Structures
Symmetric structures exhibit balanced and identical components on either side of a central axis, optimizing stability and load distribution in engineering and design. Understanding symmetric structures involves analyzing their uniform geometry, which simplifies stress analysis and enhances predictability under various forces. This inherent predictability allows for efficient material usage and easier construction compared to irregular structures that lack uniformity and consistent stress patterns.
Key Differences Between Irregular and Symmetric
Irregular shapes feature uneven sides and angles, lacking uniformity in length and symmetry, while symmetric shapes exhibit balanced proportions with equal parts mirrored across an axis. Key differences include predictability in measurement, where symmetric forms allow easier calculation due to their repetitive patterns, contrasting with irregular shapes that require individual assessment for each side and angle. The distinction impacts fields like design and geometry, influencing visual harmony and structural analysis based on symmetry or its absence.
Advantages of Symmetric Structures
Symmetric structures offer enhanced stability and uniform load distribution, reducing the likelihood of uneven stress and structural failures. Their predictable design simplifies construction processes and maintenance, leading to cost-effectiveness and increased reliability over time. These advantages make symmetric structures ideal for projects demanding durability and consistent performance.
Drawbacks of Irregular Structures
Irregular structures often suffer from unpredictable load distribution, leading to increased stress concentrations and potential structural failures. Their complex geometry complicates design, analysis, and construction processes, resulting in higher costs and longer project timelines. Maintenance and retrofitting are also more challenging compared to symmetric structures, which offer uniform behavior under loads and simplified engineering solutions.
Applications of Irregular vs Symmetric Designs
Irregular designs excel in applications requiring adaptability and custom fit, such as ergonomic products and architectural structures with unique spatial constraints. Symmetric designs dominate in fields demanding uniformity and balance, including aerospace engineering and optical systems, where consistent performance and structural integrity are critical. Understanding the distinct applications of irregular versus symmetric designs enables optimized solutions tailored to specific functional and aesthetic requirements.
Structural Performance Comparison
Irregular structures often exhibit complex load paths and stress concentrations that challenge stability and seismic performance, whereas symmetric structures provide uniform load distribution and enhanced structural integrity. Seismic response analysis indicates symmetric buildings have predictable deformation patterns, reducing torsional effects and potential failure points. Structural performance metrics show symmetric designs typically achieve higher resilience and lower maintenance costs compared to irregular configurations under dynamic loads.
Choosing Between Irregular and Symmetric Approaches
Choosing between irregular and symmetric approaches depends on the specific application requirements and data characteristics. Irregular methods offer flexibility and adaptability for handling unstructured data or complex geometries, while symmetric approaches provide consistency and efficiency in processing uniform and balanced datasets. Evaluating factors such as computational cost, data distribution, and desired accuracy is essential for selecting the optimal approach.
Conclusion: Irregular vs Symmetric
Irregular structures exhibit unpredictability and lack uniform patterns, leading to complex analysis and adaptation challenges in fields like linguistics and architecture. Symmetric structures, characterized by balanced and repetitive elements, enable easier recognition and efficient processing due to predictable patterns. Choosing between irregular and symmetric designs depends on the desired functionality, aesthetic preference, and contextual requirements, with symmetry favoring harmony and irregularity promoting uniqueness.
Irregular Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com