Transpiration is the process by which plants release water vapor from their leaves into the atmosphere, playing a crucial role in the water cycle and maintaining plant health. This natural mechanism helps regulate temperature, supports nutrient uptake, and contributes to humidity levels in the environment. Discover how understanding transpiration can enhance your knowledge of plant biology and ecosystem dynamics by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
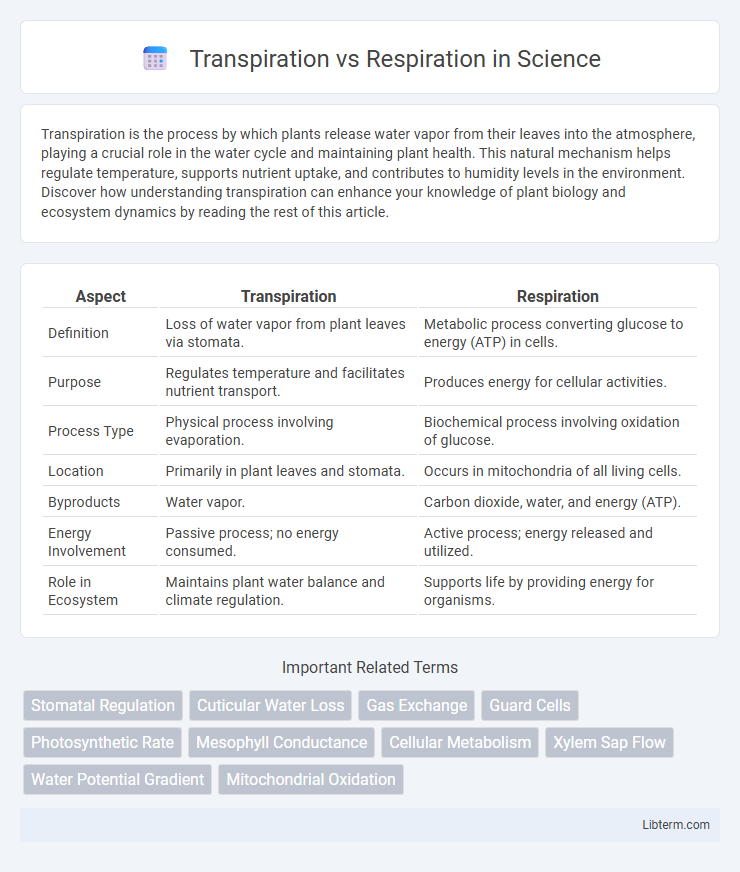
| Aspect | Transpiration | Respiration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Loss of water vapor from plant leaves via stomata. | Metabolic process converting glucose to energy (ATP) in cells. |
| Purpose | Regulates temperature and facilitates nutrient transport. | Produces energy for cellular activities. |
| Process Type | Physical process involving evaporation. | Biochemical process involving oxidation of glucose. |
| Location | Primarily in plant leaves and stomata. | Occurs in mitochondria of all living cells. |
| Byproducts | Water vapor. | Carbon dioxide, water, and energy (ATP). |
| Energy Involvement | Passive process; no energy consumed. | Active process; energy released and utilized. |
| Role in Ecosystem | Maintains plant water balance and climate regulation. | Supports life by providing energy for organisms. |
Introduction to Transpiration and Respiration
Transpiration is the process by which plants lose water vapor through stomata, playing a crucial role in nutrient uptake and temperature regulation. Respiration refers to the cellular process where glucose and oxygen are converted into energy, carbon dioxide, and water, essential for plant metabolism and growth. Both processes are fundamental for plant survival, affecting physiological functions and overall health.
Definitions: What is Transpiration?
Transpiration is the process by which plants lose water vapor through small openings called stomata, primarily on the leaves, facilitating nutrient uptake and temperature regulation. This biological mechanism drives the movement of water from roots to leaves, sustaining plant hydration and photosynthesis. Distinct from respiration, transpiration involves water vapor exchange rather than gas exchange for energy production.
Definitions: What is Respiration?
Respiration is a biochemical process in which cells convert glucose and oxygen into energy in the form of ATP, releasing carbon dioxide and water as byproducts. This vital metabolic function supports cellular activities necessary for growth, repair, and maintenance. Unlike transpiration, which involves water loss through plant leaves, respiration focuses on energy production at the cellular level.
Key Processes Involved in Transpiration
Transpiration primarily involves the evaporation of water from plant leaves through stomata, driven by water potential gradients and environmental factors such as temperature and humidity. The key processes include water uptake by roots, its movement through the xylem, and subsequent evaporation from mesophyll cells into the leaf air spaces. This process facilitates nutrient transport, maintains turgor pressure, and regulates leaf temperature, distinguishing it clearly from cellular respiration, which is focused on energy production within mitochondria.
Key Processes Involved in Respiration
Respiration involves key processes such as glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, which collectively convert glucose into usable energy in the form of ATP. Glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvate, while the citric acid cycle processes pyruvate into carbon dioxide and high-energy electron carriers. Oxidative phosphorylation uses these carriers to generate a significant amount of ATP through electron transport and chemiosmosis, distinguishing respiration from transpiration, which primarily involves water vapor loss through plant stomata.
Differences Between Transpiration and Respiration
Transpiration is the process by which plants lose water vapor through stomata primarily for cooling and nutrient transport, whereas respiration involves the breakdown of glucose to release energy for cellular activities. Transpiration mainly occurs in leaves and stems, while respiration happens in all living plant cells. The key difference lies in their purpose: transpiration regulates water balance, whereas respiration provides metabolic energy.
Importance of Transpiration in Plants
Transpiration plays a crucial role in plants by facilitating nutrient transport and regulating temperature through water evaporation from leaf surfaces. This process maintains turgor pressure, ensuring cell rigidity and supporting structural integrity. Unlike respiration, which primarily generates energy by breaking down glucose, transpiration directly influences water movement and nutrient distribution essential for plant growth and survival.
Importance of Respiration in Plants
Respiration in plants is vital for converting glucose and oxygen into energy (ATP), which fuels cellular processes essential for growth, repair, and nutrient transport. Unlike transpiration, which mainly regulates water balance and temperature, respiration provides the biochemical energy needed for biosynthesis and metabolic activities. This continuous energy supply supports seed germination, root development, and overall plant vitality.
Factors Affecting Transpiration and Respiration
Transpiration is primarily influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and light intensity, which regulate the rate of water loss through stomata. Respiration rates depend on factors like temperature, oxygen availability, and substrate concentration, directly affecting the energy production in cells. Both processes respond dynamically to environmental conditions, but transpiration is more sensitive to atmospheric variables while respiration is closely tied to metabolic and cellular activity.
Summary: Transpiration vs Respiration
Transpiration is the process by which plants lose water vapor through stomata, primarily aiding in nutrient transport and temperature regulation. Respiration involves breaking down glucose molecules to produce energy (ATP) for cellular activities in both plants and animals. While transpiration is a physical water loss process crucial for plant health, respiration is a biochemical process essential for energy production and metabolism.
Transpiration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com