Induced processes harness deliberate actions to achieve specific outcomes, often utilized in medical or scientific contexts such as induced labor or induced pluripotent stem cells. Understanding the mechanisms behind induced phenomena can enhance your ability to predict and control these events effectively. Explore the full article to uncover the detailed applications and implications of induced processes.
Table of Comparison
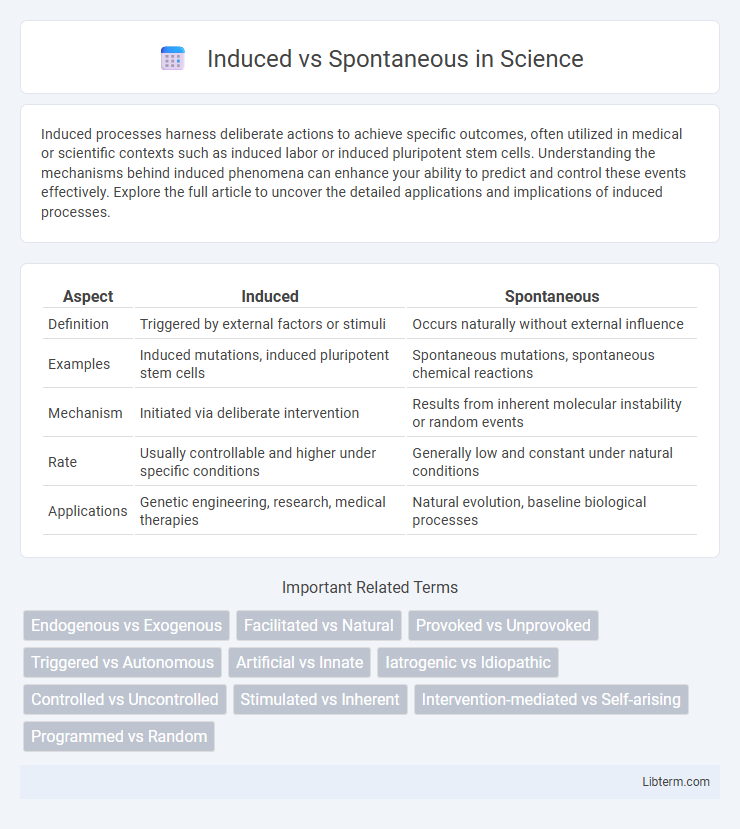
| Aspect | Induced | Spontaneous |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Triggered by external factors or stimuli | Occurs naturally without external influence |
| Examples | Induced mutations, induced pluripotent stem cells | Spontaneous mutations, spontaneous chemical reactions |
| Mechanism | Initiated via deliberate intervention | Results from inherent molecular instability or random events |
| Rate | Usually controllable and higher under specific conditions | Generally low and constant under natural conditions |
| Applications | Genetic engineering, research, medical therapies | Natural evolution, baseline biological processes |
Introduction to Induced vs Spontaneous
Induced processes are initiated by external stimuli or deliberate interventions, leading to a predictable and controlled outcome. Spontaneous processes occur naturally without external prompting, driven by inherent energy changes and entropy. Understanding the differences between induced and spontaneous phenomena is crucial in fields like chemistry, biology, and physics for predicting reaction behavior.
Defining Induced Events
Induced events are occurrences triggered by specific external factors or deliberate interventions, causing a change in the system or environment. These events contrast with spontaneous events, which arise naturally without external prompts. Defining induced events involves identifying the direct cause or agent initiating the event, such as mechanical forces, chemical reactions, or human actions.
Understanding Spontaneous Events
Spontaneous events occur naturally without external triggers, often driven by inherent system properties or random fluctuations. Understanding spontaneous events requires analyzing underlying thermodynamic conditions, such as entropy increase and energy distribution within a system. Recognizing these intrinsic factors helps differentiate spontaneous occurrences from induced events, which result from deliberate external interventions.
Key Differences Between Induced and Spontaneous
Induced processes occur due to an external trigger or influence, while spontaneous processes happen naturally without any outside intervention. Induced events often require specific conditions or stimuli to initiate, whereas spontaneous ones arise from inherent system properties or internal energy states. The key difference lies in the origin of the cause: induced is externally driven, spontaneous is internally driven.
Factors Influencing Induced Processes
Induced processes are primarily influenced by external stimuli such as environmental triggers, chemical agents, or physical factors that initiate a specific response. Factors like the intensity, duration, and nature of the inducing agent play a critical role in determining the outcome and efficiency of these processes. Cellular sensitivity and receptor availability further modulate the inducibility and kinetics of induced responses compared to spontaneous processes.
Factors Influencing Spontaneous Processes
Spontaneous processes occur naturally without external energy input, driven primarily by increases in entropy and favorable changes in Gibbs free energy (DG < 0). Temperature, pressure, and the inherent properties of reactants influence spontaneity, with higher entropy systems and lower Gibbs free energy states enhancing the likelihood of spontaneous reactions. Molecular stability, reaction environment, and thermodynamic parameters are critical factors determining whether a process proceeds spontaneously or requires induction.
Advantages of Induced Methods
Induced methods offer precise control over the timing and conditions of a response, enhancing predictability in experimental and industrial processes. These techniques enable reproducible outcomes, increasing efficiency and reducing variability compared to spontaneous methods. Induced approaches also allow targeted activation, improving specificity and minimizing unintended effects in biological, chemical, and physical applications.
Benefits of Spontaneous Methods
Spontaneous methods promote creativity and innovation by allowing ideas to flow naturally without constraints, fostering diverse and original solutions. These techniques enhance engagement and motivation as participants feel more freedom and ownership in the process, leading to higher satisfaction and better collaboration. Additionally, spontaneous approaches enable quicker problem identification and resolution, adapting flexibly to changing circumstances and reducing delays linked to structured protocols.
Risks and Considerations: Induced vs Spontaneous
Induced labor carries risks such as increased likelihood of uterine hyperstimulation, infection, and cesarean delivery, requiring careful monitoring of contractions and fetal well-being. Spontaneous labor generally presents fewer medical interventions, reducing risks linked to induction agents but may pose complications if labor prolongs excessively or fetal distress occurs. Both methods necessitate thorough assessment of maternal and fetal health to balance benefits and potential complications effectively.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Induced and Spontaneous
Choosing between induced and spontaneous labor depends on medical necessity, maternal health, and fetal well-being. Induced labor is often preferred when complications arise, such as preeclampsia or post-term pregnancy, ensuring timely delivery. Spontaneous labor is generally safer when no risks are present, promoting natural progression and reducing intervention-related complications.
Induced Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com