Activation is the crucial process of enabling a service, software, or product to function as intended, often involving entering a key or completing a verification step. Proper activation ensures access to all features, security protections, and ongoing updates that maintain optimal performance. Discover how activation impacts your experience and unlocks full potential by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
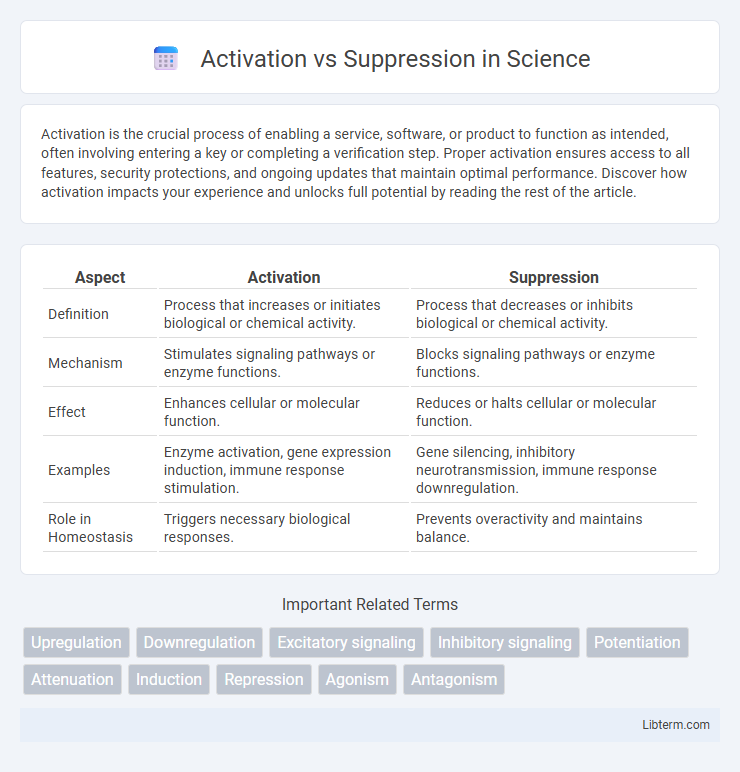
| Aspect | Activation | Suppression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process that increases or initiates biological or chemical activity. | Process that decreases or inhibits biological or chemical activity. |
| Mechanism | Stimulates signaling pathways or enzyme functions. | Blocks signaling pathways or enzyme functions. |
| Effect | Enhances cellular or molecular function. | Reduces or halts cellular or molecular function. |
| Examples | Enzyme activation, gene expression induction, immune response stimulation. | Gene silencing, inhibitory neurotransmission, immune response downregulation. |
| Role in Homeostasis | Triggers necessary biological responses. | Prevents overactivity and maintains balance. |
Introduction to Activation vs Suppression
Activation and suppression are fundamental mechanisms in neural and cognitive processes that regulate response patterns. Activation involves initiating or enhancing neural signals to promote specific behaviors or functions, while suppression inhibits or dampens these signals to prevent unwanted responses. Understanding the balance between activation and suppression is crucial for studying brain function, behavioral control, and various psychological disorders.
Defining Activation and Suppression
Activation refers to the process of initiating or increasing the activity of a biological system, such as gene expression, neural pathways, or immune responses, by specific stimuli or signals. Suppression involves the inhibition or downregulation of these activities to maintain homeostasis or prevent overactivity, commonly seen in immune regulation or gene expression control. Both mechanisms are critical for balanced physiological function and adaptive responses in organisms.
Psychological Foundations of Activation
Activation in psychology refers to the process by which certain stimuli or internal cues trigger neural and behavioral responses, facilitating goal-directed behavior and emotional arousal. The psychological foundations of activation involve mechanisms such as the brain's reticular activating system, which regulates wakefulness and attention, and the limbic system, which modulates motivation and emotional responses. Understanding activation is crucial for exploring how individuals initiate actions, maintain focus, and exhibit readiness in both cognitive and physiological contexts.
Mechanisms of Suppression in Human Behavior
Mechanisms of suppression in human behavior primarily involve the inhibition of automatic or unwanted responses through cognitive control processes located in the prefrontal cortex. Neural circuits modulate emotional and impulse-related responses to prevent maladaptive actions, engaging areas such as the anterior cingulate cortex to monitor conflict and regulate suppression efficacy. Suppression also relies on top-down control to override subcortical activation, shaping behavior by decreasing the salience of distracting or harmful stimuli.
Activation vs Suppression in Decision-Making
Activation in decision-making involves engaging relevant neural circuits and cognitive processes to initiate and execute choices efficiently. Suppression, on the other hand, refers to the inhibition of competing impulses, distractions, or inappropriate responses to maintain focus on goal-directed behaviors. Balancing activation and suppression is critical for adaptive decision-making, as it allows for the selection of optimal options while avoiding cognitive overload and impulsive errors.
Impact on Emotional Regulation
Activation enhances emotional regulation by stimulating brain regions such as the prefrontal cortex, which improves cognitive control over emotional responses. Suppression, conversely, often leads to increased physiological stress and decreased prefrontal activity, impairing the ability to manage emotions effectively. Studies show that activation strategies correlate with reduced negative affect and better psychological well-being compared to suppression, which is linked to heightened anxiety and depressive symptoms.
Activation and Suppression in Learning and Memory
Activation and suppression in learning and memory involve distinct neural mechanisms that regulate information processing and retention. Activation enhances synaptic connections and neural circuitry, facilitating the encoding and retrieval of memories, whereas suppression inhibits irrelevant or interfering information to improve focus and prevent cognitive overload. Effective learning depends on the dynamic balance between these processes, optimizing memory consolidation and adaptive behavior.
Social Implications of Activation and Suppression
Activation in social contexts often leads to increased collective action, fostering community engagement and empowerment through shared goals and mobilization. Suppression, conversely, can result in social fragmentation, marginalization, and decreased public participation, frequently exacerbating inequality and limiting diverse voices. These dynamics critically influence social cohesion, political representation, and the capacity for societal change.
Strategies to Balance Activation and Suppression
Effective strategies to balance activation and suppression involve targeted cognitive-behavioral techniques that enhance neural activation while controlling inhibitory processes. Incorporating mindfulness practices can improve attentional control, fostering selective activation of relevant neural pathways and reducing excessive suppression. Utilizing neurofeedback and adaptive training protocols further optimizes this balance by modulating cortical excitability and inhibitory neurotransmission.
Conclusion: Integrating Activation and Suppression
Integrating activation and suppression mechanisms enhances cognitive flexibility and emotional regulation by balancing neural excitation and inhibition. Effective coordination between these processes supports adaptive responses to environmental demands and improves decision-making accuracy. Advancements in neuroscience suggest that targeting both activation and suppression pathways offers promising interventions for neuropsychiatric disorders.
Activation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com