Arbitrary decisions often lack a clear rationale, leading to unpredictability and inconsistency in outcomes. Understanding the implications of arbitrary choices can help you recognize when they affect your daily life or work environment. Explore the rest of this article to learn how to identify and manage arbitrary actions effectively.
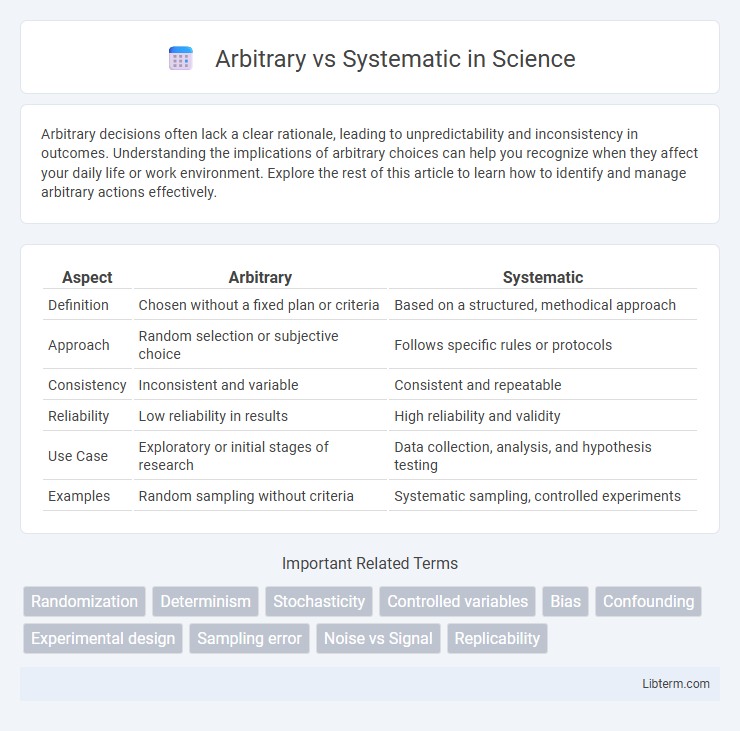
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Arbitrary | Systematic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chosen without a fixed plan or criteria | Based on a structured, methodical approach |
| Approach | Random selection or subjective choice | Follows specific rules or protocols |
| Consistency | Inconsistent and variable | Consistent and repeatable |
| Reliability | Low reliability in results | High reliability and validity |
| Use Case | Exploratory or initial stages of research | Data collection, analysis, and hypothesis testing |
| Examples | Random sampling without criteria | Systematic sampling, controlled experiments |
Understanding Arbitrary and Systematic Approaches
Arbitrary approaches rely on random or subjective choices without a structured plan, often leading to inconsistent or unpredictable results. Systematic approaches follow a defined, methodical process based on clear rules and criteria, ensuring repeatability and reliability in outcomes. Understanding the distinction between these approaches is crucial for improving decision-making quality and optimizing problem-solving efficiency.
Defining Arbitrary: Key Characteristics
Arbitrary decisions are characterized by a lack of consistent criteria, relying on random choice or personal whim rather than a structured method. These decisions often lack predictability and are influenced by subjective preferences instead of objective standards. This unpredictability contrasts sharply with systematic approaches that follow defined rules and logical procedures.
What Makes a Systematic Method?
A systematic method is characterized by a structured, repeatable approach that follows clearly defined procedures or rules to ensure consistency and reliability in results. It relies on thorough planning, documentation, and analysis, often incorporating standardized tools or frameworks to minimize bias and enhance accuracy. This method contrasts with arbitrary approaches by emphasizing rational decision-making grounded in evidence and logical sequencing.
Differences Between Arbitrary and Systematic Processes
Arbitrary processes rely on random or subjective choices without consistent rules, leading to unpredictable outcomes, whereas systematic processes follow structured, methodical steps designed for repeatability and predictability. In systematic processes, each action is guided by specific criteria or algorithms, ensuring consistency and reliability across iterations. The key difference lies in the presence of order and logic in systematic processes versus the lack of predefined structure in arbitrary ones.
Advantages of Systematic Approaches
Systematic approaches offer advantages such as enhanced consistency and reliability by following structured, repeatable procedures that minimize errors and biases. These methods facilitate comprehensive data analysis, leading to more accurate and objective conclusions compared to arbitrary techniques. By implementing clearly defined criteria, systematic approaches improve transparency and reproducibility in research and decision-making processes.
Risks Associated with Arbitrary Decisions
Arbitrary decisions often lead to increased risks such as inconsistent outcomes, lack of accountability, and diminished trust from stakeholders due to the absence of standardized criteria. Systematic decision-making frameworks mitigate these risks by applying data-driven analysis, clear protocols, and repeatable processes that enhance predictability and transparency. Organizations employing systematic strategies reduce legal liabilities and operational errors compared to those relying on arbitrary judgments.
Real-World Examples: Arbitrary vs Systematic
Arbitrary decisions often arise in scenarios like random lottery selections, where outcomes lack predictable patterns or rules, contrasting with systematic approaches such as quality control in manufacturing that rely on structured procedures and data analysis. In real-world examples, arbitrary methods may lead to inconsistent results, while systematic strategies enhance reliability and efficiency across processes like inventory management and clinical trials. Businesses leveraging systematic frameworks can better forecast trends and optimize operations, whereas arbitrary choices might introduce unpredictability and risk.
When to Use Systematic Methods
Systematic methods are ideal when consistency, replicability, and thorough coverage are critical in research or data collection, especially in fields like clinical trials, qualitative studies, and inventory audits. These methods ensure minimal bias by following predefined protocols and structured procedures, making them suitable for large datasets or complex experimental designs. Employing systematic approaches enhances precision and reliability, facilitating accurate pattern identification and informed decision-making.
Impact of Arbitrary Choices in Business and Science
Arbitrary choices in business and science can lead to inconsistent outcomes, reduced reproducibility, and loss of stakeholder trust, as they lack a rational basis or clear criteria. In contrast, systematic decision-making, grounded in data and standardized methodologies, enhances reliability, predictability, and efficiency across processes and research. The impact of arbitrary decisions often manifests as increased risk, resource misallocation, and obstacles to scaling or scientific validation.
Moving from Arbitrary to Systematic: Best Practices
Moving from arbitrary to systematic approaches enhances consistency and efficiency by implementing standardized processes and clear guidelines. Best practices include defining repeatable workflows, leveraging data-driven decision-making, and regularly auditing procedures to identify gaps and improvements. Emphasizing documentation and employee training ensures alignment and sustained execution of systematic methods across teams.
Arbitrary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com