Encapsulation is a fundamental principle of object-oriented programming that restricts direct access to an object's internal state, ensuring data integrity and security. By bundling related variables and methods within a class, it promotes modularity and simplifies maintenance. Explore the rest of the article to learn how encapsulation can enhance your software design and development practices.
Table of Comparison
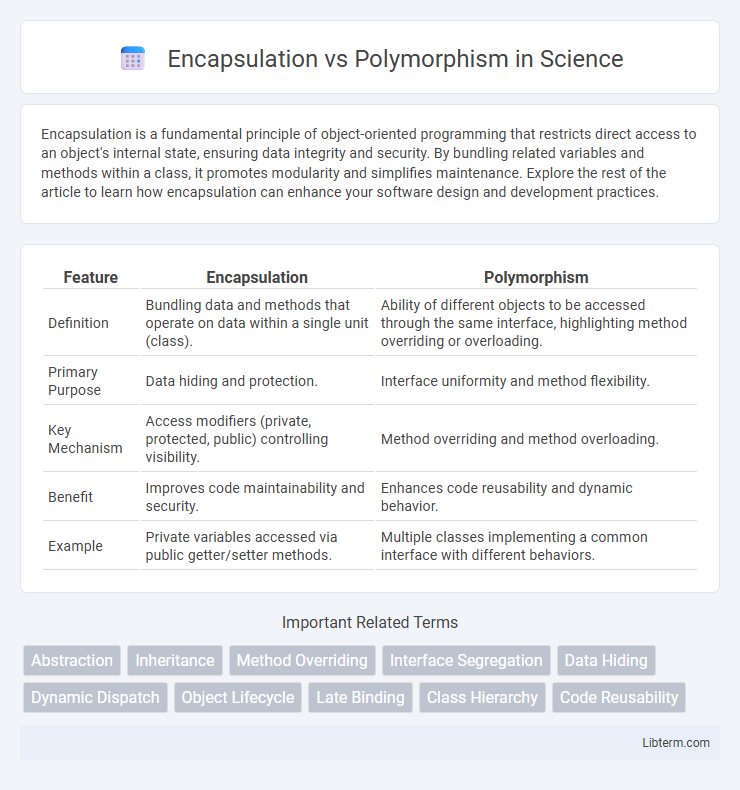
| Feature | Encapsulation | Polymorphism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bundling data and methods that operate on data within a single unit (class). | Ability of different objects to be accessed through the same interface, highlighting method overriding or overloading. |
| Primary Purpose | Data hiding and protection. | Interface uniformity and method flexibility. |
| Key Mechanism | Access modifiers (private, protected, public) controlling visibility. | Method overriding and method overloading. |
| Benefit | Improves code maintainability and security. | Enhances code reusability and dynamic behavior. |
| Example | Private variables accessed via public getter/setter methods. | Multiple classes implementing a common interface with different behaviors. |
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Concepts
Encapsulation is the object-oriented programming principle that restricts access to an object's internal state by bundling data with methods that manipulate it, ensuring data integrity and security. Polymorphism allows objects of different classes to be treated as instances of the same class through a shared interface, enabling method overriding and dynamic method dispatch. Both concepts are fundamental for designing flexible, maintainable, and modular software systems in languages like Java, C++, and Python.
Defining Encapsulation in Programming
Encapsulation in programming refers to the technique of bundling data and methods that operate on the data within a single unit, such as a class, to restrict direct access to some of an object's components. This concept promotes data hiding by using access modifiers like private, protected, and public, ensuring controlled interaction with object properties and methods. Encapsulation enhances code maintainability, security, and modularity by preventing unauthorized manipulation and exposing only necessary functionalities.
Key Features of Encapsulation
Encapsulation involves bundling data and methods within a single unit, restricting direct access to some of an object's components to safeguard data integrity and enhance security. Key features include data hiding, which prevents external code from manipulating internal object states, and controlled access via getter and setter methods that enforce validation and maintain consistent object behavior. This contrasts with polymorphism, which centers on the ability of different object types to be accessed through the same interface, enabling method overriding and dynamic method binding.
Understanding Polymorphism in OOP
Polymorphism in object-oriented programming (OOP) enables objects of different classes to be treated as instances of a common superclass, primarily through method overriding and interface implementation. This concept allows for dynamic method binding, where the appropriate method is selected at runtime based on the object's actual class, enhancing code flexibility and scalability. Encapsulation, on the other hand, restricts access to an object's data, maintaining integrity by exposing only necessary components, but it does not directly enable the dynamic behavior central to polymorphism.
Types of Polymorphism Explained
Polymorphism is classified into two primary types: compile-time polymorphism and runtime polymorphism. Compile-time polymorphism, also known as method overloading, allows multiple methods in the same class to have the same name but different parameters, enhancing code readability and reusability. Runtime polymorphism, or method overriding, involves a subclass providing a specific implementation of a method already defined in its superclass, enabling dynamic method dispatch and flexible program behavior during execution.
Encapsulation vs Polymorphism: Core Differences
Encapsulation involves bundling data and methods within a class, restricting direct access to some of the object's components to ensure data integrity and maintain control over how data is modified. Polymorphism allows objects of different classes to be treated as instances of the same class through a common interface, enabling methods to behave differently based on the object's actual class. The core difference lies in encapsulation focusing on data protection and hiding, while polymorphism emphasizes method overriding and dynamic method dispatch for flexible and reusable code.
Benefits of Encapsulation in Software Design
Encapsulation in software design enhances modularity by restricting access to an object's internal state and exposing only necessary components, which reduces system complexity and increases maintainability. It improves security by preventing unauthorized access and modification of data, ensuring integrity throughout the software lifecycle. This separation of concerns facilitates easier debugging, testing, and future enhancements while promoting a clear and structured code architecture.
Advantages of Polymorphism in Code Reusability
Polymorphism enhances code reusability by allowing objects of different classes to be treated through a common interface, enabling the same method to operate differently based on the object's actual type. This dynamic method dispatch reduces code duplication and promotes flexibility, making it easier to extend applications without modifying existing code. By supporting method overriding and overloading, polymorphism streamlines the integration of new functionalities, leading to more maintainable and scalable software designs.
Real-World Examples: Encapsulation and Polymorphism
Encapsulation is demonstrated in a banking system where account details are hidden within classes, allowing only authorized methods to access or modify account balances, enhancing data security and integrity. Polymorphism appears in smartphone applications where a single interface, such as a "play" command, works differently across audio, video, and game apps, enabling diverse functionality through a common method. These real-world examples highlight encapsulation's role in protecting data and polymorphism's power in creating flexible, reusable code systems.
Choosing Between Encapsulation and Polymorphism
Choosing between encapsulation and polymorphism depends on the design goals of a software system. Encapsulation emphasizes data hiding and protecting object integrity by restricting access to internal states through methods, enhancing security and modularity. Polymorphism enables objects to be treated as instances of their parent class, promoting flexibility and scalability by allowing multiple implementations through a common interface.
Encapsulation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com