Quantitative analysis focuses on measurable data and statistical methods to evaluate trends, patterns, and relationships in various fields such as finance, marketing, and research. It provides objective insights through numerical evidence, enabling informed decision-making based on empirical results. Discover how quantitative techniques can enhance your understanding by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
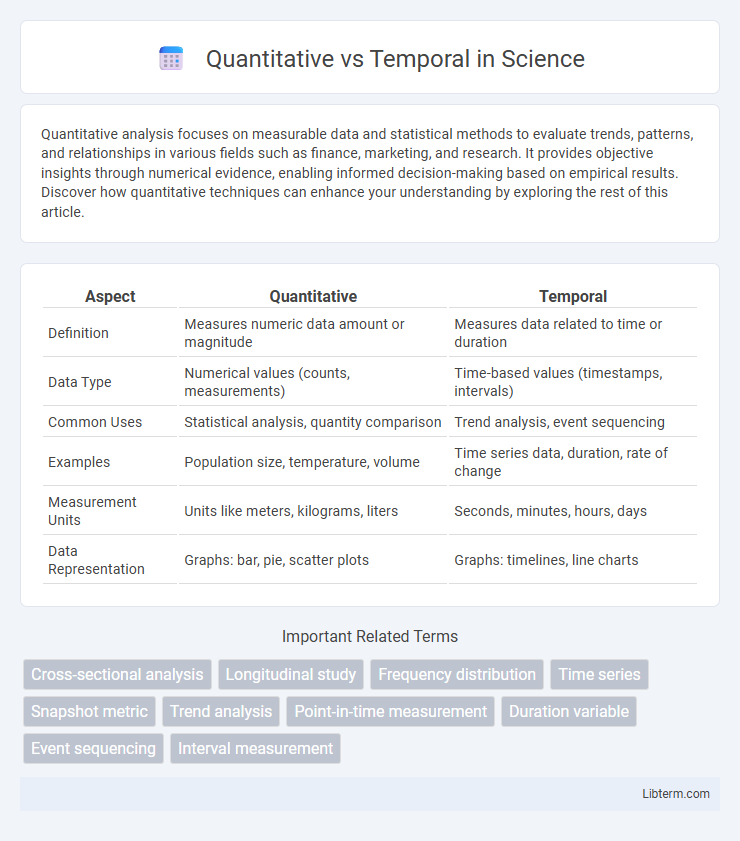
| Aspect | Quantitative | Temporal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures numeric data amount or magnitude | Measures data related to time or duration |
| Data Type | Numerical values (counts, measurements) | Time-based values (timestamps, intervals) |
| Common Uses | Statistical analysis, quantity comparison | Trend analysis, event sequencing |
| Examples | Population size, temperature, volume | Time series data, duration, rate of change |
| Measurement Units | Units like meters, kilograms, liters | Seconds, minutes, hours, days |
| Data Representation | Graphs: bar, pie, scatter plots | Graphs: timelines, line charts |
Introduction: Understanding Quantitative and Temporal
Quantitative data measures numerical values such as quantities, frequencies, and magnitudes, providing precise metrics for analysis. Temporal data captures information related to time, including sequences, durations, and chronological events, enabling the study of trends and patterns over periods. Understanding the distinction between quantitative and temporal data is essential for selecting appropriate analytical methods in fields like data science, economics, and healthcare.
Defining Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis involves the systematic examination of measurable data using statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques to identify patterns and relationships. It emphasizes numerical measurement and objective metrics, such as frequency, volume, or magnitude, to support decision-making processes. This approach contrasts with temporal analysis, which focuses on changes and trends over time rather than static numerical values.
Exploring Temporal Analysis
Temporal analysis examines data changes over specific time intervals to uncover patterns, trends, and seasonal effects critical for forecasting and decision-making. It leverages time-series data techniques such as moving averages, autocorrelation, and time decomposition to identify temporal dependencies and anomalies. This approach enables businesses to optimize operations by understanding fluctuations in customer behavior, sales cycles, and resource utilization across different temporal scales.
Core Differences: Quantitative vs Temporal
Quantitative data measures numerical values and quantities, such as sales figures, population counts, or temperature readings, enabling statistical analysis and precise calculations. Temporal data captures time-based information, detailing when events occur or how they evolve over intervals, essential for trend analysis, forecasting, and time series modeling. The core difference lies in quantitative data representing measurable amounts, while temporal data emphasizes the timing and sequence of occurrences.
Applications in Data Science
Quantitative data, consisting of numerical values such as sales figures, sensor readings, or survey scores, enables precise statistical analysis and predictive modeling in data science applications. Temporal data, representing time-stamped information like timestamps, event sequences, or time-series data, is essential for trend analysis, forecasting, and anomaly detection across various domains. Integrating quantitative and temporal data facilitates comprehensive insights in fields including finance, healthcare, and IoT, enhancing decision-making and operational efficiency.
Benefits of Quantitative Approaches
Quantitative approaches provide precise measurement and statistical analysis, enabling data-driven decision-making across industries such as finance, healthcare, and marketing. These methods facilitate the identification of patterns and trends through large datasets, ensuring replicable results and minimizing subjectivity. By leveraging quantitative data, organizations improve forecasting accuracy and operational efficiency, supporting scalability and strategic planning.
Advantages of Temporal Perspectives
Temporal perspectives in data analysis offer the advantage of capturing trends and patterns over time, enabling dynamic decision-making and forecasting. They allow businesses to identify seasonality, detect anomalies, and understand the evolution of key performance indicators. This time-based insight provides a deeper contextual understanding compared to purely quantitative snapshots, enhancing strategic planning and operational efficiency.
Common Challenges and Limitations
Quantitative and temporal analyses often face challenges such as data accuracy, measurement errors, and the complexity of integrating diverse datasets. Quantitative methods may struggle with capturing contextual nuances, while temporal analysis encounters limitations in identifying causality over time and handling irregular time intervals. Both approaches require careful consideration of data quality, appropriate modeling techniques, and potential biases to ensure reliable and meaningful results.
Integrating Quantitative and Temporal Methods
Integrating quantitative and temporal methods enables the comprehensive analysis of data by combining numerical measurement with time-based patterns, enhancing predictive accuracy in fields like epidemiology and finance. Quantitative methods provide statistical rigor through metrics and models, while temporal approaches track changes and trends over specific periods, facilitating dynamic insights and real-time decision-making. This integration supports advanced data analytics, machine learning algorithms, and longitudinal studies, driving innovation in temporal data mining and time series forecasting.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Choosing between quantitative and temporal data analysis depends on the specific objectives and nature of the project; quantitative methods excel in measuring and comparing numerical data for statistical accuracy, while temporal analysis provides critical insights into patterns and trends over time. Integrating both approaches can enhance understanding by combining precise quantification with dynamic temporal context. Prioritizing the appropriate method ensures more effective decision-making and targeted outcomes in data-driven environments.
Quantitative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com