Cultural pluralism celebrates the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a unified society, promoting mutual respect and understanding among different groups. It encourages the preservation of unique traditions while fostering inclusive social environments where everyone feels valued. Explore the rest of the article to discover how cultural pluralism can enrich Your community and personal growth.
Table of Comparison
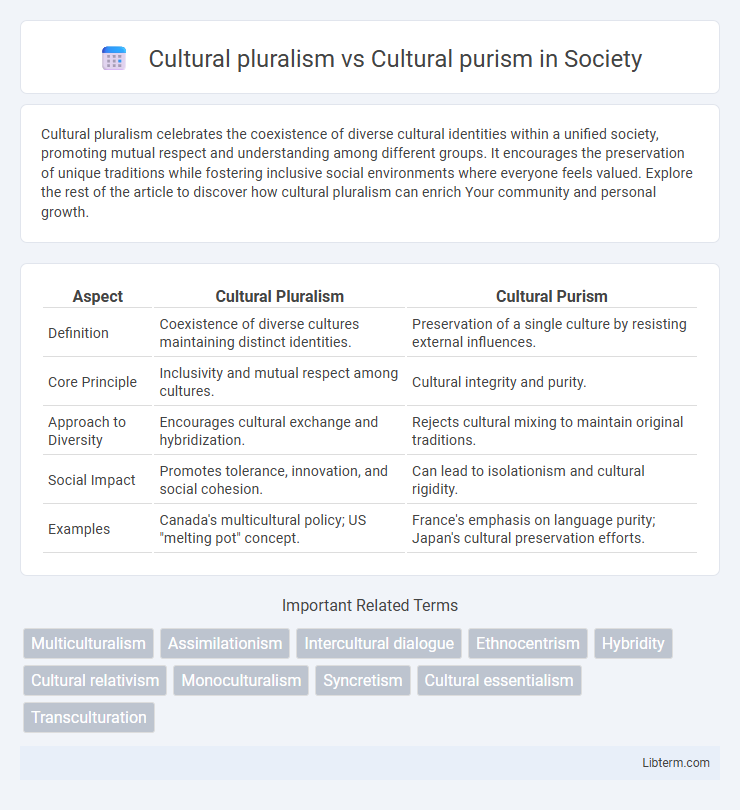
| Aspect | Cultural Pluralism | Cultural Purism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coexistence of diverse cultures maintaining distinct identities. | Preservation of a single culture by resisting external influences. |
| Core Principle | Inclusivity and mutual respect among cultures. | Cultural integrity and purity. |
| Approach to Diversity | Encourages cultural exchange and hybridization. | Rejects cultural mixing to maintain original traditions. |
| Social Impact | Promotes tolerance, innovation, and social cohesion. | Can lead to isolationism and cultural rigidity. |
| Examples | Canada's multicultural policy; US "melting pot" concept. | France's emphasis on language purity; Japan's cultural preservation efforts. |
Defining Cultural Pluralism and Cultural Purism
Cultural pluralism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural groups within a society, emphasizing mutual respect and the equal value of different traditions, languages, and customs. Cultural purism advocates for the preservation of a singular, dominant culture, often resisting influences from other cultures to maintain perceived cultural purity. These contrasting ideologies shape societal approaches to multiculturalism, integration, and identity politics, impacting policies on immigration, education, and social cohesion.
Historical Roots of Cultural Ideologies
Cultural pluralism traces its historical roots to the Enlightenment and the rise of liberal democracies, emphasizing coexistence and mutual respect among diverse cultural groups within a society. Cultural purism, often linked to nationalist movements in the 19th and early 20th centuries, seeks to preserve a dominant cultural identity by resisting external influences and promoting cultural homogeneity. The ideological divide reflects differing responses to modernization, colonization, and globalization, shaping contemporary debates on multiculturalism and national identity.
Key Principles of Cultural Pluralism
Cultural pluralism emphasizes the coexistence of diverse cultural groups within a society, promoting mutual respect, equality, and the preservation of distinct cultural identities. It supports the integration of multiple cultural traditions while allowing individuals to maintain their unique cultural practices without pressure to assimilate. Key principles include inclusivity, intercultural dialogue, and the protection of minority rights to foster social harmony and multicultural understanding.
Central Tenets of Cultural Purism
Cultural purism centers on preserving a distinct cultural identity by maintaining traditional customs, language, and values while resisting external influences and hybridization. This approach emphasizes cultural homogeneity and often views purity as essential to the survival and authenticity of a particular group. In contrast to cultural pluralism, which embraces diversity and intercultural exchange, cultural purism prioritizes safeguarding national or ethnic heritage against perceived dilution.
Benefits of Embracing Cultural Diversity
Embracing cultural pluralism promotes social cohesion by fostering mutual respect and understanding among diverse communities, which leads to richer cultural exchanges and innovative problem-solving. Cultural diversity enhances creativity and economic growth by integrating varied perspectives and skills from multiple ethnic and cultural backgrounds. The acceptance of multiple cultural identities strengthens democratic values and encourages inclusive policies, improving social equity and community resilience.
Challenges Associated with Cultural Homogeneity
Cultural pluralism promotes diversity and coexistence of multiple cultural identities, which challenges the notion of cultural homogeneity by encouraging inclusivity and adaptation. Cultural purism seeks to maintain a single, dominant culture, often resulting in resistance to change and exclusion of minority groups. Challenges associated with cultural homogeneity include social fragmentation, reduced innovation, and the marginalization of diverse perspectives, which can hinder social cohesion and economic development.
Social Dynamics: Integration vs. Preservation
Cultural pluralism promotes social integration by encouraging diverse groups to coexist while maintaining their unique identities within a shared society, fostering mutual respect and collaboration. Cultural purism prioritizes the preservation of a singular cultural heritage, often resisting external influences to maintain traditional values and practices. These contrasting social dynamics influence community cohesion, identity politics, and policies related to multiculturalism and assimilation.
Impacts on Policy and Governance
Cultural pluralism fosters inclusive policy frameworks that recognize and accommodate diverse cultural identities, promoting social cohesion and equitable representation in governance. Cultural purism often drives policies aimed at preserving a dominant cultural narrative, which can marginalize minority groups and undermine multicultural integration. The tension between these approaches influences legislative priorities, affecting immigration, education, and language policies within pluralistic societies.
Globalization and the Evolution of Cultural Concepts
Cultural pluralism emphasizes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a globalized society, fostering intercultural dialogue and mutual respect that evolve alongside globalization's interconnected networks. Cultural purism, by contrast, advocates for maintaining traditional cultural boundaries and resisting external influences to preserve original cultural forms amidst the pressures of global integration. The evolution of cultural concepts under globalization highlights the dynamic tension between embracing hybridity and reinforcing cultural authenticity in an increasingly interconnected world.
Future Perspectives: Towards Coexistence or Division?
Cultural pluralism promotes the coexistence of diverse ethnic, religious, and linguistic groups, fostering social harmony and innovation through mutual respect and intercultural dialogue. Cultural purism, emphasizing cultural homogeneity and the preservation of traditional identities, risks social fragmentation and heightened tensions in increasingly globalized societies. Future perspectives suggest that embracing pluralism through inclusive policies and education can mitigate divisions, enabling multicultural coexistence rather than exacerbating cultural conflicts.
Cultural pluralism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com