Social awareness involves understanding and empathizing with the emotions, needs, and perspectives of others within a community or social setting. Developing strong social awareness enhances your communication skills, fosters positive relationships, and promotes inclusivity. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical ways to cultivate social awareness in your daily interactions.
Table of Comparison
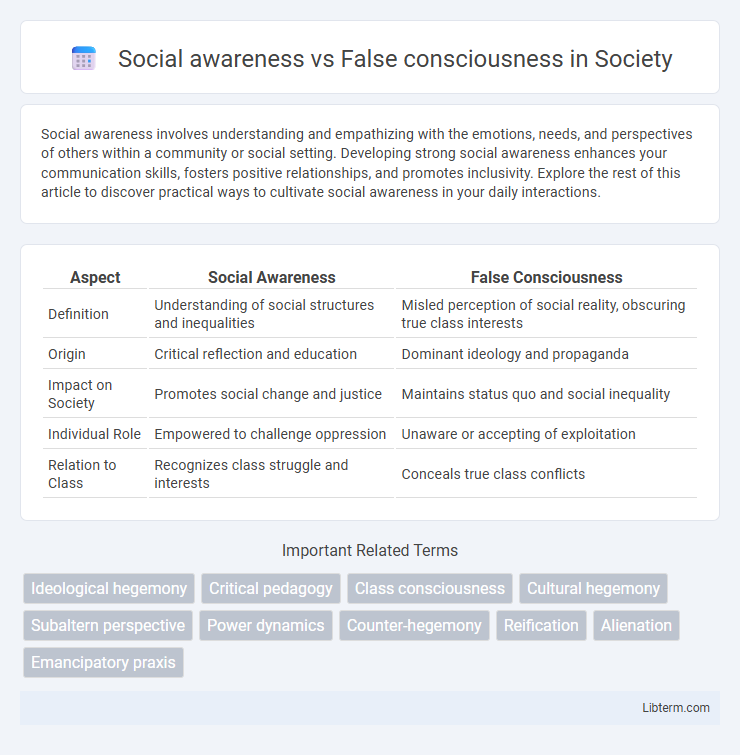
| Aspect | Social Awareness | False Consciousness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Understanding of social structures and inequalities | Misled perception of social reality, obscuring true class interests |
| Origin | Critical reflection and education | Dominant ideology and propaganda |
| Impact on Society | Promotes social change and justice | Maintains status quo and social inequality |
| Individual Role | Empowered to challenge oppression | Unaware or accepting of exploitation |
| Relation to Class | Recognizes class struggle and interests | Conceals true class conflicts |
Understanding Social Awareness: A Foundational Overview
Social awareness involves recognizing and understanding the dynamics of society, including issues related to culture, power, and inequality, enabling individuals to critically assess social structures. False consciousness refers to a distorted perception where individuals misinterpret or underestimate the true nature of social relations, often due to ideological manipulation or lack of critical insight. Grasping the concept of social awareness is foundational for distinguishing genuine societal understanding from the misleading narratives characteristic of false consciousness.
Defining False Consciousness in Contemporary Society
False consciousness in contemporary society refers to a distorted understanding of social realities where individuals misinterpret their social position and the systemic forces shaping their lives, often internalizing dominant ideologies that obscure class struggles or inequalities. This concept highlights how media, cultural narratives, and institutional power perpetuate misinformation, leading people to accept unjust conditions as natural or inevitable. Social awareness counters false consciousness by promoting critical thinking and awareness of structural injustices, empowering individuals to recognize and challenge exploitation and oppression.
Historical Roots of Social Awareness and False Consciousness
The historical roots of social awareness trace back to early social movements and critical theories that emphasized collective consciousness as a means to recognize systemic inequalities and promote social change. False consciousness, a concept developed in Marxist theory, originated from the critique of capitalism, describing the distorted perception of social realities that prevents working-class individuals from recognizing their exploitation. Both concepts highlight the interplay between awareness and ideology in shaping individuals' understanding of class structures and power dynamics throughout history.
Key Differences: Social Awareness vs False Consciousness
Social awareness involves recognizing and understanding social inequalities and systemic issues, while false consciousness denotes a distorted perception that obscures these realities, often aligning individuals with dominant power structures. Social awareness enables critical thinking and collective action for social justice, whereas false consciousness perpetuates acceptance of the status quo and hinders social change. The key difference lies in the clarity and accuracy of social perception, where social awareness promotes empowerment, and false consciousness fosters complacency.
The Role of Education in Shaping Consciousness
Education serves as a crucial mechanism in shaping social awareness by providing individuals with critical thinking skills and factual knowledge about societal structures and inequalities. It helps dismantle false consciousness by encouraging questioning of dominant ideologies and promoting an understanding of systemic oppression. Effective educational systems empower learners to recognize their social conditions and advocate for transformative social change.
Media’s Influence: Spreading Awareness or Reinforcing False Beliefs?
Media plays a pivotal role in shaping social awareness by disseminating information that can educate and mobilize communities toward social justice. However, it can also reinforce false consciousness by perpetuating stereotypes, misinformation, and dominant ideological narratives that obscure systemic inequalities. The framing and agenda-setting functions of media outlets critically influence whether audiences develop a genuine understanding of social realities or remain trapped in distorted perceptions.
Psychological Factors Driving False Consciousness
Psychological factors driving false consciousness include cognitive dissonance, where individuals rationalize oppressive conditions to reduce mental discomfort, and internalized beliefs shaped by social conditioning that distort self-perception and class identity. Mechanisms such as selective perception and denial hinder recognition of systemic inequalities, reinforcing acceptance of status quo. These psychological processes obscure social awareness by limiting critical reflection on power dynamics and societal structures.
Social Movements: Awakening Collective Social Awareness
Social awareness in social movements reflects a collective recognition of systemic inequalities and shared interests, empowering groups to mobilize for change. False consciousness, conversely, occurs when dominant ideologies obscure these realities, preventing collective action by fostering acceptance of oppressive conditions. Awakening collective social awareness is crucial for social movements to challenge entrenched power structures and achieve social justice objectives.
Overcoming False Consciousness: Strategies and Solutions
Overcoming false consciousness requires critical education that empowers individuals to recognize and challenge ideological distortions imposed by dominant powers. Enhancing social awareness through participatory dialogue and media literacy fosters the dismantling of misleading beliefs that inhibit collective action for social justice. Implementing community-based programs focused on critical thinking and socio-political empowerment promotes the transition from false consciousness to genuine social awareness.
The Future of Social Awareness in a Changing World
The future of social awareness hinges on deepening collective understanding of systemic inequalities while combating false consciousness that obscures these realities. Enhanced access to education and digital communication tools empowers individuals to recognize and challenge misleading narratives perpetuated by dominant power structures. As societies evolve, cultivating critical thinking and media literacy becomes essential in fostering genuine social awareness and promoting equitable progress.
Social awareness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com