Solidarism emphasizes the importance of social unity and mutual responsibility among individuals within a community, advocating for a balanced approach between individual rights and collective well-being. It seeks to foster cooperation and support systems that benefit society as a whole, promoting justice and shared values. Explore the rest of this article to understand how solidarism can influence your perspective on social cohesion and policy development.
Table of Comparison
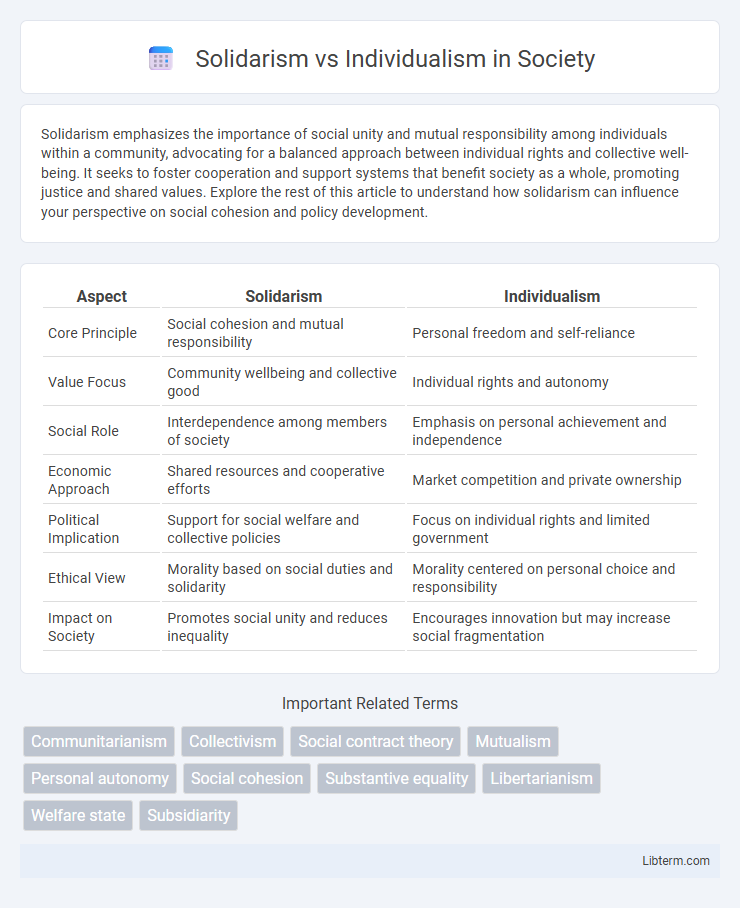
| Aspect | Solidarism | Individualism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Social cohesion and mutual responsibility | Personal freedom and self-reliance |
| Value Focus | Community wellbeing and collective good | Individual rights and autonomy |
| Social Role | Interdependence among members of society | Emphasis on personal achievement and independence |
| Economic Approach | Shared resources and cooperative efforts | Market competition and private ownership |
| Political Implication | Support for social welfare and collective policies | Focus on individual rights and limited government |
| Ethical View | Morality based on social duties and solidarity | Morality centered on personal choice and responsibility |
| Impact on Society | Promotes social unity and reduces inequality | Encourages innovation but may increase social fragmentation |
Understanding Solidarism: Core Principles
Solidarism emphasizes the interconnectedness of individuals within society, advocating for social cohesion and mutual responsibility to promote the common good. It prioritizes collective welfare, balanced by respect for individual rights, creating a framework where cooperation and social justice coexist. Core principles include solidarity, social harmony, and the integration of personal interests with communal well-being to address inequality and foster societal stability.
Defining Individualism: Key Concepts
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy, self-reliance, and the primacy of individual rights over collective interests. Key concepts include individual freedom, personal responsibility, and the pursuit of self-interest as fundamental to social and economic interactions. This philosophy supports limited government intervention, valuing individual choice and meritocratic principles in shaping society.
Historical Roots of Solidarism and Individualism
Solidarism originated in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, influenced by Catholic social teaching and the works of thinkers like Emile Durkheim who emphasized social cohesion and collective responsibility. Individualism traces back to Enlightenment philosophers such as John Locke and Jean-Jacques Rousseau, advocating personal liberty, individual rights, and self-reliance. The historical roots of solidarism and individualism reflect contrasting responses to industrialization and modernity, with solidarism promoting social integration and individualism emphasizing personal freedom.
Moral Foundations: Collective Good vs Personal Freedom
Solidarism emphasizes the moral foundation of collective good, prioritizing social responsibility, mutual support, and community well-being as essential ethical duties. Individualism centers on personal freedom, valuing autonomy, self-expression, and individual rights as primary moral imperatives. The tension between these frameworks reflects differing ethical priorities: solidarity fosters cooperation for societal benefit, while individualism champions liberty and personal choice.
Economic Implications: Cooperation or Competition?
Solidarism emphasizes economic cooperation by promoting collective ownership and shared responsibility, leading to policies that support social welfare, wealth redistribution, and labor rights to reduce inequality. Individualism prioritizes competition through private ownership and market freedom, encouraging innovation, entrepreneurial risk-taking, and personal wealth accumulation. These contrasting approaches impact economic growth, social equity, and government intervention levels within different market systems.
Social Structures: Community Bonds vs Autonomy
Solidarism emphasizes strong social structures where community bonds and collective responsibilities reinforce societal cohesion and mutual support. Individualism prioritizes personal autonomy and self-reliance, fostering social arrangements that celebrate individual rights and freedoms. These contrasting approaches shape how communities organize, either valuing interconnectedness or promoting independent decision-making within social frameworks.
Political Systems: Governance and Representation
Solidarism promotes governance structures emphasizing collective responsibility and social cohesion, advocating for policies that prioritize community welfare and equitable resource distribution. Individualism supports political systems centered on personal liberty and autonomy, valuing minimal state intervention and protecting individual rights in governance. Representation under solidarism often involves inclusive decision-making mechanisms to reflect collective interests, while individualism favors representative frameworks ensuring individual freedoms and property rights are upheld.
Cultural Impact: Identity and Belonging
Solidarism fosters a collective cultural identity by emphasizing social cohesion, mutual responsibility, and shared values that strengthen community bonds and a sense of belonging. Individualism promotes personal autonomy and self-expression, encouraging diverse identities that highlight individual uniqueness but may challenge communal ties. The cultural impact of these ideologies shapes how societies define identity and belonging, influencing social behaviors, traditions, and the balance between collective unity and personal freedom.
Modern Challenges: Balancing Solidarism and Individualism
Modern challenges in balancing solidarism and individualism revolve around integrating collective welfare with personal autonomy. Socioeconomic systems must navigate tensions between community-oriented policies and individual rights, promoting social cohesion while respecting personal freedoms. Technological advancements and global interconnectedness intensify the need for adaptive frameworks that harmonize solidarity with individualism in governance and social structures.
Future Perspectives: Harmonizing Solidarity and Individual Rights
Future perspectives on Solidarism emphasize integrating collective well-being with individual rights by promoting policies that balance social responsibilities and personal freedoms. Emerging models advocate for cooperative frameworks in economic and political systems that ensure equity without suppressing personal autonomy. Technological advancements and global challenges, such as climate change and digital privacy, necessitate novel approaches that harmonize community solidarity with individual empowerment.
Solidarism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com