Formal social control involves the use of laws, regulations, and official institutions to regulate behavior and maintain order within society. It relies on codified rules enforced by authorities such as police, courts, and government agencies to ensure compliance and address violations. Discover how formal social control shapes society and influences Your everyday interactions in the full article.
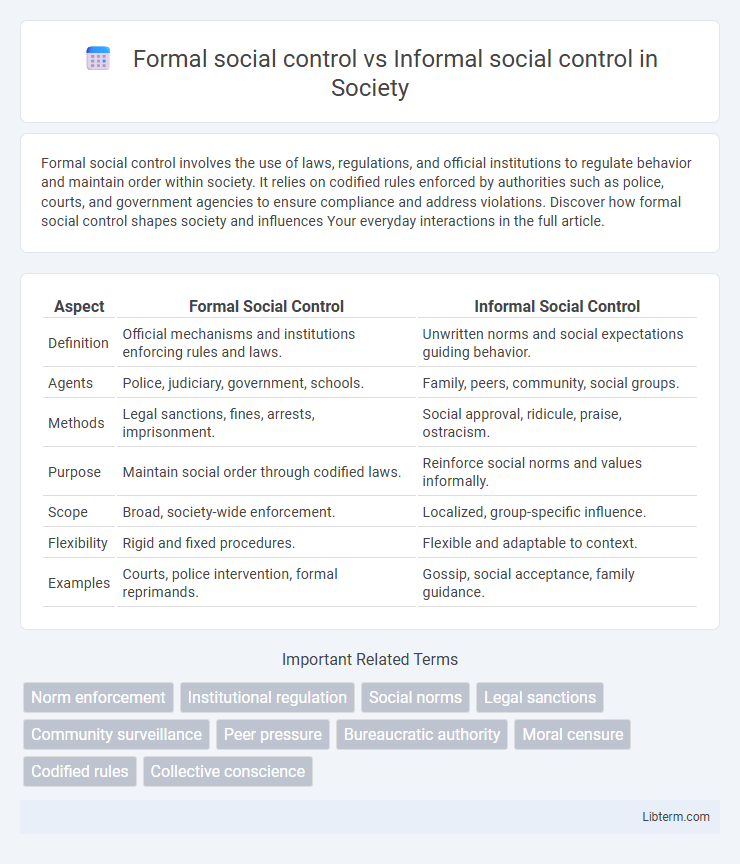
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Formal Social Control | Informal Social Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official mechanisms and institutions enforcing rules and laws. | Unwritten norms and social expectations guiding behavior. |
| Agents | Police, judiciary, government, schools. | Family, peers, community, social groups. |
| Methods | Legal sanctions, fines, arrests, imprisonment. | Social approval, ridicule, praise, ostracism. |
| Purpose | Maintain social order through codified laws. | Reinforce social norms and values informally. |
| Scope | Broad, society-wide enforcement. | Localized, group-specific influence. |
| Flexibility | Rigid and fixed procedures. | Flexible and adaptable to context. |
| Examples | Courts, police intervention, formal reprimands. | Gossip, social acceptance, family guidance. |
Defining Formal Social Control
Formal social control refers to the mechanisms, such as laws, regulations, and official policies, implemented by authorized institutions like the government, police, and judicial system to regulate individual and group behavior. It involves written rules enforced through sanctions, including fines, imprisonment, and legal penalties, aiming to maintain order and prevent deviance in society. This type of control contrasts with informal social control, which relies on unwritten norms, customs, and social pressures exerted by family, peers, and community members.
Understanding Informal Social Control
Informal social control operates through unwritten social norms, peer pressure, and community expectations that regulate individual behavior without formal laws or sanctions. It relies on socialization processes within families, schools, and neighborhoods to reinforce conformity and maintain societal order. Understanding informal social control highlights its subtle yet powerful role in shaping everyday interactions and sustaining social cohesion.
Key Differences Between Formal and Informal Social Control
Formal social control involves established institutions like law enforcement and judicial systems that enforce rules through codified laws and official sanctions, whereas informal social control relies on unwritten norms, peer pressure, and community expectations to regulate behavior. Formal mechanisms are characterized by explicit authority and legal consequences, while informal mechanisms operate through social interactions and collective values without official enforcement. The key differences lie in the source of authority, methods of enforcement, and the nature of consequences imposed for deviance or nonconformity.
Mechanisms of Formal Social Control
Mechanisms of formal social control include laws, regulations, and institutional policies enforced by authorized bodies such as the police, courts, and government agencies. These mechanisms rely on codified rules and official sanctions like fines, imprisonment, or probation to maintain social order and deter deviance. Formal social control operates through structured procedures and documented processes designed to uphold societal norms systematically and predictably.
Mechanisms of Informal Social Control
Mechanisms of informal social control include social norms, peer pressure, family expectations, and community values that guide behavior without formal sanctions. These mechanisms rely on socialization, approval, disapproval, and symbolic rewards or punishments such as praise, gossip, or ostracism to maintain order. Informal social control operates through everyday interactions and shared cultural understandings within groups, reinforcing conformity and deterring deviance in a flexible, non-institutionalized manner.
Roles of Institutions in Formal Social Control
Institutions such as the police, courts, and correctional facilities enforce formal social control by establishing and implementing laws to maintain order and punish violations. These organizations create standardized procedures and sanctions that regulate behavior systematically across society. Formal social control relies on institutional authority and legal frameworks to ensure compliance and social stability.
Influence of Family and Community in Informal Social Control
Informal social control relies heavily on family and community to shape individual behavior through norms, values, and expectations rather than laws or official sanctions. Families instill moral principles and social norms early in life, guiding members toward accepted behavior patterns, while communities enforce social cohesion through peer pressure, public opinion, and shared cultural practices. This grassroots influence fosters internal regulation of conduct, reducing the need for formal mechanisms of control.
Effectiveness of Social Control Methods
Formal social control, exercised through laws, regulations, and official sanctions, ensures consistent enforcement and clear consequences, making it highly effective in deterring severe deviant behavior. Informal social control relies on community norms, peer pressure, and socialization processes, often producing immediate feedback and promoting internalized conformity, which is effective for minor infractions and maintaining daily social order. The combination of formal and informal mechanisms tends to maximize overall social control effectiveness by addressing different levels of deviance and reinforcing normative behavior through both external enforcement and internalized values.
Challenges and Limitations of Formal vs Informal Social Control
Formal social control faces challenges such as rigid legal frameworks, slow bureaucratic processes, and potential biases in law enforcement, which can limit its effectiveness in rapidly changing social contexts. Informal social control struggles with inconsistency, cultural subjectivity, and limited reach, often relying on social norms and peer pressure that may not uniformly influence all individuals. Both systems exhibit limitations in addressing complex social behaviors, requiring a careful balance for maintaining social order and cohesion.
Impact on Society: Balancing Formal and Informal Controls
Formal social control, enforced through laws and institutions like police and courts, establishes clear guidelines and consequences to maintain societal order and protect citizens. Informal social control, driven by community norms, family, and peer influence, fosters social cohesion and encourages conformity through approval or disapproval within everyday interactions. Balancing both forms of control optimizes societal stability by combining authoritative enforcement with social influence, reducing deviance while promoting cooperative behavior.
Formal social control Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com