Isolationism focuses on limiting a nation's involvement in international affairs to prioritize domestic interests and security. This policy reduces political, economic, and military engagements with other countries, aiming to avoid conflicts and external influences. Explore the rest of the article to understand how isolationism impacts global relations and Your country's stance.
Table of Comparison
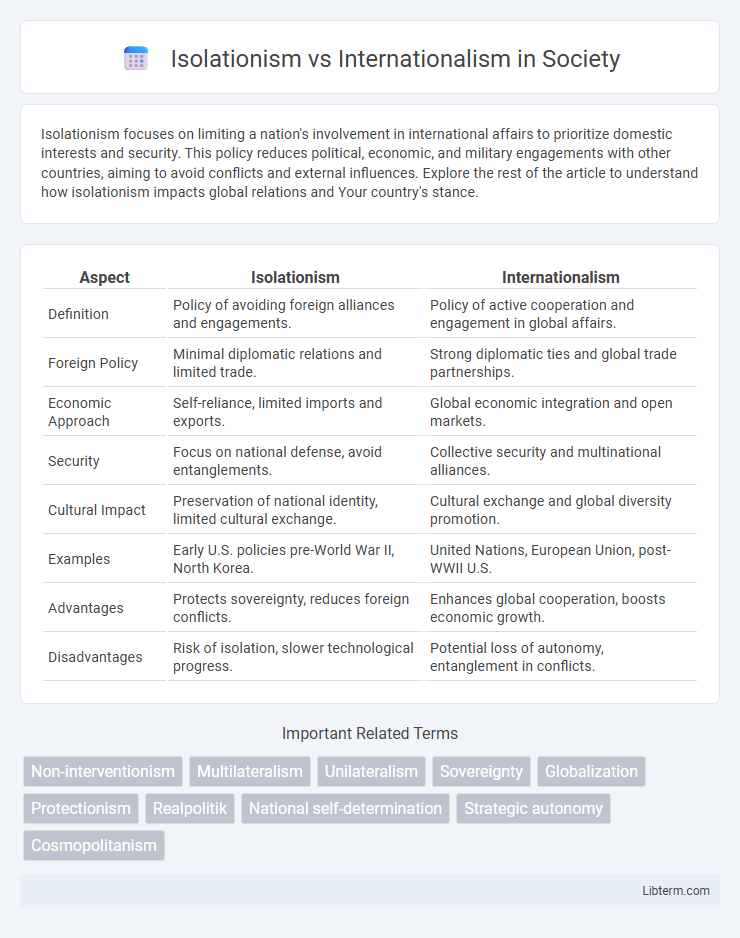
| Aspect | Isolationism | Internationalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Policy of avoiding foreign alliances and engagements. | Policy of active cooperation and engagement in global affairs. |
| Foreign Policy | Minimal diplomatic relations and limited trade. | Strong diplomatic ties and global trade partnerships. |
| Economic Approach | Self-reliance, limited imports and exports. | Global economic integration and open markets. |
| Security | Focus on national defense, avoid entanglements. | Collective security and multinational alliances. |
| Cultural Impact | Preservation of national identity, limited cultural exchange. | Cultural exchange and global diversity promotion. |
| Examples | Early U.S. policies pre-World War II, North Korea. | United Nations, European Union, post-WWII U.S. |
| Advantages | Protects sovereignty, reduces foreign conflicts. | Enhances global cooperation, boosts economic growth. |
| Disadvantages | Risk of isolation, slower technological progress. | Potential loss of autonomy, entanglement in conflicts. |
Understanding Isolationism: Definition and Origins
Isolationism is a foreign policy approach advocating minimal involvement in international political and economic relations to preserve national sovereignty and avoid entanglements in conflicts. Its origins trace back to 18th-century American principles, notably George Washington's Farewell Address warning against permanent alliances, reflecting a desire to protect the young nation's interests and security. This doctrine emphasizes self-reliance and prioritizes domestic affairs over global engagement, differentiating it from internationalism, which promotes active participation in worldwide cooperation and institutions.
The Rise of Internationalism: Key Principles
The rise of internationalism emphasizes cooperation among nations to address global challenges such as climate change, security threats, and economic instability. Key principles include multilateralism, where countries work through international organizations like the United Nations and World Trade Organization to create binding agreements and enforce global norms. This approach prioritizes collective action, interconnected diplomacy, and the promotion of peace through shared responsibility.
Historical Examples of Isolationist Policies
Isolationist policies shaped U.S. foreign relations during the interwar period, exemplified by the Neutrality Acts of the 1930s designed to avoid entanglement in European conflicts. Japan's Sakoku policy (1633-1853) strictly limited foreign interaction to maintain national sovereignty and avoid colonial influence. Similarly, China's Ming Dynasty implemented maritime bans to restrict trade and contact with foreign powers, reflecting isolationist tendencies aimed at preserving cultural integrity.
Notable Internationalist Movements and Milestones
The League of Nations, established after World War I, marked a significant milestone for internationalism by promoting collective security and conflict resolution among member states. The formation of the United Nations in 1945 further advanced international cooperation, focusing on peacekeeping, human rights, and sustainable development. Internationalist movements such as the Anti-Apartheid Movement and the global environmental efforts, including the Paris Agreement, underscore the ongoing commitment to transnational collaboration on social justice and climate change.
Economic Impacts: Isolationism vs Internationalism
Isolationism often leads to reduced trade volumes, limiting access to global markets and causing inefficiencies in resource allocation, which can slow economic growth. In contrast, internationalism promotes trade liberalization, fostering competitive markets, innovation, and increased foreign direct investment, which boost productivity and GDP. Countries embracing internationalism typically experience higher economic diversification and resilience against domestic economic shocks.
Political Implications on Global Governance
Isolationism limits a nation's political influence by restricting engagement in multinational institutions, reducing its ability to shape global governance frameworks such as the United Nations and World Trade Organization. Internationalism promotes active participation in international alliances and diplomatic cooperation, enhancing global policymaking and enforcement of international laws. The political implications affect sovereignty, with isolationist states prioritizing national control, while internationalist states often cede some autonomy to supranational entities to address transnational challenges effectively.
Security Dilemmas: Risks and Rewards
Isolationism reduces exposure to international conflicts, lowering immediate security risks but potentially increasing vulnerability to unforeseen threats and diminishing influence in global security arrangements. Internationalism fosters alliances and collective defense mechanisms, enhancing deterrence and crisis management capabilities, yet it may entangle nations in external conflicts and provoke security dilemmas through perceived power imbalances. Balancing these approaches involves assessing trade-offs between national sovereignty, strategic influence, and the risk of escalation inherent in complex security environments.
Cultural and Social Consequences
Isolationism often leads to cultural stagnation and restricted social exchange, limiting exposure to diverse ideas, traditions, and innovations. Internationalism fosters cultural hybridization and social inclusivity, enhancing mutual understanding and cooperation among global populations. Societies embracing internationalism benefit from increased cultural empathy, diversified social networks, and enriched artistic expression.
Major Debates: Which Approach Benefits Nations?
Isolationism emphasizes national sovereignty and economic self-sufficiency, arguing that minimizing foreign entanglements preserves security and protects domestic industries. Internationalism advocates for cooperation through global alliances and trade, promoting collective security, economic growth, and diplomatic influence. Debates center on balancing national interests with global responsibilities, assessing which approach fosters long-term stability and prosperity.
The Future: Navigating Between Isolationism and Internationalism
Navigating the future requires balancing isolationism's focus on national sovereignty and economic self-reliance with internationalism's emphasis on global cooperation and multilateralism. Emerging challenges like climate change, pandemics, and cybersecurity threats demand collaborative solutions, yet rising nationalism and protectionism test international alliances. The strategic management of diplomacy, trade agreements, and global governance institutions will shape whether nations prioritize inward policies or embrace interconnected global frameworks.
Isolationism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com