Implicit bias refers to unconscious attitudes or stereotypes that affect understanding, decisions, and actions without intentional awareness. These biases influence behavior in various contexts, including hiring, education, and healthcare, often leading to unfair treatment or missed opportunities. Explore the rest of the article to understand how implicit bias shapes your perceptions and what steps you can take to counteract it.
Table of Comparison
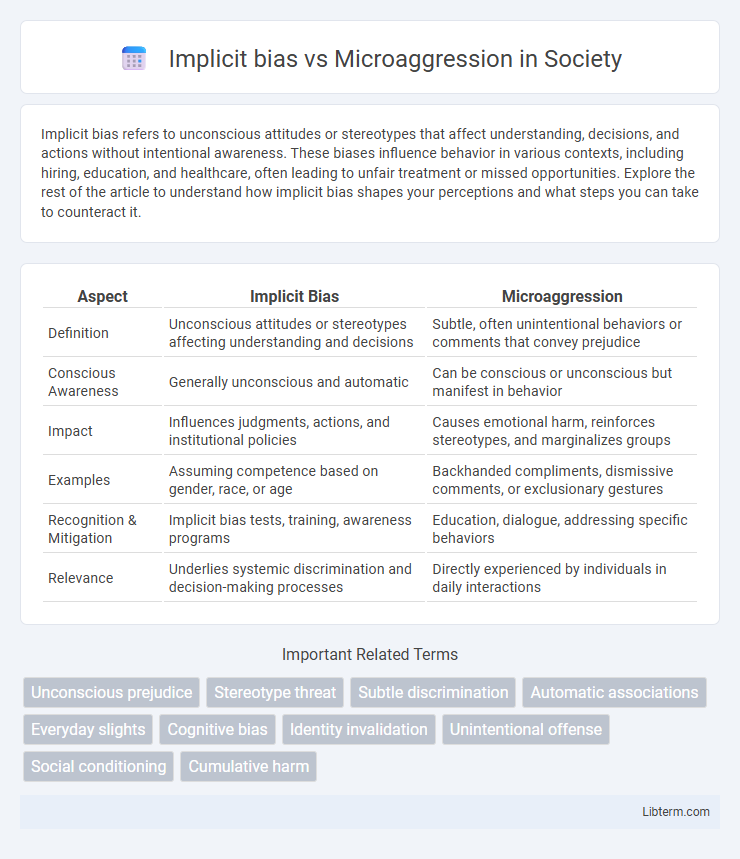
| Aspect | Implicit Bias | Microaggression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unconscious attitudes or stereotypes affecting understanding and decisions | Subtle, often unintentional behaviors or comments that convey prejudice |
| Conscious Awareness | Generally unconscious and automatic | Can be conscious or unconscious but manifest in behavior |
| Impact | Influences judgments, actions, and institutional policies | Causes emotional harm, reinforces stereotypes, and marginalizes groups |
| Examples | Assuming competence based on gender, race, or age | Backhanded compliments, dismissive comments, or exclusionary gestures |
| Recognition & Mitigation | Implicit bias tests, training, awareness programs | Education, dialogue, addressing specific behaviors |
| Relevance | Underlies systemic discrimination and decision-making processes | Directly experienced by individuals in daily interactions |
Understanding Implicit Bias: Definition and Examples
Implicit bias refers to the unconscious attitudes or stereotypes that influence our understanding, actions, and decisions without conscious awareness. Examples include associating certain racial groups with negative traits or making automatic assumptions about someone's abilities based on gender. Understanding implicit bias is crucial for recognizing how these hidden prejudices shape behavior and contribute to microaggressions in everyday interactions.
What Are Microaggressions? Key Features and Types
Microaggressions are subtle, often unintentional, behaviors or remarks that convey prejudiced attitudes toward marginalized groups. Key features include their repetitive nature, indirect expression, and cumulative impact on mental health and social well-being. Types of microaggressions encompass microassaults (explicit derogatory actions), microinsults (subtle snubs or dismissive comments), and microinvalidations (actions that negate or dismiss the experiences of marginalized individuals).
Origins and Psychology Behind Implicit Bias
Implicit bias originates from the brain's automatic processing system, shaped by societal norms, cultural experiences, and personal upbringing, leading to unconscious attitudes toward certain groups. Psychological studies indicate that these biases form through associative learning and cognitive shortcuts designed to simplify complex social environments. Unlike explicit prejudices, implicit biases operate below conscious awareness, influencing behavior and decision-making subtly yet persistently.
Common Types of Microaggressions in Everyday Life
Common types of microaggressions in everyday life include microassaults, which are explicit derogatory actions or slurs, microinsults that subtly convey rudeness or insensitivity, and microinvalidations that dismiss or negate the experiences of marginalized groups. These microaggressions often stem from implicit biases--unconscious attitudes or stereotypes influencing behavior without deliberate intent. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for addressing subtle discrimination and promoting inclusivity in social and professional environments.
Implicit Bias vs Microaggression: Core Differences
Implicit bias refers to unconscious attitudes or stereotypes that influence perceptions and behaviors toward different social groups without conscious awareness. Microaggressions are subtle, often unintentional verbal or behavioral slights that communicate negative or derogatory messages to individuals based on their marginalized identities. The core difference lies in implicit bias being an internal, subconscious process, while microaggressions are the external manifestations or expressions of those biases in everyday interactions.
How Implicit Bias Leads to Microaggressions
Implicit bias, unconscious attitudes or stereotypes influencing perceptions and actions, often manifests as microaggressions--subtle, indirect, or unintentional discriminatory comments or behaviors targeting marginalized groups. These biases shape automatic reactions and judgments, leading to microaggressions that perpetuate stereotypes and reinforce systemic inequalities. Understanding the connection between implicit bias and microaggressions is critical for addressing hidden prejudices and promoting inclusive environments.
Real-World Impacts: Consequences of Both Behaviors
Implicit bias contributes to systemic inequalities by influencing decisions in employment, healthcare, and law enforcement, often without conscious awareness. Microaggressions create hostile environments that damage mental health, reduce workplace productivity, and exacerbate social exclusion. Both behaviors perpetuate discrimination and hinder efforts toward diversity, equity, and inclusion in real-world settings.
Recognizing Implicit Bias Within Ourselves
Recognizing implicit bias within ourselves requires acknowledging subconscious associations that influence our behavior and decisions without conscious awareness. Tools such as Implicit Association Tests (IAT) and reflective journaling can help identify patterns rooted in race, gender, or age biases. Understanding these hidden biases is crucial for reducing microaggressions in daily interactions and fostering inclusive environments.
Strategies to Address and Reduce Microaggressions
Strategies to address and reduce microaggressions include fostering awareness through comprehensive training programs that highlight implicit bias and its impact on marginalized groups. Implementing inclusive workplace policies encourages open dialogue and accountability, allowing individuals to recognize and challenge their unconscious behaviors. Regular feedback mechanisms and support systems empower affected individuals while promoting a culture of respect and equity.
Building Inclusive Environments: Solutions and Best Practices
Addressing implicit bias involves training programs that increase self-awareness and promote perspective-taking to reduce unconscious stereotypes. Combating microaggressions requires establishing clear communication channels, encouraging open dialogue, and implementing restorative practices to address impacts on marginalized groups. Organizations should embed inclusive policies, continuous education, and accountability measures to foster environments where all individuals feel respected and valued.
Implicit bias Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com