Institutions play a crucial role in shaping society by establishing norms, policies, and systems that govern behavior and interactions. Understanding how these entities function can help you navigate social, economic, and political landscapes more effectively. Explore the rest of this article to learn how different types of institutions impact your daily life and broader community.
Table of Comparison
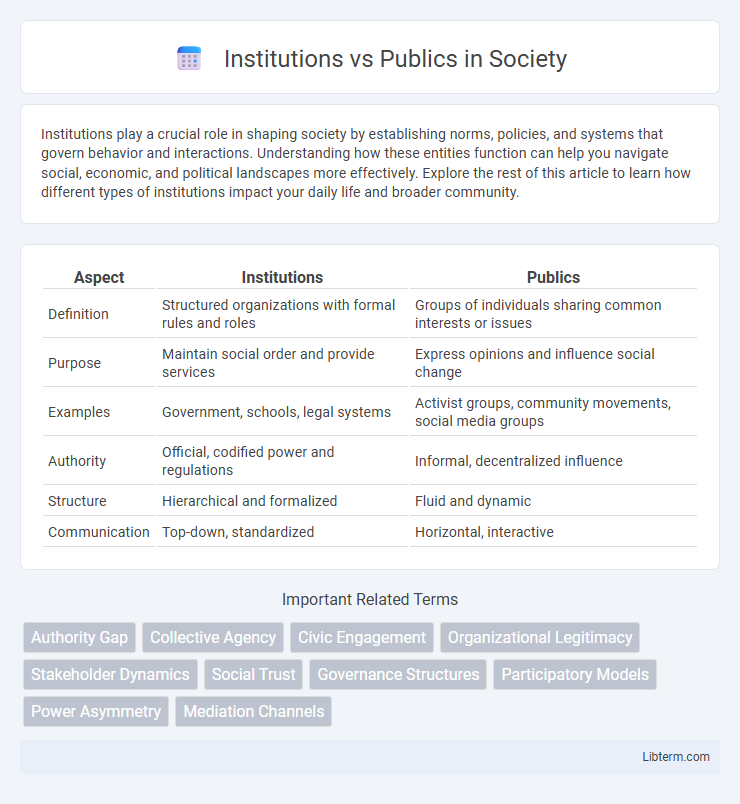
| Aspect | Institutions | Publics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured organizations with formal rules and roles | Groups of individuals sharing common interests or issues |
| Purpose | Maintain social order and provide services | Express opinions and influence social change |
| Examples | Government, schools, legal systems | Activist groups, community movements, social media groups |
| Authority | Official, codified power and regulations | Informal, decentralized influence |
| Structure | Hierarchical and formalized | Fluid and dynamic |
| Communication | Top-down, standardized | Horizontal, interactive |
Defining Institutions and Publics
Institutions are established organizations or systems with structured rules and norms that govern behavior, such as governments, educational bodies, or financial entities. Publics refer to groups of individuals or communities that engage with or are affected by these institutions, often characterized by shared interests or concerns. Understanding the interaction between institutions and publics is essential for analyzing social dynamics and policy impacts.
Historical Context of Institutions and Publics
Institutions have historically evolved as organized structures with established rules and norms, designed to govern behavior and maintain social order across political, economic, and cultural domains. Publics emerged as dynamic groups characterized by shared interests and collective action, often arising in response to institutional authority or societal changes, particularly during the Enlightenment and democratic revolutions. The interplay between institutions and publics has shaped governance systems, reflecting shifts in power, citizenship, and societal engagement over centuries.
Key Differences Between Institutions and Publics
Institutions are formal organizations or systems established to govern or regulate specific functions within society, featuring defined structures, rules, and roles. Publics refer to groups of individuals or communities sharing interests or concerns, often influencing or reacting to institutional decisions but lacking formal organizational frameworks. The key differences lie in institutions' structured authority and governance compared to publics' informal, interest-based collective nature.
Roles and Functions in Society
Institutions establish structured norms and rules that guide societal behavior, ensuring social order and stability through roles such as governance, education, and law enforcement. Publics represent diverse groups within society that actively engage with institutions by expressing opinions, advocating for change, and participating in decision-making processes. Together, institutions maintain systemic functionality while publics drive social responsiveness and accountability.
Power Dynamics: Institutions vs Publics
Institutions wield authoritative power through structured hierarchies and regulatory control, shaping public behavior and policy enforcement. Publics exert influence via collective action, social movements, and public opinion, challenging institutional decisions and demanding accountability. The dynamic tension between institutions and publics drives societal change, negotiating power distribution and governance legitimacy.
Influence on Policy and Governance
Institutions shape policy and governance through formal structures, established rules, and authoritative decision-making processes that enforce compliance and ensure stability. Publics influence policy by expressing demands, opinions, and mobilizing collective action, which can pressure institutions to adapt or reform governance practices. The dynamic interaction between institutions and publics determines policy responsiveness and the effectiveness of governance systems.
Communication Channels and Strategies
Institutions deploy communication channels such as official websites, press releases, and social media platforms to maintain formal and consistent messaging tailored to diverse publics. Publics engage through interactive channels like community forums, feedback surveys, and informal social networks, facilitating two-way communication and participatory dialogue. Strategic use of multichannel communication ensures institutions can effectively manage public perception while publics influence institutional responses through active engagement and information exchange.
Impact on Social Change
Institutions shape social change through established norms, policies, and governance structures, influencing collective behavior and societal stability. Publics act as dynamic agents of change by expressing opinions, mobilizing movements, and challenging institutional frameworks to drive reforms. The interaction between institutions and publics creates a feedback loop where institutional policies adapt in response to public demands, catalyzing progressive social transformation.
Challenges and Conflicts Between Institutions and Publics
Conflicts between institutions and publics often arise from misaligned interests, with institutions prioritizing organizational goals while publics demand transparency and accountability. Power imbalances exacerbate challenges, as institutions may impose policies that publics perceive as restrictive or unjust, leading to distrust and resistance. Communication gaps and differing values intensify these conflicts, requiring institutions to adopt inclusive strategies and responsive governance to rebuild legitimacy and public confidence.
Future Trends: Evolving Relationships
Institutions are increasingly leveraging digital platforms to engage publics, fostering transparent and interactive communication channels that enhance trust and collaboration. The rise of social media and AI-driven analytics enables institutions to tailor messages and anticipate public concerns, shifting from one-way dissemination to dynamic dialogue. Future trends indicate a continued blending of institutional authority with grassroots activism, creating hybrid governance models responsive to diverse societal needs.
Institutions Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com