Competition drives innovation and pushes businesses to improve their products and services to stand out in the market. Understanding your competitors' strategies can help you identify opportunities for growth and areas where you can differentiate your offerings. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to leverage competition to your advantage effectively.
Table of Comparison
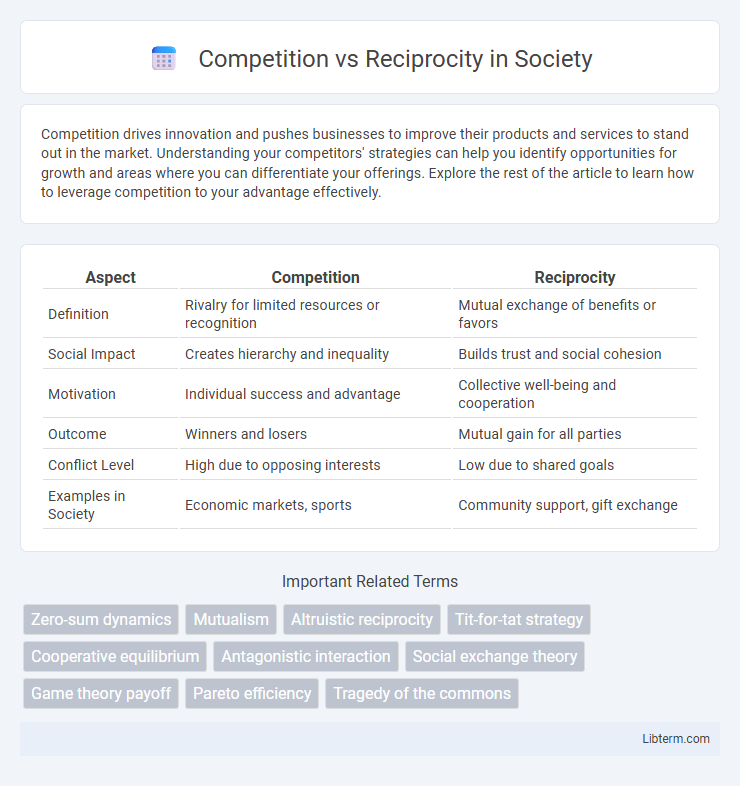
| Aspect | Competition | Reciprocity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rivalry for limited resources or recognition | Mutual exchange of benefits or favors |
| Social Impact | Creates hierarchy and inequality | Builds trust and social cohesion |
| Motivation | Individual success and advantage | Collective well-being and cooperation |
| Outcome | Winners and losers | Mutual gain for all parties |
| Conflict Level | High due to opposing interests | Low due to shared goals |
| Examples in Society | Economic markets, sports | Community support, gift exchange |
Understanding Competition: Definition and Dynamics
Competition refers to the rivalry among individuals or groups striving for limited resources, recognition, or success, often driving innovation and performance improvements. Its dynamics involve strategic behaviors such as cooperation within teams, conflict between competitors, and adaptation to evolving environments. Understanding competition requires analyzing how incentives, resource scarcity, and social interactions influence motivation and outcomes in various contexts.
The Essence of Reciprocity in Human Interaction
Reciprocity in human interaction fosters mutual trust and cooperation, creating social bonds that enhance group cohesion and collective well-being. Unlike competition, which emphasizes individual gain and often leads to conflict, reciprocity encourages balanced exchange and long-term relationships. This fundamental mechanism supports cooperation in diverse social settings, from family units to global communities, driving societal stability and growth.
Competition vs Reciprocity: Core Differences
Competition centers on individuals or groups striving to outperform each other to achieve superior results, often emphasizing scarcity and winning. Reciprocity involves mutual exchange and cooperation, fostering trust and long-term relationships through balanced give-and-take interactions. Core differences lie in their motivational frameworks: competition drives self-interest and comparative success, while reciprocity prioritizes collaboration and shared benefit.
Psychological Impacts of Competitive Environments
Competitive environments often trigger heightened stress and anxiety levels due to constant pressure to outperform peers, leading to decreased overall well-being. The persistent focus on winning can undermine intrinsic motivation and foster feelings of inadequacy, negatively impacting self-esteem. Research indicates that reciprocity-based interactions promote cooperation and psychological safety, contrasting with the isolating effects observed in competition-driven settings.
Social Benefits of Reciprocal Relationships
Reciprocal relationships foster trust and cooperation, enhancing social cohesion and collective well-being within communities. These mutual exchanges promote psychological resilience by creating supportive networks that reduce stress and improve mental health outcomes. Social benefits of reciprocity include increased resource sharing, stronger social capital, and sustained collaborative efforts that outperform competitive interactions in long-term societal development.
Competition in the Workplace: Boost or Barrier?
Competition in the workplace drives employees to enhance productivity, improve skills, and achieve targets, fostering a results-oriented environment. However, excessive competition can create stress, reduce collaboration, and encourage a cutthroat culture that hinders teamwork and innovation. Balancing competitive incentives with collaborative practices is crucial to maximizing overall organizational performance and employee satisfaction.
Reciprocity as a Catalyst for Collaboration
Reciprocity serves as a powerful catalyst for collaboration by fostering trust and mutual benefit among participants, which enhances collective problem-solving and innovation. Unlike competition that often drives individuals to prioritize personal gain, reciprocity encourages sharing resources and knowledge, creating a cooperative environment that amplifies productivity. Empirical studies demonstrate that teams practicing reciprocal behaviors outperform competitive groups in achieving long-term goals and sustaining partnerships.
Finding the Balance: When to Compete, When to Collaborate
Finding the balance between competition and reciprocity requires understanding context-specific goals and outcomes. Compete when driving innovation, efficiency, and market differentiation, but shift towards collaboration to leverage shared resources, foster trust, and create synergistic value. Strategic decision-making involves assessing whether aggressive rivalry or cooperative partnerships best serve long-term growth and mutual benefit.
Strategies for Fostering Reciprocity Over Rivalry
Implementing transparent communication channels and emphasizing shared goals cultivates an environment where reciprocity thrives over competition. Encouraging collaborative problem-solving and recognizing team contributions reinforce mutual trust and collective success. Integrating incentive systems that reward cooperative behavior further shifts focus from rivalry to partnership.
The Future: Evolving from Competition to Reciprocity
The future of human interaction envisions a transformative shift from competition to reciprocity, emphasizing collaborative networks that foster mutual benefit and sustainable growth. Emerging technologies like blockchain and decentralized platforms enhance transparency and trust, enabling reciprocal exchanges at scale. Social and economic systems evolving towards reciprocity promise to address global challenges by prioritizing shared value creation over zero-sum competition.
Competition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com