Social change transforms communities by reshaping cultural norms, values, and behaviors to address evolving needs and challenges. It influences economic structures, political institutions, and social relationships, creating opportunities for improved equality and justice. Explore the rest of this article to understand how social change impacts your world and what drives these dynamic shifts.
Table of Comparison
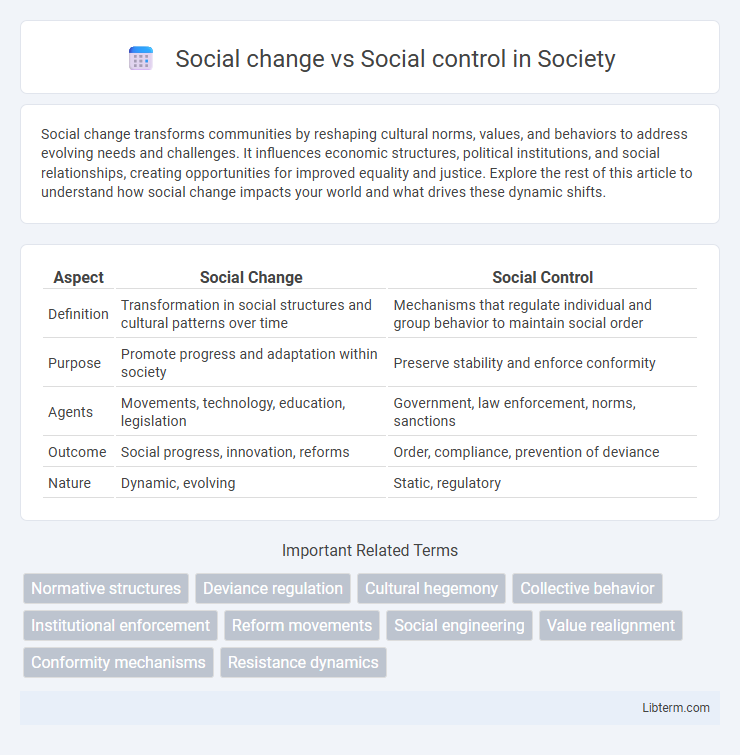
| Aspect | Social Change | Social Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transformation in social structures and cultural patterns over time | Mechanisms that regulate individual and group behavior to maintain social order |
| Purpose | Promote progress and adaptation within society | Preserve stability and enforce conformity |
| Agents | Movements, technology, education, legislation | Government, law enforcement, norms, sanctions |
| Outcome | Social progress, innovation, reforms | Order, compliance, prevention of deviance |
| Nature | Dynamic, evolving | Static, regulatory |
Introduction to Social Change and Social Control
Social change refers to significant alterations in cultural patterns, behaviors, or social structures over time, driven by factors such as technological advancements, economic shifts, and cultural movements. Social control encompasses mechanisms, strategies, and institutions that regulate individual and group behavior to maintain social order and prevent deviance. Understanding the balance between social change and social control is essential for analyzing how societies evolve while preserving stability and cohesion.
Defining Social Change
Social change refers to significant alterations over time in behavior patterns, cultural values, norms, and social structures within a society. It encompasses developments such as technological advancements, shifts in population demographics, and evolving political or economic systems, driving progress or transformation. Defining social change involves recognizing its dynamic and multifaceted nature, highlighting how it reshapes societal institutions and everyday interactions.
Understanding Social Control
Social control refers to the mechanisms, strategies, and institutions that societies use to regulate individual behavior and maintain social order. It encompasses formal sanctions like laws and regulations enforced by authorities, as well as informal controls such as social norms, traditions, and peer pressure that influence conformity. Understanding social control involves analyzing how these processes balance the need for stability while responding to ongoing social changes.
Key Differences Between Social Change and Social Control
Social change refers to significant transformations in societal structures, cultural patterns, and behaviors, often driven by innovation, social movements, or external influences, whereas social control involves mechanisms, such as laws, norms, and sanctions, designed to maintain order and stability within a society. Social change emphasizes dynamic evolution and adaptation to new conditions, while social control focuses on preserving existing social norms and preventing deviance. The key difference lies in social change promoting progress and reform, contrasting with social control's role in enforcing conformity and continuity.
Causes and Drivers of Social Change
Social change is driven by factors such as technological innovation, economic shifts, cultural evolution, and social movements that challenge established norms and structures. Social control operates through mechanisms like laws, regulations, customs, and institutions to maintain social order and stability amid these changes. Understanding the causes of social change helps explain how societies adapt, while social control ensures continuity and limits disruptive impacts.
Mechanisms and Agents of Social Control
Social control operates through mechanisms such as laws, norms, and sanctions that regulate individual and group behavior to maintain societal order. Agents of social control include institutions like the family, education system, law enforcement, and religious organizations, which enforce conformity and discourage deviance. In contrast, social change occurs when these mechanisms and agents evolve or are challenged, leading to shifts in cultural values, power structures, and social practices.
The Interplay Between Social Change and Social Control
Social change and social control are interdependent forces shaping societal evolution, where social change refers to the transformation of culture, institutions, and social behavior over time, while social control encompasses mechanisms like laws, norms, and sanctions that maintain order and conformity. The interplay between these concepts manifests as social control can both resist and facilitate social change, with institutions adapting rules to accommodate emerging social movements or innovations. Understanding this dynamic highlights how regulatory frameworks evolve in response to shifting social values, ensuring stability amidst transformation.
Social Institutions: Roles in Change and Control
Social institutions serve as pivotal arenas where social change and social control intersect, shaping societal norms and behaviors. Institutions like family, education, religion, and government facilitate social change by promoting innovation, reform, and adaptation to evolving values and technologies. Simultaneously, these institutions enforce social control through established rules, norms, and sanctions that maintain order and stability within society.
Impact on Society: Positive and Negative Outcomes
Social change drives societal progress by addressing inequalities and promoting innovation, leading to improved living standards and greater social justice. Social control maintains order and stability through laws and norms, preventing chaos but sometimes suppressing individual freedoms and hindering reform. Both processes impact society by balancing the need for security with the demand for transformation, shaping cultural evolution and social cohesion.
Conclusion: Balancing Social Change and Social Control
Balancing social change and social control is essential for maintaining societal stability while fostering progress. Effective social control mechanisms must adapt to evolving social norms to support positive change without suppressing innovation. Societies thrive when they find equilibrium between preserving order and embracing transformative social movements.
Social change Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com