Social acceptance plays a crucial role in building meaningful relationships and fostering a sense of belonging within communities. It impacts mental well-being and influences how you perceive yourself in social settings. Explore the full article to understand the importance of social acceptance and strategies to enhance your connections.
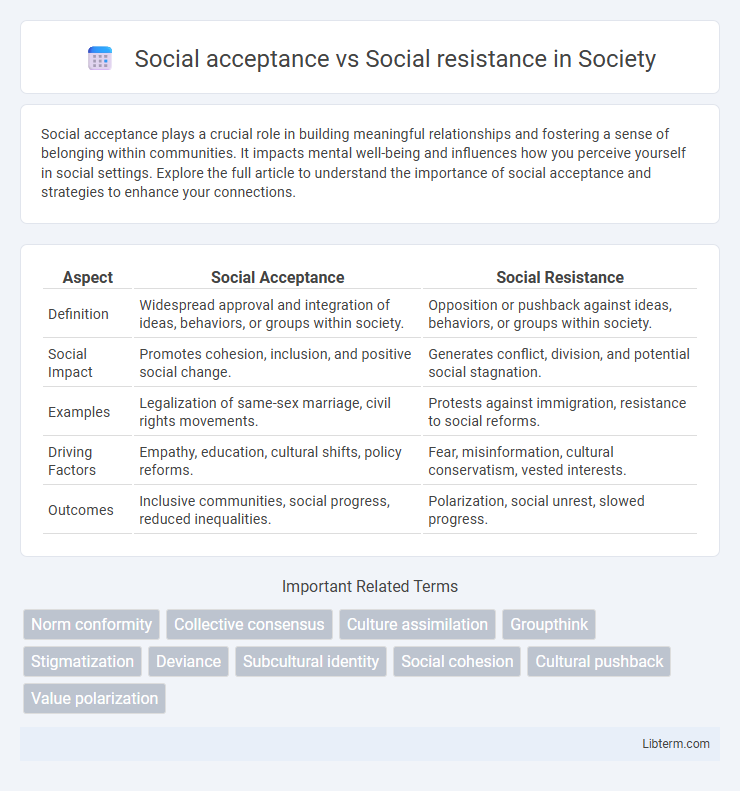
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Acceptance | Social Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Widespread approval and integration of ideas, behaviors, or groups within society. | Opposition or pushback against ideas, behaviors, or groups within society. |
| Social Impact | Promotes cohesion, inclusion, and positive social change. | Generates conflict, division, and potential social stagnation. |
| Examples | Legalization of same-sex marriage, civil rights movements. | Protests against immigration, resistance to social reforms. |
| Driving Factors | Empathy, education, cultural shifts, policy reforms. | Fear, misinformation, cultural conservatism, vested interests. |
| Outcomes | Inclusive communities, social progress, reduced inequalities. | Polarization, social unrest, slowed progress. |
Understanding Social Acceptance: Definition and Importance
Social acceptance refers to the degree to which individuals or groups are embraced and valued within a society, influencing cohesion and collective well-being. It plays a crucial role in fostering inclusion, reducing discrimination, and enhancing cooperation among diverse populations. Understanding social acceptance is essential for developing policies and practices that promote harmony and equitable social integration.
Unpacking Social Resistance: Causes and Manifestations
Social resistance arises from factors such as cultural differences, fear of change, and perceived threats to identity or resources, often manifesting through protests, refusal to comply, or spreading dissenting narratives. Deep-rooted social resistance can hinder policy implementation, innovation adoption, and social cohesion within communities. Understanding these causes and manifestations enables targeted strategies to address resistance and foster constructive social acceptance.
Key Differences Between Social Acceptance and Social Resistance
Social acceptance involves the widespread approval and integration of ideas, behaviors, or groups within a community, fostering cooperation and social cohesion. In contrast, social resistance signifies opposition or rejection aimed at preserving existing norms or challenging change, often manifesting through protests or social movements. Key differences include acceptance's role in maintaining stability versus resistance's function in driving societal transformation, alongside varying emotional responses such as conformity versus dissent.
Historical Examples of Social Acceptance and Resistance
Historical examples of social acceptance include the Civil Rights Movement in the United States, which gained widespread support and led to significant legal reforms like the Civil Rights Act of 1964. In contrast, social resistance is exemplified by the anti-apartheid movement in South Africa, where activists faced harsh opposition before achieving the dismantling of apartheid laws. Both movements demonstrate how collective action can shape societal norms through acceptance or resistance to prevailing injustices.
The Role of Culture in Shaping Acceptance and Resistance
Cultural norms and values significantly influence social acceptance and resistance by shaping collective beliefs and behaviors toward change or innovation. Societies with a high value on tradition may exhibit greater social resistance, while cultures emphasizing openness and adaptability tend to foster acceptance. This dynamic interplay between culture and social responses highlights the importance of understanding cultural context in managing social change effectively.
Factors Influencing Social Acceptance
Factors influencing social acceptance include cultural values, perceived benefits, and trust in institutions or technologies, which shape public attitudes toward innovations or policies. Social norms and community engagement often determine the degree of acceptance, as inclusive dialogue fosters understanding and reduces opposition. Economic incentives and transparent communication further enhance acceptance by addressing concerns and demonstrating tangible advantages.
Drivers and Triggers of Social Resistance
Social resistance arises primarily from fear of change, perceived threats to cultural identity, and economic disadvantages caused by new policies or technologies. Drivers including misinformation, lack of trust in authorities, and historical grievances significantly amplify community pushback. Triggers such as rapid implementation without community involvement or visible negative impacts activate resistance movements and hinder social acceptance.
Psychological Impacts of Acceptance versus Resistance
Social acceptance fosters psychological well-being by promoting a sense of belonging, increased self-esteem, and reduced stress levels, supporting mental health resilience. In contrast, social resistance often triggers feelings of isolation, anxiety, and lowered self-worth, which can lead to chronic stress and negative emotional outcomes. The dynamic between acceptance and resistance significantly influences individual identity formation and overall psychological stability in social contexts.
Strategies to Foster Social Acceptance
Effective strategies to foster social acceptance include inclusive communication that respects diverse perspectives and actively addresses concerns through transparent dialogue. Implementing community engagement initiatives that empower stakeholders and build trust promotes collaborative problem-solving and mutual understanding. Leveraging positive role models and social norm interventions can accelerate shifts in attitudes and behaviors towards greater acceptance.
Navigating and Managing Social Resistance
Navigating social resistance requires a deep understanding of underlying community values and the ability to engage stakeholders through transparent communication and empathy. Managing social resistance effectively involves developing adaptive strategies that address concerns, foster dialogue, and build trust among diverse social groups. Leveraging social acceptance often depends on collaborative efforts that promote inclusion, cultural sensitivity, and shared benefits to overcome opposition and achieve sustainable social integration.
Social acceptance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com