Social preservation ensures the continuity of cultural values, traditions, and community bonds that shape collective identity across generations. It plays a critical role in fostering social cohesion and resilience by maintaining shared history and practices. Explore the rest of this article to understand how social preservation impacts your community and what measures can support its future.
Table of Comparison
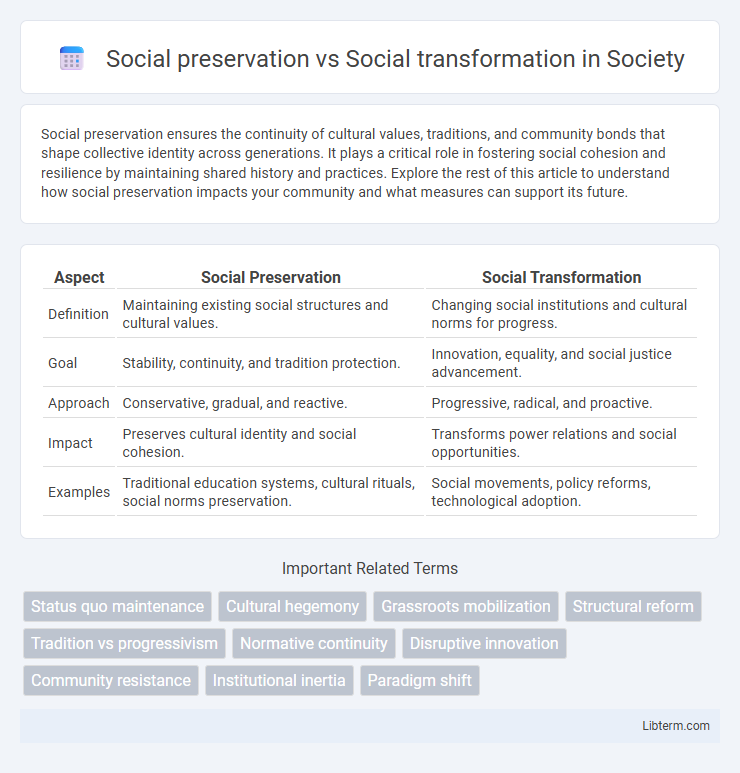
| Aspect | Social Preservation | Social Transformation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintaining existing social structures and cultural values. | Changing social institutions and cultural norms for progress. |
| Goal | Stability, continuity, and tradition protection. | Innovation, equality, and social justice advancement. |
| Approach | Conservative, gradual, and reactive. | Progressive, radical, and proactive. |
| Impact | Preserves cultural identity and social cohesion. | Transforms power relations and social opportunities. |
| Examples | Traditional education systems, cultural rituals, social norms preservation. | Social movements, policy reforms, technological adoption. |
Understanding Social Preservation and Social Transformation
Social preservation involves maintaining existing social structures, cultural norms, and traditions to ensure continuity and stability within communities. Social transformation focuses on fundamental changes in societal values, power dynamics, and institutions aimed at achieving equity, justice, and innovation. Understanding the balance between preserving cultural heritage and promoting progressive social change is crucial for sustainable development and social cohesion.
Historical Contexts of Social Preservation
Historical contexts of social preservation emphasize maintaining cultural heritage, traditions, and societal norms rooted in past generations. This process involves safeguarding historical landmarks, language, and social institutions to uphold community identity amidst rapid modernization. Preservation efforts often arise in response to colonialism, industrialization, or political upheaval, aiming to protect social cohesion and continuity.
Drivers and Motivations for Social Transformation
Social transformation is driven primarily by motivations such as addressing systemic inequalities, enhancing social justice, and fostering innovation to adapt to evolving cultural and economic landscapes. Key drivers include technological advancements, grassroots activism, policy reforms, and shifts in collective values that challenge the status quo. These movements aim to restructure social norms and institutions, contrasting with social preservation which emphasizes maintaining existing traditions and stability.
Key Theories Behind Preservation and Transformation
Key theories behind social preservation emphasize maintaining cultural heritage, social norms, and institutional continuity, rooted in functionalism and structuralism. Social transformation theories draw on critical theory and conflict theory, focusing on power dynamics, social change, and emancipation from oppressive structures. Both perspectives provide frameworks for analyzing the stability and evolution of societies through diverse ideological lenses.
Impact of Preservation on Cultural Identity
Social preservation plays a crucial role in maintaining cultural identity by safeguarding traditions, languages, and rituals that define community heritage. This process strengthens collective memory and fosters a sense of belonging across generations, ensuring cultural continuity amid globalization pressures. However, strict preservation may also limit social evolution by resisting necessary adaptations that address contemporary challenges and diversity.
Transformation and Progressive Social Change
Social transformation drives progressive social change by fundamentally altering cultural norms, power structures, and institutional frameworks to foster equity and inclusion. This dynamic process challenges existing social hierarchies and promotes innovation in policies related to human rights, economic justice, and environmental sustainability. Emphasizing systemic change over mere social preservation, social transformation seeks to dismantle oppression and create opportunities for marginalized communities to thrive.
Tensions and Conflicts Between Preservationists and Reformers
Tensions between social preservationists and reformers arise from conflicting goals: preservationists aim to maintain existing social structures and cultural norms, while reformers push for systemic change and innovation. This clash often results in disputes over policies related to civil rights, education, and economic redistribution, where preservationists view reforms as threats to social stability. Deep-seated ideological differences exacerbate conflicts, leading to polarized debates on the pace and scope of social change.
Case Studies: Societies Balancing Preservation and Transformation
Case studies of societies balancing social preservation and transformation highlight strategies that maintain cultural heritage while embracing modernization, such as Bhutan's Gross National Happiness framework integrating tradition with sustainable development. Indigenous communities in Canada exemplify this balance by preserving language and customs alongside adapting to economic opportunities through technology and education initiatives. These examples demonstrate how societies can concurrently safeguard identity and promote progressive change, ensuring resilience in cultural and social structures.
Factors Influencing the Choice: When to Preserve, When to Transform
Social preservation is favored when cultural identity, historical continuity, and community stability are prioritized, ensuring traditions and values remain intact amid change. Social transformation becomes essential in contexts of systemic inequality, technological advancement, or environmental crises requiring adaptive innovation to improve societal well-being. Factors influencing this choice include the urgency of social issues, stakeholder consensus, power dynamics, and the potential impact on marginalized groups.
Future Outlook: Integrating Preservation with Transformation
Future outlook in social dynamics emphasizes integrating social preservation with social transformation to foster sustainable development. Balancing traditional cultural values and evolving societal norms supports resilience while embracing innovation in education, technology, and governance. This integration promotes inclusive growth and adaptive communities equipped to address emerging global challenges such as climate change and social inequality.
Social preservation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com