Social networks enable seamless connection with friends, family, and communities worldwide, fostering communication and content sharing. These platforms also provide powerful tools for businesses to engage customers and enhance brand visibility. Explore the rest of this article to discover how you can effectively leverage social networks for personal and professional growth.
Table of Comparison
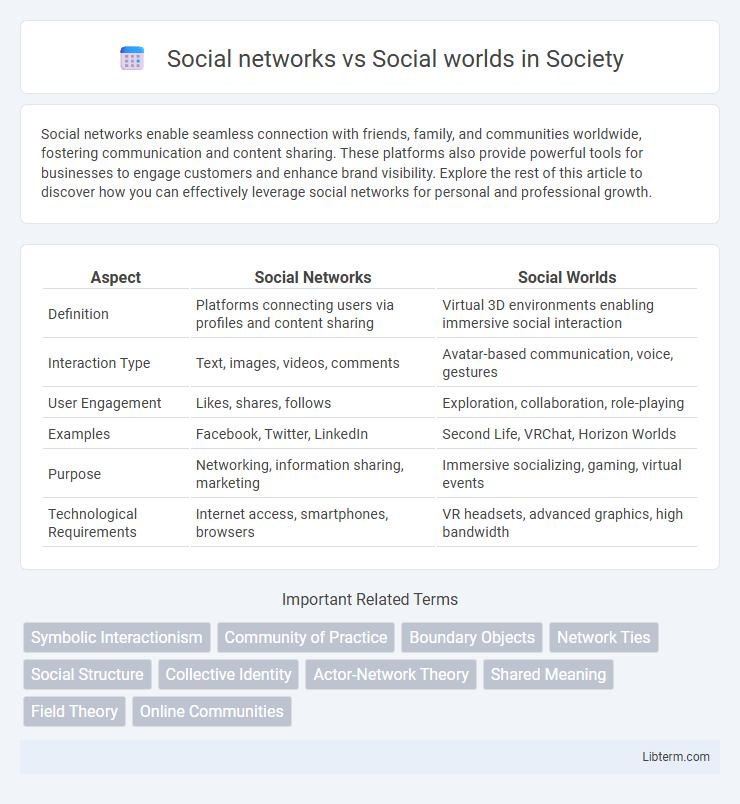
| Aspect | Social Networks | Social Worlds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Platforms connecting users via profiles and content sharing | Virtual 3D environments enabling immersive social interaction |
| Interaction Type | Text, images, videos, comments | Avatar-based communication, voice, gestures |
| User Engagement | Likes, shares, follows | Exploration, collaboration, role-playing |
| Examples | Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn | Second Life, VRChat, Horizon Worlds |
| Purpose | Networking, information sharing, marketing | Immersive socializing, gaming, virtual events |
| Technological Requirements | Internet access, smartphones, browsers | VR headsets, advanced graphics, high bandwidth |
Understanding Social Networks: A Brief Overview
Social networks consist of interconnected individuals or organizations linked by various social relationships, enabling information exchange and influence patterns. Understanding social networks involves analyzing nodes (people or entities) and ties (connections) to uncover network structures such as clusters, hubs, and bridges that facilitate communication flow. These structural properties impact social behavior, information dissemination, and community formation within both online platforms and real-world environments.
Defining Social Worlds: More Than Connections
Social worlds extend beyond mere social networks by encompassing shared meanings, practices, and identities that shape group interactions and collective experiences. These worlds are defined by common goals, cultural norms, and sustained engagements rather than just individual relationships or connections. Understanding social worlds involves analyzing the context and content of interactions that form cohesive, meaning-rich communities.
Key Differences: Social Networks vs Social Worlds
Social networks emphasize individual connections and interactions through nodes and links, highlighting patterns of relationships among people or organizations. Social worlds involve shared meanings, practices, and cultural norms within groups, focusing on collective identities and social contexts beyond mere connections. Key differences lie in social networks' structural approach versus social worlds' interpretive and cultural emphasis.
Structure and Functionality in Social Networks
Social networks consist of nodes representing individuals or organizations connected through ties that indicate relationships such as friendship, collaboration, or communication, emphasizing the pattern and strength of these connections. Their primary functionality revolves around information exchange, relationship building, and influence propagation within a defined network structure. In contrast, social worlds encompass broader cultural and social contexts where interactions are shaped by shared meanings, norms, and identities beyond mere network ties.
The Dynamics of Belonging in Social Worlds
Social worlds revolve around shared values, practices, and identities that foster a deep sense of belonging among members, contrasting with social networks which primarily map connections between individuals. The dynamics of belonging within social worlds emphasize continuous interaction, negotiation, and co-construction of meanings that solidify group membership and collective identity. This ongoing engagement in social worlds generates trust, shared knowledge, and cultural cohesion beyond the mere structural links found in social networks.
Interactions: How Relationships Develop and Evolve
Social networks facilitate interactions through structured connections where relationships develop based on shared interests and frequent communication, emphasizing direct links between individuals. In social worlds, relationships evolve within broader cultural contexts, shaped by collective practices, norms, and identities that influence continuous interaction dynamics. The evolution of relationships in social worlds often involves deeper social integration and role adaptation beyond mere network ties.
Technology’s Impact on Social Networks and Worlds
Technology transforms social networks by enabling real-time global communication, fostering connections across diverse communities and accelerating information exchange. Social worlds evolve as digital platforms create immersive environments where users interact beyond traditional boundaries, shaping virtual identities and shared cultural experiences. Advances in AI algorithms and data analytics personalize content delivery, influencing social behavior and the dynamics within these interconnected digital landscapes.
Building Community: From Networks to Worlds
Building community shifts from mere social networks, which connect individuals through relationships, to rich social worlds that cultivate shared identities, values, and immersive interactions. Social worlds enable deeper engagement by fostering collective experiences, narratives, and cultural meanings beyond transactional connections. This transformation enhances group cohesion, collaborative creativity, and sustained participation within digital and physical environments.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Model
Social networks face challenges such as limited insight into users' immersive experiences and the superficiality of connections driven primarily by algorithms prioritizing engagement metrics. Social worlds encounter limitations in scalability and complexity, making it difficult to analyze or quantify user interactions within richly layered virtual environments. Both models struggle with privacy concerns, but while social networks risk data exploitation through centralized control, social worlds contend with safeguarding user identity and behavior in decentralized, persistent spaces.
The Future of Human Connection: Bridging Networks and Worlds
The future of human connection lies in seamlessly integrating social networks with immersive social worlds, enhancing real-time interaction and shared experiences through advanced virtual reality and AI technologies. This convergence fosters deeper emotional engagement and collaborative opportunities beyond traditional online platforms. By bridging these dimensions, social connectivity evolves into dynamic ecosystems where individual relationships form part of expansive, interactive communities.
Social networks Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com